You have not yet added any article to your bookmarks!

Join 10k+ people to get notified about new posts, news and tips.
Do not worry we don't spam!
Post by : Anis Farhan
Quantum computing is no longer a distant theory—it’s becoming one of the most powerful technological revolutions of the 21st century. Unlike traditional computers that process data in binary bits (0s and 1s), quantum computers leverage quantum bits, or qubits, which can exist in multiple states simultaneously. This unique property allows quantum machines to perform calculations that would take even the fastest supercomputers thousands of years to complete.
From drug discovery to financial modeling, logistics to cybersecurity, quantum computing is set to disrupt industries and redefine the boundaries of scientific and business problem-solving. This article explores how quantum computing works, its real-world applications, challenges, and what it means for the future of innovation.
At its core, quantum computing is built on the principles of quantum mechanics, the science governing the behavior of matter and energy at atomic and subatomic levels. While classical computers use bits that represent either 0 or 1, quantum computers use qubits, which can represent both at the same time through superposition.
Additionally, qubits can be entangled, meaning the state of one qubit is directly related to another, regardless of distance. This allows quantum computers to process vast amounts of information simultaneously, enabling exponential computational power compared to classical systems.
For instance, a traditional computer analyzing a molecular structure might take weeks, while a quantum computer could do it in minutes—revealing new insights into medicine, chemistry, and materials science.
To understand the impact of quantum computing, it’s important to compare it with classical computing:
Processing Power: Classical computers handle one calculation at a time, while quantum systems can evaluate many possibilities simultaneously.
Data Representation: Classical bits represent binary states (0 or 1), while qubits leverage superposition, enabling multiple states at once.
Error Correction: Quantum computers use complex algorithms to handle errors caused by qubit instability.
Speed and Efficiency: Quantum computers could outperform even the most advanced supercomputers for certain problems, such as cryptographic analysis or optimization challenges.
These differences make quantum computing a game-changer for industries requiring massive data processing and complex modeling.
Three fundamental quantum principles drive this technology:
Superposition – Enables qubits to exist in multiple states simultaneously, vastly increasing computing power.
Entanglement – Links qubits together, allowing instant information correlation and faster problem-solving.
Quantum Interference – Optimizes results by canceling out incorrect calculations and reinforcing correct ones.
Together, these principles make quantum computing capable of solving problems beyond the reach of even the most powerful traditional computers.
Businesses worldwide are exploring quantum computing’s potential to revolutionize operations. Major corporations, startups, and governments are investing heavily in quantum research and development. Here’s how businesses stand to benefit:
Banks and investment firms use quantum algorithms to analyze market fluctuations, manage portfolios, and optimize trading strategies. Quantum computing enables faster simulations and more accurate risk assessments, leading to smarter investment decisions.
Quantum computing can handle complex logistical networks with countless variables—helping global supply chains optimize routes, manage inventory, and minimize costs even during disruptions.
Quantum computers can crack traditional encryption, but they can also create quantum-safe encryption methods, strengthening digital security and protecting sensitive data from potential cyber threats.
AI models require enormous processing power for training. Quantum computing could drastically speed up AI development, improve machine learning models, and enhance data analytics precision.
Quantum simulations can predict how molecules interact, accelerating drug discovery and reducing the cost of developing new medicines.
Beyond business, quantum computing is revolutionizing the scientific world:
Climate Modeling: Quantum computers can simulate climate systems with high accuracy, helping predict environmental changes and design sustainable solutions.
Material Science: Scientists can discover new materials for batteries, solar cells, and semiconductors by modeling atomic-level interactions faster than ever.
Space Exploration: Quantum algorithms are being used to analyze astronomical data, model cosmic phenomena, and improve spacecraft navigation.
Genetic Research: Quantum computing helps process complex biological data, advancing genomics, personalized medicine, and DNA analysis.
The technology’s ability to model complex systems in real time could lead to breakthroughs once considered impossible.
Nations around the world recognize quantum computing’s potential to shape economic power and innovation leadership. The U.S., China, and the European Union are leading the race, investing billions into research, development, and quantum infrastructure.
In 2025, countries are building quantum ecosystems—combining academia, industry, and government support—to develop practical quantum applications. Startups are also playing a critical role, driving innovation and commercial applications, while tech giants like IBM, Google, and Microsoft develop cloud-based quantum computing platforms accessible to businesses and researchers.
As a result, the global quantum computing market is projected to exceed $65 billion by 2030, transforming industries and creating new sectors of employment and expertise.
Despite its promise, quantum computing faces significant obstacles:
Hardware Limitations: Qubits are highly sensitive and require extremely low temperatures and stable environments to function reliably.
Error Correction: Quantum decoherence, or loss of qubit state, remains a major technical challenge.
High Cost: Developing and maintaining quantum computers is expensive, restricting access for smaller enterprises.
Scalability Issues: Building large-scale, fault-tolerant quantum computers remains a work in progress.
Lack of Skilled Professionals: The world currently faces a shortage of quantum computing experts, slowing widespread adoption.
Overcoming these barriers will be crucial for quantum computing to transition from research labs to real-world applications.
Quantum computing’s future is bright and transformative. Experts predict the next decade will witness major breakthroughs, including:
Quantum Cloud Services: Businesses will access quantum power through cloud platforms without owning hardware.
Quantum Artificial Intelligence: Merging quantum computing with AI could unlock new frontiers in automation, prediction, and decision-making.
Post-Quantum Cryptography: New encryption methods will secure data against quantum-level attacks.
Quantum Internet: Future communication networks will use entanglement-based quantum links to provide ultra-secure data transmission.
While full-scale quantum dominance is still years away, its gradual integration into industries will redefine the digital landscape.
With great power comes responsibility. The rise of quantum computing raises ethical and societal questions:
Could quantum computing deepen the digital divide between nations or companies?
How will cybersecurity evolve in a world where encryption becomes vulnerable?
What regulatory frameworks will ensure responsible use of quantum technologies?
Governments and organizations must collaborate to establish global standards, ensuring quantum computing benefits humanity equitably and safely.
The rise of quantum technology demands a new generation of skilled professionals. Universities are introducing specialized quantum computing programs, while online platforms provide accessible courses for engineers and scientists. Building a strong global quantum workforce will determine how quickly and effectively industries adopt this revolutionary technology.
Quantum computing is not just another technological advancement—it represents a paradigm shift in how we process, analyze, and understand information. Its impact on business, science, and society will be profound, from discovering new medicines to securing data and designing smarter cities.
As research accelerates and challenges are overcome, quantum computing will transition from experimental labs to practical, accessible solutions. The nations and organizations that harness its potential responsibly will shape the next era of human progress—ushering in what many call the “Quantum Age.”
This article is intended for informational purposes only. The content should not be considered professional or financial advice. Readers are encouraged to conduct further research or consult experts before making decisions related to quantum computing technologies.










India Says J&K Budget Exceeds Pakistan’s IMF Bailout
India slammed Pakistan at UNHRC, stating J&K’s development budget exceeds Pakistan’s IMF bailout and

UP CM Holds Talks With Ex Japan Economy Minister in Tokyo
Yogi Adityanath met former Japan economy minister Nishimura Yasutoshi in Tokyo to boost UP-Japan coo

Hiroshima Teacher Arrested for Alleged Sexual Assault of Minor
A 37-year-old high school teacher in Hiroshima was arrested on suspicion of sexually assaulting a te

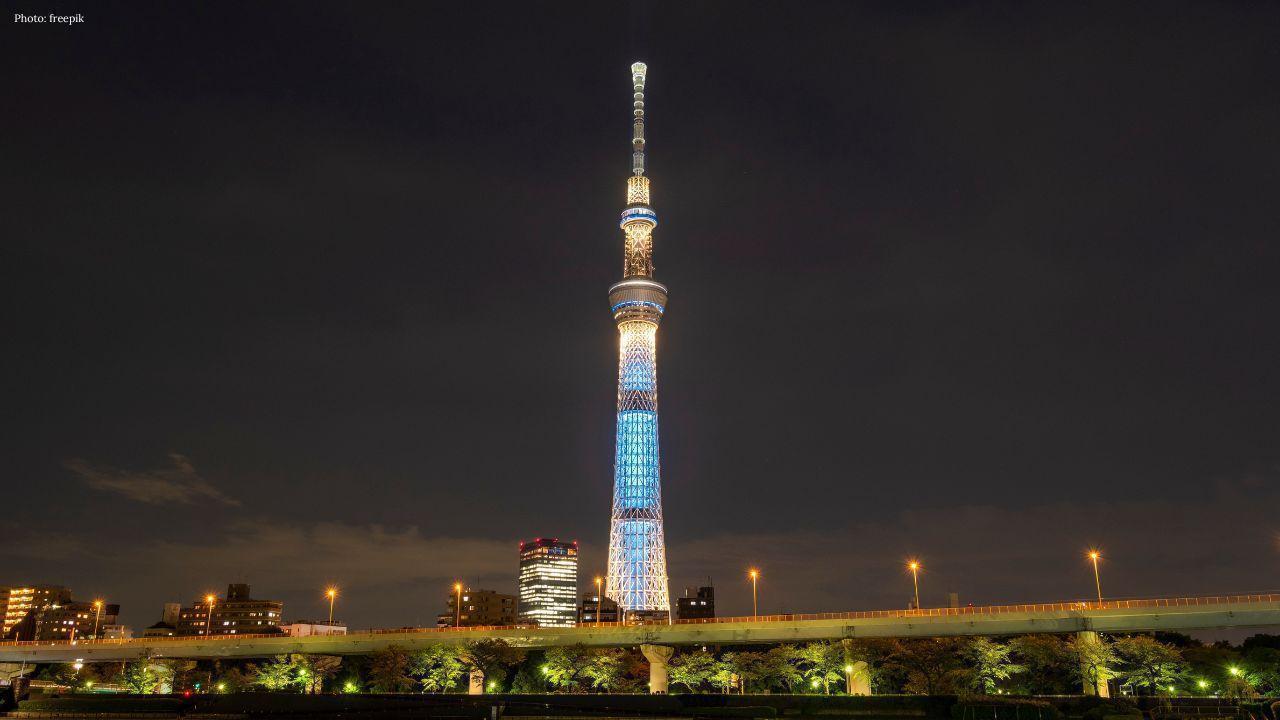
Tokyo Skytree Reopens After Elevator Malfunction Suspension
Tokyo Skytree resumed operations after a three-day closure caused by an elevator failure that trappe
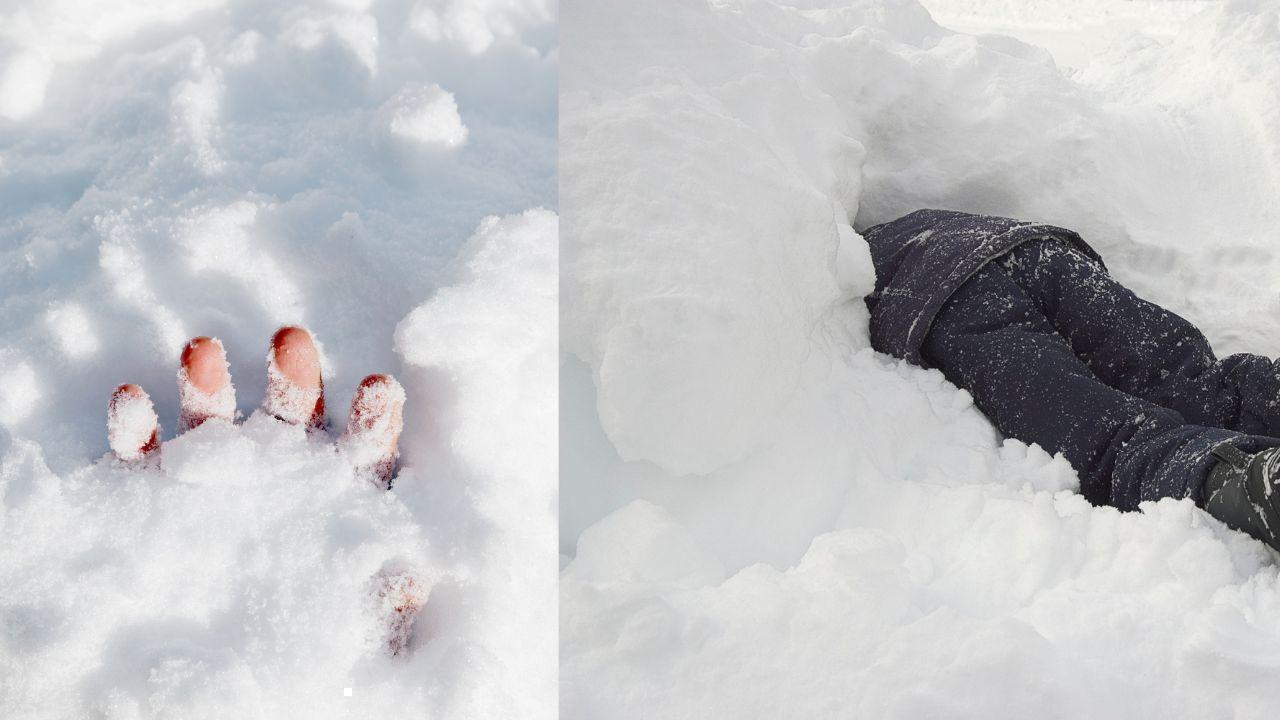

Skiers Rescue Man Buried Under Snow at California Resort
A dramatic rescue at Palisades Tahoe shows two skiers saving a man suffocating under deep snow durin
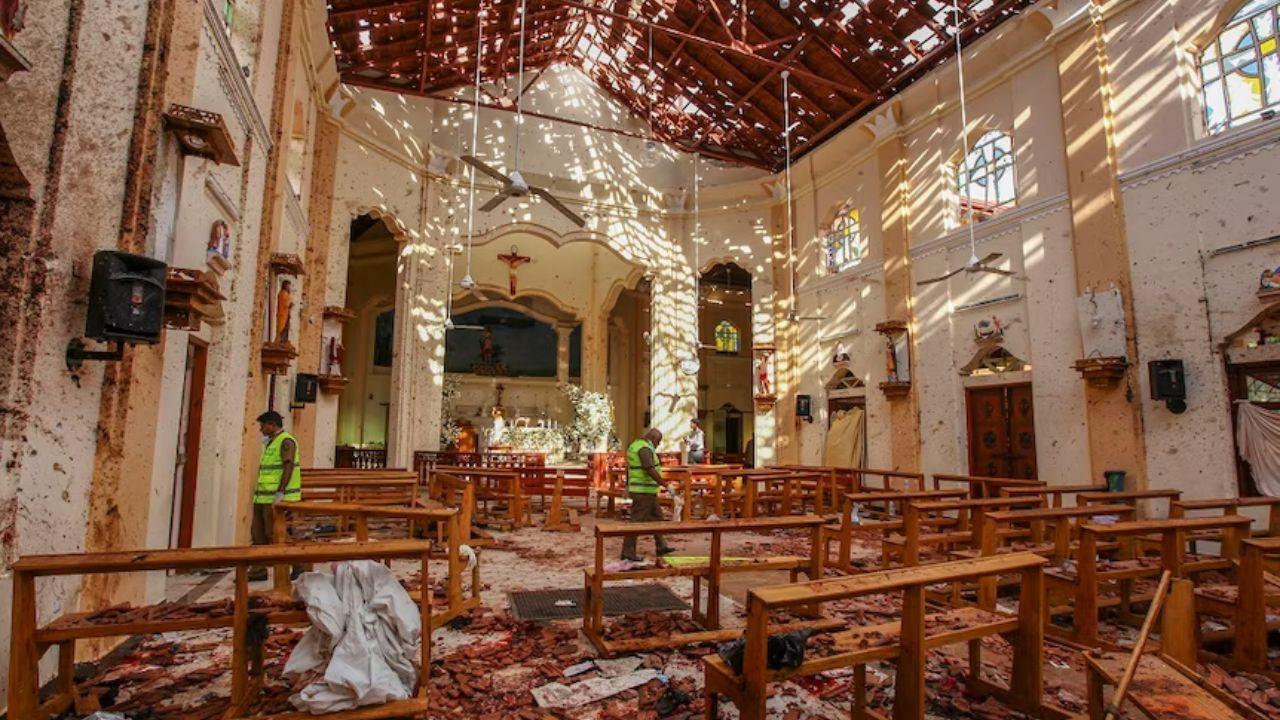

Sri Lanka Ex-Intel Chief Arrested Over Easter Attacks
Former SIS Chief Suresh Sallay arrested by CID in connection with the 2019 Easter Sunday bombings th