
Join 10k+ people to get notified about new posts, news and tips.
Do not worry we don't spam!

Post by : Anis Farhan
Chronic illnesses, including heart disease, diabetes, obesity, and certain cancers, are long-lasting conditions that can profoundly impact quality of life. Unlike acute illnesses, they develop over years, often influenced by genetics, environment, and, crucially, lifestyle choices.
Preventing chronic disease is a global health priority. Studies consistently show that lifestyle interventions can dramatically reduce the risk of developing these conditions, improve longevity, and enhance overall well-being. While medical interventions are critical, the power of daily habits in prevention cannot be overstated.
Nutrition is central to chronic illness prevention. Diets rich in whole foods—vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats—support immune function, maintain healthy weight, and reduce inflammation, a key contributor to chronic diseases.
Processed foods, excessive sugars, and trans fats increase the risk of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular issues. Transitioning to a balanced, nutrient-dense diet is one of the most effective lifestyle shifts for long-term health.
Certain foods possess protective properties. Foods high in antioxidants, such as berries, leafy greens, and nuts, combat oxidative stress. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, flaxseeds, and chia seeds support heart and brain health. Fiber-rich foods maintain digestive health and regulate blood sugar.
Incorporating functional foods into daily meals enhances disease prevention and supports overall wellness.
Regular physical activity lowers the risk of chronic diseases by improving cardiovascular health, regulating blood sugar, and maintaining healthy body composition. Moderate activities—such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling—performed consistently, are more beneficial than sporadic high-intensity workouts.
In addition to aerobic exercise, strength training helps preserve muscle mass, supports metabolic health, and strengthens bones. Resistance exercises, performed 2–3 times per week, contribute to long-term mobility and reduce the risk of osteoporosis and frailty in later life.
Even small daily habits—taking stairs, short walking breaks, or stretching—compound over time to create significant health benefits. The key is consistency and integrating movement into daily routines.
Chronic stress is a silent contributor to chronic illness. Elevated cortisol levels and persistent stress increase inflammation, blood pressure, and risk for heart disease and diabetes.
Meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises reduce stress and improve mental clarity. Even a few minutes daily can lower physiological stress markers, improving resilience against chronic disease.
Strong social connections buffer stress and promote healthy behaviors. Regular interactions with friends, family, or support groups provide emotional stability, reduce isolation, and positively influence lifestyle choices.
Quality sleep is critical for preventing chronic illness. Adults typically require 7–9 hours per night. Inadequate sleep disrupts metabolism, impairs glucose regulation, and increases appetite for unhealthy foods, contributing to obesity and diabetes.
Maintain a consistent sleep schedule.
Limit exposure to screens before bedtime.
Create a calm, dark, and cool sleeping environment.
Avoid heavy meals and stimulants close to bedtime.
Prioritizing sleep enhances physical and mental health, reinforcing other preventive lifestyle measures.
Limiting or eliminating harmful substances significantly reduces chronic disease risk.
Smoking is a major contributor to cardiovascular disease, lung cancer, and multiple other chronic illnesses. Avoiding tobacco entirely is essential for prevention.
Moderate alcohol consumption may offer some benefits for certain individuals, but excessive intake increases the risk of liver disease, heart problems, and cancers. Mindful drinking or abstaining altogether supports long-term health.
Minimizing exposure to pollutants, chemicals, and excessive sunlight also contributes to disease prevention. Choosing safe household products, limiting processed foods with additives, and using protective measures outdoors reduce cumulative health risks.
Maintaining a healthy weight is central to preventing chronic illnesses such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease. Lifestyle shifts that support metabolic health include:
Balanced nutrition with controlled portions.
Regular physical activity.
Stress management.
Adequate sleep.
Monitoring body composition and metabolic markers allows for early detection of risk factors and proactive lifestyle adjustments.
Lifestyle shifts work best when complemented by regular medical check-ups. Early detection through screenings—such as blood pressure, cholesterol, blood sugar, and cancer screenings—enables timely interventions before chronic conditions become severe.
Preventive care also includes vaccinations, dental hygiene, and vision checks, all of which contribute to overall wellness and disease prevention.
Clear, realistic goals increase adherence to lifestyle changes. Breaking larger health goals into manageable steps helps maintain motivation and track progress over time.
Journaling food intake, physical activity, and sleep patterns fosters awareness and accountability. Digital tools and health apps can provide reminders and track improvements, reinforcing positive habits.
Small, sustainable changes are more effective than radical transformations. Gradually adopting healthier eating patterns, increasing physical activity, and improving sleep ensures lasting impact and reduces the risk of burnout or regression.
Engaging with like-minded communities enhances lifestyle adherence. Fitness groups, wellness programs, and online forums provide motivation, shared experiences, and practical advice.
Supportive environments reinforce behavior change and reduce the likelihood of relapse into unhealthy patterns, particularly when facing challenges such as stress, busy schedules, or social pressures.
Preventing chronic illnesses through lifestyle choices also has societal benefits. Reduced disease prevalence decreases healthcare costs, increases workforce productivity, and enhances quality of life for communities.
Individuals who adopt preventive practices experience improved physical fitness, mental clarity, and social engagement, contributing to long-term life satisfaction.
Despite awareness, many struggle to implement sustainable changes. Common barriers include:
Busy schedules and competing priorities.
Lack of knowledge or guidance.
Environmental or social influences that promote unhealthy habits.
Addressing these challenges requires practical strategies, education, and gradual integration of new behaviors into daily life.
The field of lifestyle medicine emphasizes using lifestyle interventions as primary tools for preventing and managing chronic disease. Healthcare providers increasingly recommend dietary counseling, structured physical activity, stress management, and sleep optimization as part of standard care.
As research evolves, personalized lifestyle plans—considering genetics, environment, and behavior—will enable more precise and effective chronic illness prevention strategies.
Preventing chronic illness is not about drastic overnight transformations; it’s about consistent, intentional lifestyle choices. Nutrition, physical activity, sleep, stress management, and avoiding harmful substances collectively create a foundation for lifelong health.
Even small, incremental changes—like walking 20 minutes a day, reducing sugar intake, or practicing mindfulness—can dramatically lower disease risk. By prioritizing preventive habits and integrating them into daily routines, individuals gain control over their health trajectory, enhance quality of life, and reduce reliance on medical interventions.
Chronic illness prevention is a proactive journey, where the cumulative effect of small lifestyle shifts matters most. The earlier these habits are adopted, the greater their long-term benefits, demonstrating that prevention is not only possible but highly impactful.
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional medical advice. Readers should consult healthcare providers before making significant lifestyle changes, especially if managing existing health conditions.
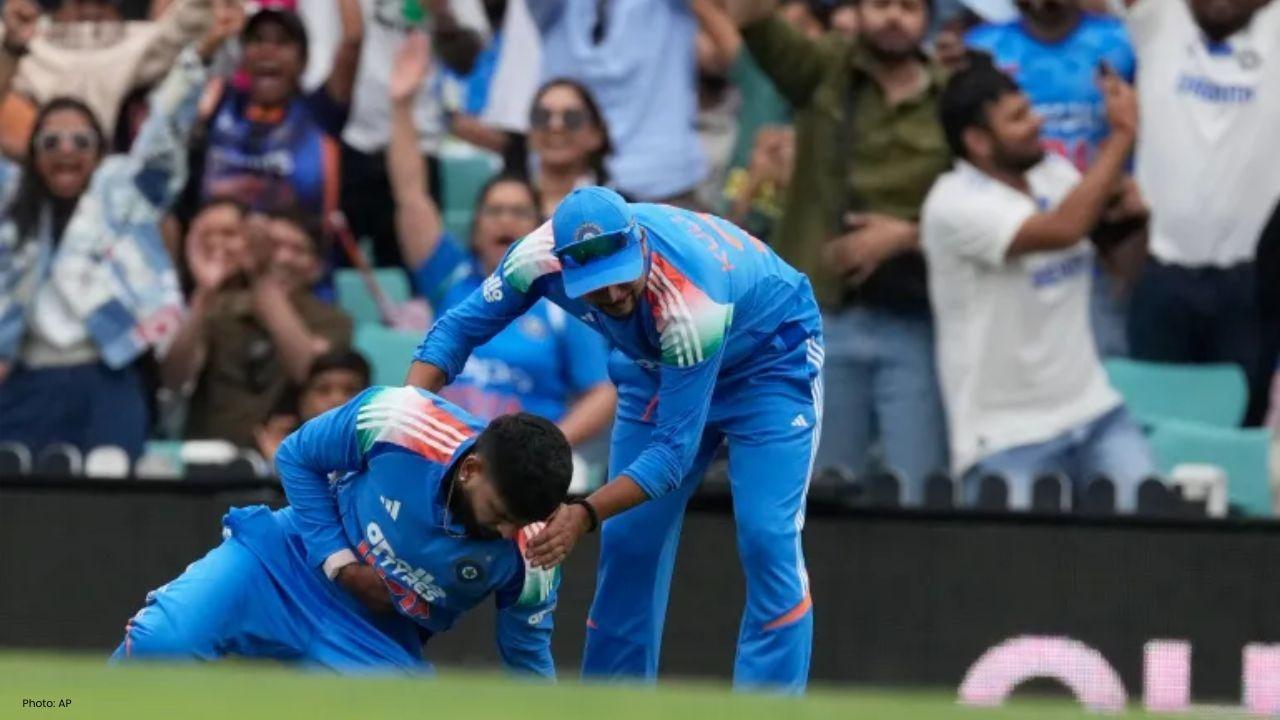









Shreyas Iyer’s Recovery Underway After Spleen Laceration in Sydney ODI
Shreyas Iyer is recovering after a spleen laceration sustained while taking a catch in the Sydney OD
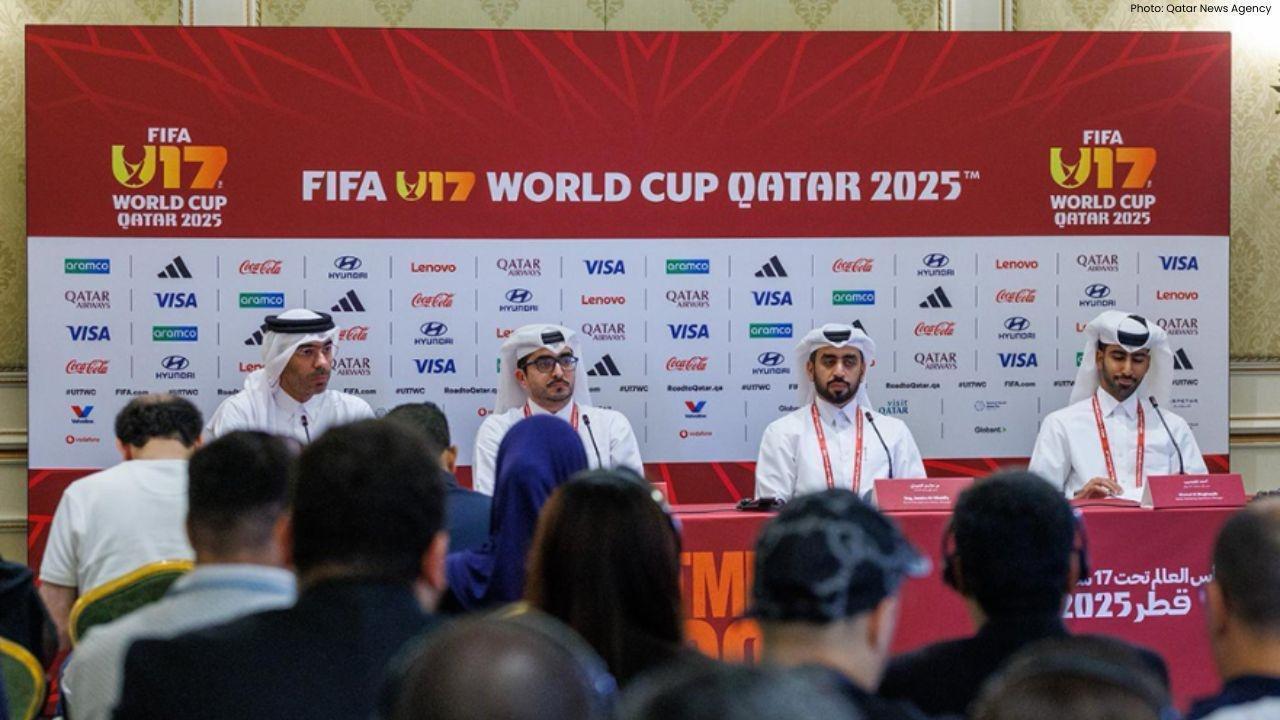

Qatar Ready to Host FIFA U-17 World Cup 2025 in Aspire
Qatar confirms full readiness to host the FIFA U-17 World Cup 2025 from November 3–27, with world-cl
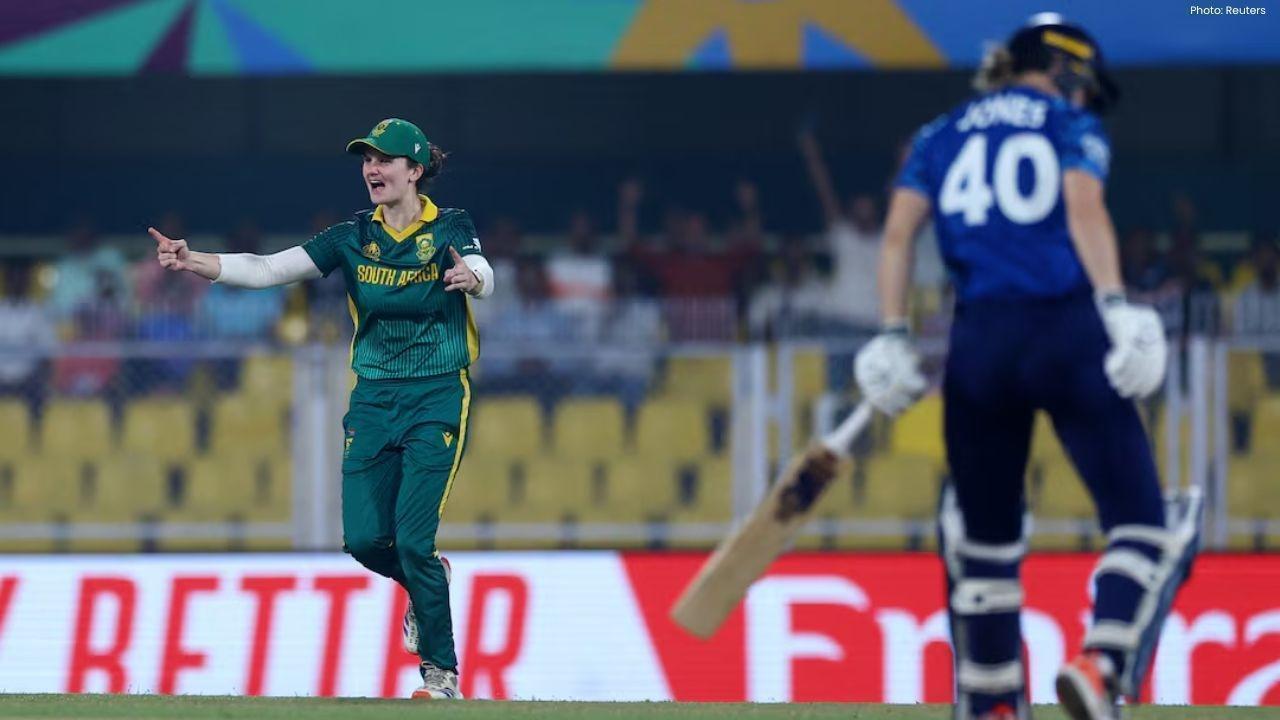

Wolvaardt’s 169 Sends South Africa Into Women’s World Cup Final
Laura Wolvaardt’s 169 powered South Africa to a 125-run semi-final win over England, booking a place

Vacherot Beats Cousin Rinderknech to Reach Paris Masters Last 16
Valentin Vacherot overcame cousin Arthur Rinderknech in three sets to secure a place in the Paris Ma
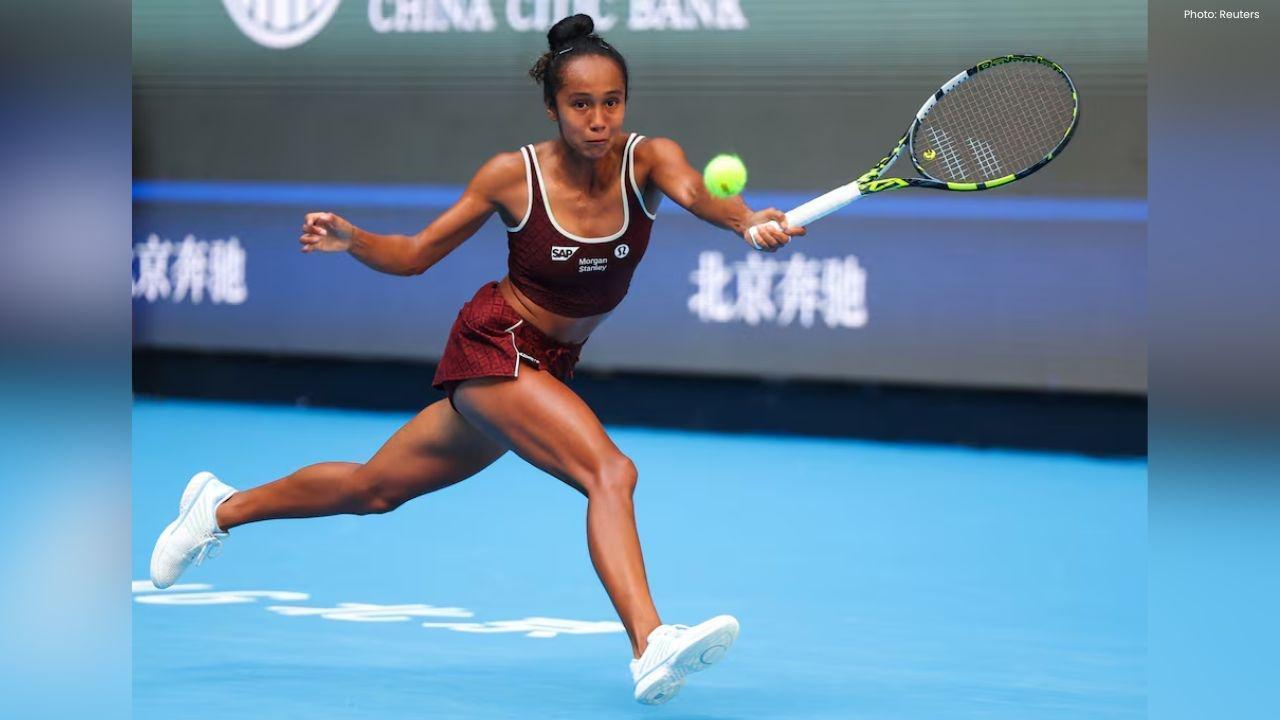

Fernandez Reaches Hong Kong Tennis Open Quarterfinals
Leylah Fernandez moved into the Hong Kong Tennis Open quarterfinals with a straight-sets win, as maj
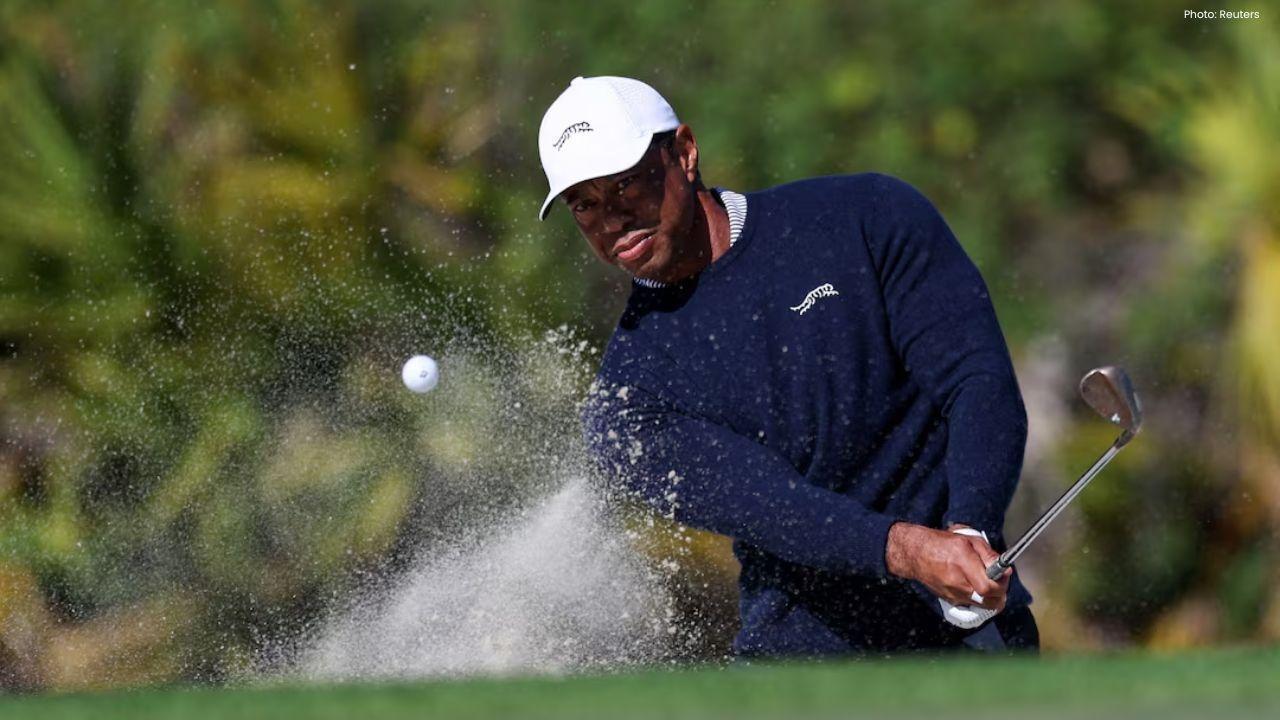

Tiger Woods Withdraws From 2024 Hero World Challenge After Back Surgery
Tiger Woods will not compete at the 2024 Hero World Challenge after lumbar disc replacement surgery,