You have not yet added any article to your bookmarks!

Join 10k+ people to get notified about new posts, news and tips.
Do not worry we don't spam!
Post by : Anis Farhan
Vaccines are one of the most important public health tools in the world. They protect individuals and communities from infectious diseases by training the immune system to recognize and respond to harmful pathogens. While most people are familiar with vaccines as injections, the science behind how they work is complex and fascinating.
Understanding vaccines requires knowledge of the immune system, how pathogens cause disease, and how immunity develops. In simple terms, vaccines prepare the body to fight off infections without causing the illness itself. Over the past century, vaccines have helped eradicate or control deadly diseases such as smallpox, polio, measles, and influenza, saving millions of lives worldwide.
The immune system is the body’s defense mechanism against infections caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other pathogens. It consists of multiple components, including white blood cells, antibodies, and specialized organs like the thymus and spleen.
When a pathogen enters the body, the immune system identifies it as foreign and mounts a response. This includes producing antibodies, which are proteins that attach to the pathogen and neutralize it, and activating immune cells that destroy infected cells. The first exposure to a pathogen is usually slower because the body needs time to recognize and respond effectively.
Vaccines work by simulating this first exposure, allowing the immune system to “learn” how to fight the pathogen safely. When the actual pathogen enters the body later, the immune system responds much faster and stronger, preventing illness or reducing its severity.
Live attenuated vaccines use a weakened form of the virus or bacteria that cannot cause severe disease in healthy individuals. Examples include the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine and the varicella (chickenpox) vaccine.
These vaccines generally provide long-lasting immunity with one or two doses because the weakened pathogen closely mimics a natural infection. However, they are usually not recommended for people with weakened immune systems.
Inactivated vaccines contain pathogens that have been killed or inactivated so they cannot replicate. Examples include the polio vaccine (IPV) and the hepatitis A vaccine.
Because the immune system encounters a non-replicating form of the pathogen, multiple doses may be necessary to achieve full protection. Inactivated vaccines are safe for people with compromised immunity.
These vaccines use specific pieces of the pathogen, such as proteins or sugars, to trigger an immune response. Examples include the hepatitis B vaccine, HPV vaccine, and pneumococcal vaccines.
By focusing on essential components of the pathogen, these vaccines reduce the risk of side effects while still providing effective immunity. Some may require booster doses to maintain long-term protection.
mRNA vaccines are a newer technology that uses messenger RNA to instruct cells to produce a protein that triggers an immune response. COVID-19 vaccines like Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna use this approach.
mRNA vaccines do not contain live virus and cannot cause the disease. They have shown high effectiveness and a rapid development timeline, making them valuable tools during pandemics.
Viral vector vaccines use a harmless virus to deliver genetic material from the target pathogen into cells, prompting an immune response. The Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine and the Ebola vaccine use this technology.
These vaccines combine safety with strong immune activation and can be designed quickly in response to emerging diseases.
Vaccines train the immune system by exposing it to antigens, which are molecules recognized as foreign. When vaccinated, the body produces antibodies and memory cells. These memory cells remain in the body for months or years, enabling a faster and more effective response upon future exposure to the actual pathogen.
This concept is known as adaptive immunity. Unlike innate immunity, which responds the same way to all pathogens, adaptive immunity is specific and improves upon repeated exposure. Vaccines essentially provide a controlled, safe way to achieve this immunity without suffering from the disease itself.
Vaccination not only protects individuals but also communities. When a large portion of the population is vaccinated, the spread of infectious diseases is slowed or stopped, a concept known as herd immunity.
Herd immunity is critical for protecting those who cannot be vaccinated, such as infants, elderly individuals, or people with compromised immune systems. Widespread vaccination reduces the chances of outbreaks and helps prevent epidemics and pandemics.
Vaccines prevent serious illness and death from diseases such as measles, polio, influenza, and COVID-19. They reduce hospitalizations and long-term complications associated with infections.
By preventing disease, vaccines reduce healthcare costs, absenteeism from work and school, and economic burdens on families and governments. Healthy populations contribute to more productive societies.
Vaccination programs strengthen global health security by reducing the risk of disease outbreaks spreading across borders. Initiatives like the World Health Organization’s immunization campaigns have been instrumental in eradicating smallpox and nearly eliminating polio.
New vaccine technologies, such as mRNA and viral vector vaccines, allow rapid response to emerging infectious diseases, reducing mortality and morbidity during pandemics.
Despite overwhelming evidence, vaccine hesitancy persists due to myths and misinformation. Common misconceptions include beliefs that vaccines cause the disease they prevent, lead to autism, or contain harmful ingredients.
Scientific research consistently shows that vaccines are safe and effective. Minor side effects, such as soreness or mild fever, are temporary and far outweighed by the protection vaccines provide. Public health education and transparent communication are essential to counter misinformation.
Vaccine research continues to evolve, focusing on improving effectiveness, accessibility, and coverage. Innovations include:
Universal flu vaccines that protect against multiple strains.
Personalized vaccines for cancer and autoimmune diseases.
Oral and nasal vaccines for easier administration.
Thermostable vaccines that do not require refrigeration, aiding distribution in remote regions.
These advances promise to expand protection against a wider range of diseases while simplifying global immunization efforts.
Vaccines remain one of the most powerful tools in preventing infectious diseases. By understanding how they work, individuals and communities can make informed decisions about immunization. Vaccination not only protects individuals but also strengthens public health, reduces economic burdens, and supports global health security.
As new technologies and research continue to advance, vaccines will play a crucial role in safeguarding populations from both existing and emerging diseases. Awareness, education, and accessibility are key to maximizing the life-saving benefits of vaccines worldwide.
This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Individuals should consult healthcare providers regarding vaccinations suitable for their age, health conditions, and geographic location. Vaccine recommendations may vary based on national guidelines and individual health circumstances.










India Says J&K Budget Exceeds Pakistan’s IMF Bailout
India slammed Pakistan at UNHRC, stating J&K’s development budget exceeds Pakistan’s IMF bailout and

UP CM Holds Talks With Ex Japan Economy Minister in Tokyo
Yogi Adityanath met former Japan economy minister Nishimura Yasutoshi in Tokyo to boost UP-Japan coo

Hiroshima Teacher Arrested for Alleged Sexual Assault of Minor
A 37-year-old high school teacher in Hiroshima was arrested on suspicion of sexually assaulting a te

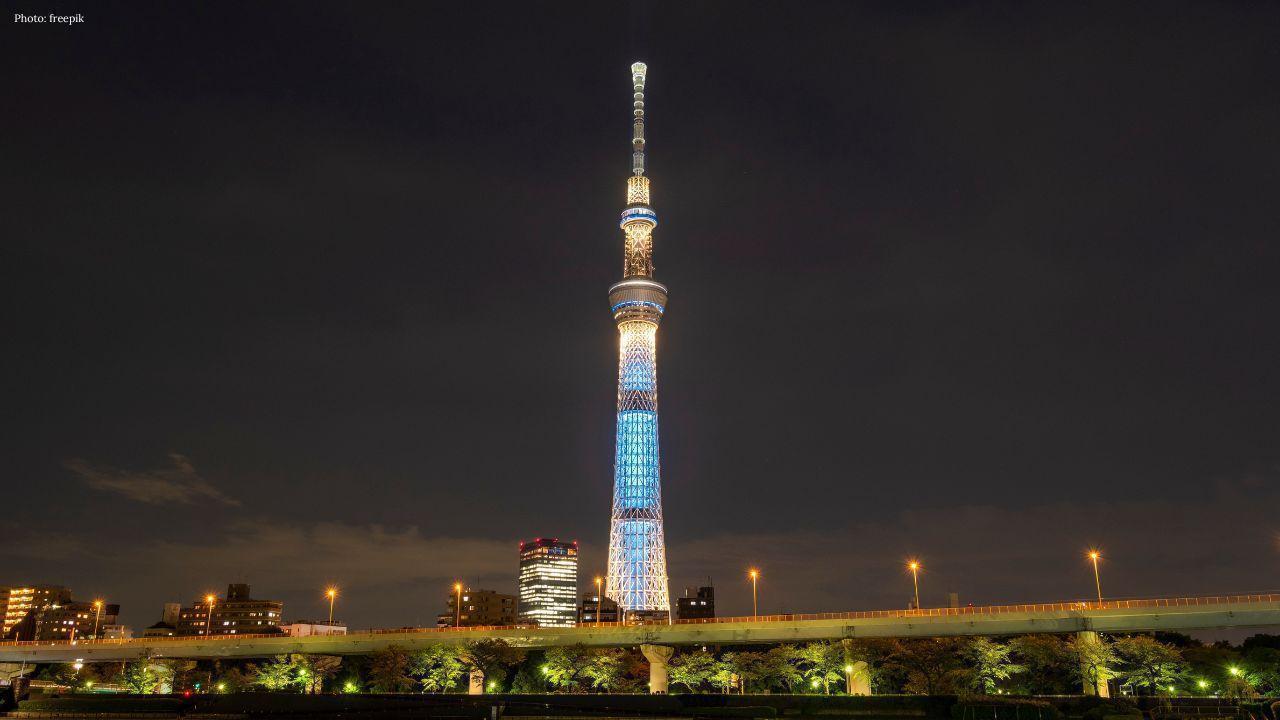
Tokyo Skytree Reopens After Elevator Malfunction Suspension
Tokyo Skytree resumed operations after a three-day closure caused by an elevator failure that trappe
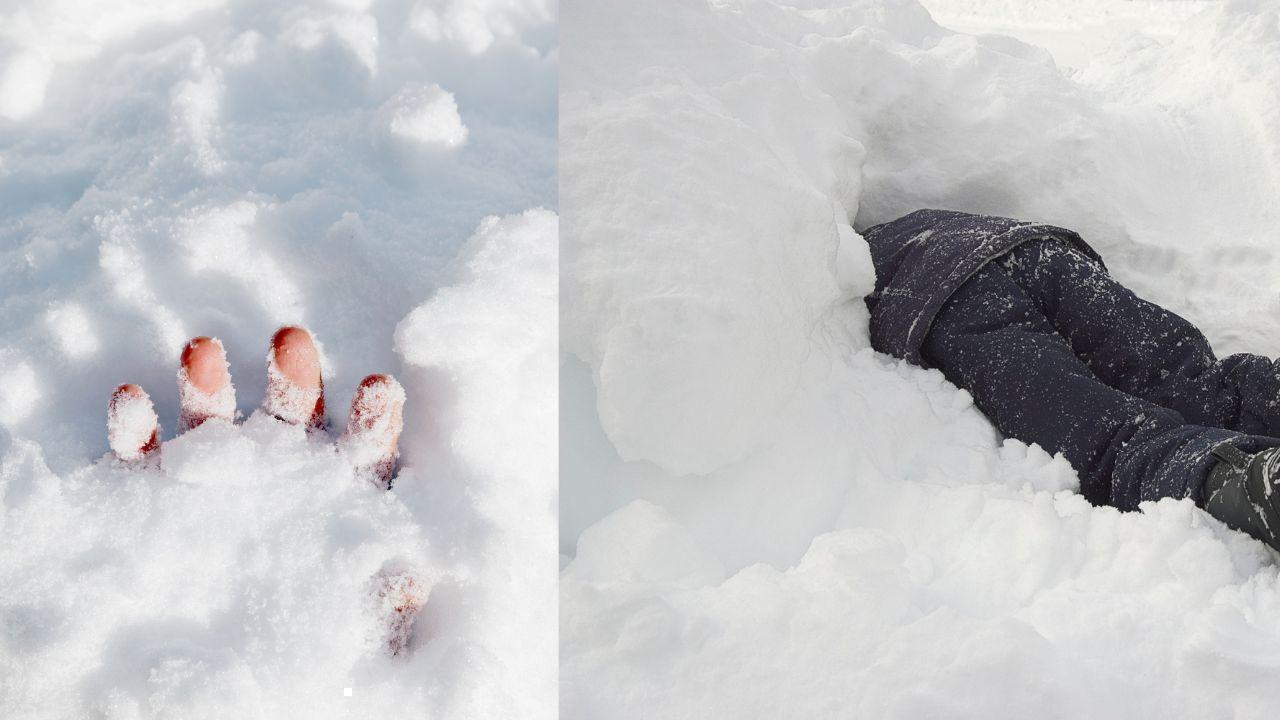

Skiers Rescue Man Buried Under Snow at California Resort
A dramatic rescue at Palisades Tahoe shows two skiers saving a man suffocating under deep snow durin
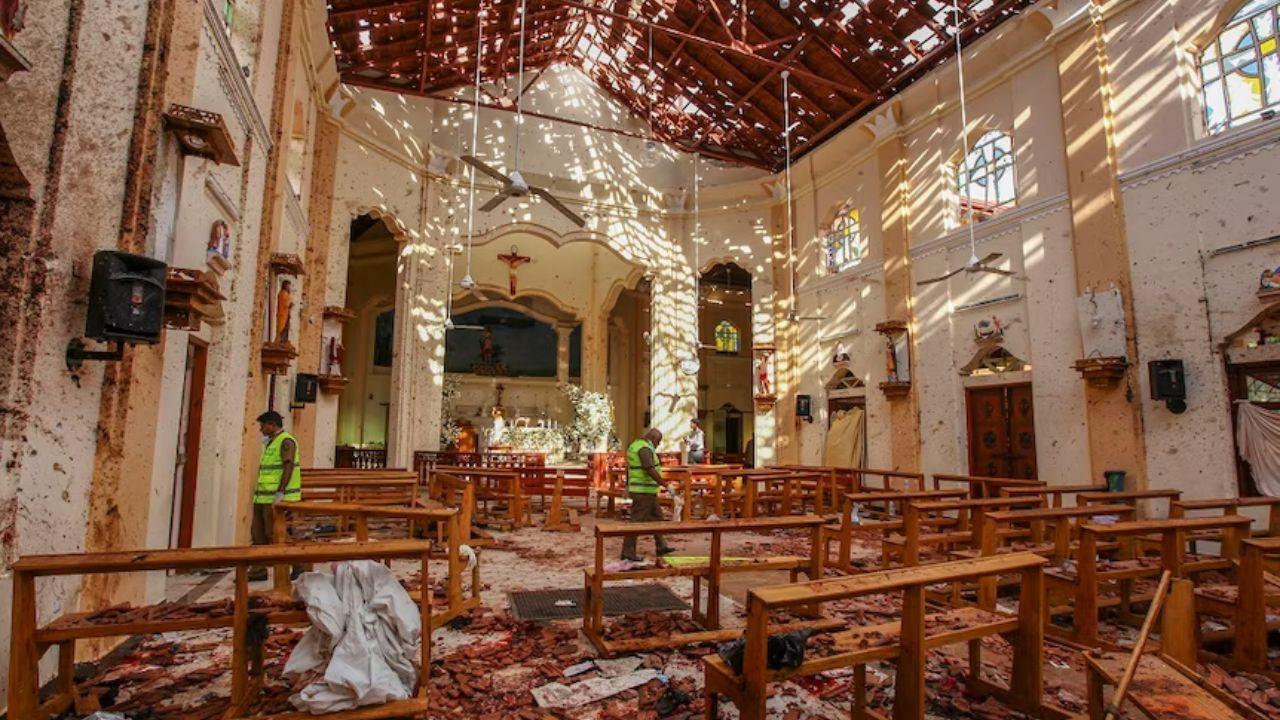

Sri Lanka Ex-Intel Chief Arrested Over Easter Attacks
Former SIS Chief Suresh Sallay arrested by CID in connection with the 2019 Easter Sunday bombings th