You have not yet added any article to your bookmarks!

Join 10k+ people to get notified about new posts, news and tips.
Do not worry we don't spam!

Post by : Anis Farhan
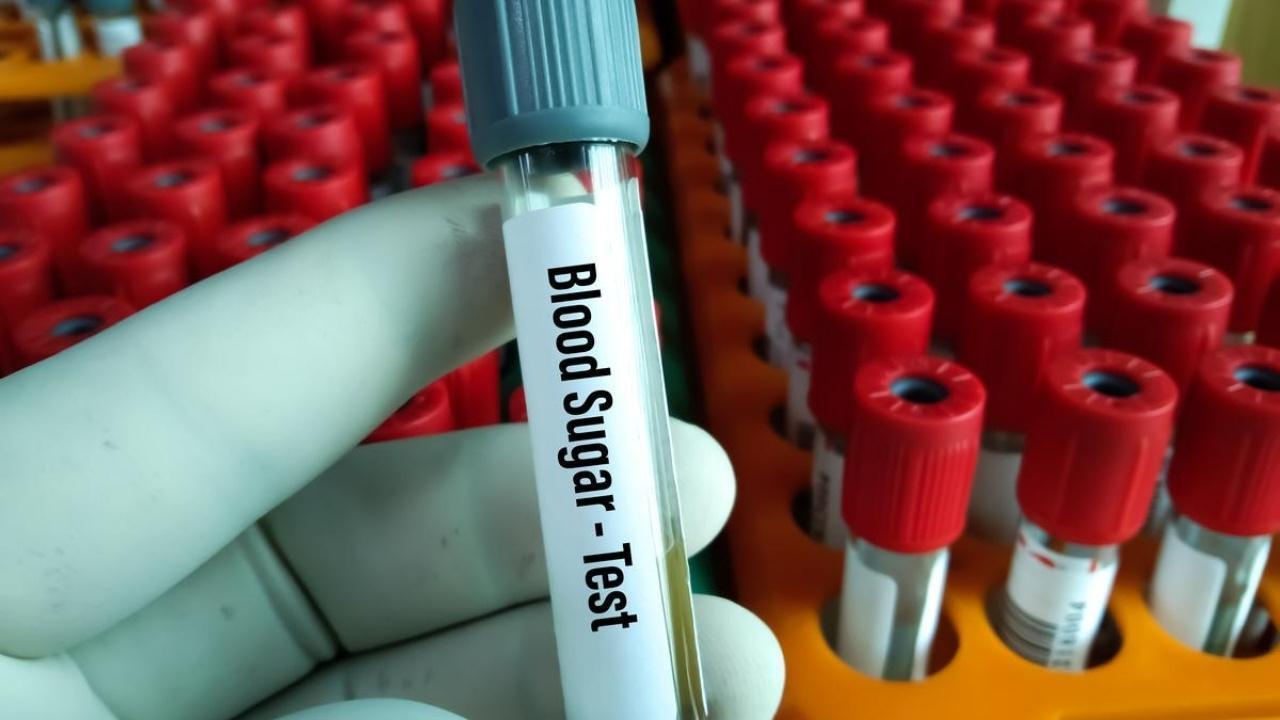
The widely used glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) test, long considered a mainstay for diagnosing and monitoring diabetes, may not provide accurate assessments for millions of people in India’s population, experts have warned. A new evidence-based viewpoint published in The Lancet Regional Health: Southeast Asia highlights significant limitations of relying solely on HbA1c measurements in a country where anaemia, hemoglobin disorders and other red blood cell conditions are common.
Healthcare professionals and researchers in India say that while HbA1c has been widely promoted as a convenient diagnostic tool, its results might be misleading in substantial segments of the population — potentially delaying diagnosis, obscuring true disease burden, and compromising effective diabetes care.
HbA1c — also referred to as glycated haemoglobin — measures the percentage of haemoglobin in the blood that has glucose attached to it, reflecting average blood sugar levels over the previous two to three months. It has become a standard diagnostic and monitoring test for type-2 diabetes because it does not require fasting and offers a snapshot of long-term glucose control.
International guidelines, including those from the World Health Organization (WHO) and the American Diabetes Association (ADA), recognise HbA1c as a useful marker for diabetes screening and management. However, this globally endorsed approach may be ill-fitted for populations with widespread variations in haemoglobin and red blood cell dynamics.
India faces a high prevalence of conditions such as iron deficiency anaemia, haemoglobinopathies (including thalassaemia and sickle-cell traits), and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency. These disorders can significantly affect the lifespan, structure or quantity of red blood cells — factors that distort HbA1c readings.
According to the Lancet review, such distortions can result in under- or over-estimation of average blood glucose levels, leading to misclassification of diabetes status. In some cases, reliance solely on HbA1c could delay diagnosis by several years — especially in individuals with undetected enzyme deficiencies like G6PD, which accelerates red blood cell breakdown and can lower HbA1c readings even in the presence of high blood sugar.
Experts also note that inconsistent laboratory standards for measuring HbA1c across India may compound inaccuracies for both diagnosis and ongoing treatment monitoring.
The potential inaccuracies in HbA1c measurements carry important clinical and public health implications. Misleading results could delay the timely initiation of diabetes management, increasing the risk of serious complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, neuropathy and vision loss.
For public health planning, over-reliance on HbA1c could also skew national estimates of diabetes prevalence. Surveys that depend solely on this measure risk portraying an inaccurate picture of the disease burden, with consequent implications for resource allocation and policy decisions.
India already accounts for one of the highest numbers of people living with diabetes globally — an estimated hundreds of millions affected by type-2 diabetes with varying degrees of control and awareness.
Given these limitations, researchers and endocrinologists are urging healthcare systems in India to adopt a multidimensional testing strategy rather than depending on HbA1c alone. Such an approach includes:
Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT): Measures blood sugar levels after fasting and then two hours after ingesting a glucose solution, offering a direct assessment of glucose handling.
Fasting plasma glucose (FPG): Assesses blood sugar after an overnight fast, helping diagnose diabetes or prediabetes.
Self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG): Frequent home testing can provide real-time insights into glucose fluctuations, helping patients and physicians tailor treatment plans.
Hematologic screening: Assessments of haemoglobin levels and red blood cell characteristics to identify anaemia or inherited conditions that can distort HbA1c.
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM): Offers detailed glycemic profiles over time, particularly useful in monitoring treatment effectiveness and identifying glucose swings not captured by HbA1c.
Such comprehensive monitoring protocols, tailored to local health resources and patient risk profiles, could provide more accurate and actionable diabetes assessments.
Adopting a broader testing framework will require adjustments in clinical practice, laboratory infrastructure and healthcare policy. While HbA1c testing remains useful as a supporting tool, clinicians are encouraged to interpret its results cautiously — especially in patients with anaemia, red cell disorders or other complicating factors.
In low-resource settings, prioritising OGTT and basic blood glucose measurements may offer more reliable diagnostic insight. Meanwhile, tertiary care centres might integrate advanced methods such as CGM alongside traditional tests.
Public health messages may also need updating to increase awareness among physicians and patients about the limitations of HbA1c and the importance of additional tests for accurate diabetes diagnosis and monitoring.
The Lancet study and expert commentary underscore a crucial message: no single test should be relied upon in isolation — particularly in diverse populations like India’s where biological and environmental factors significantly influence test outcomes.
As diabetes continues to rise in India and across South Asia, refining diagnostic protocols will be vital to improve early detection, effective management and long-term health outcomes — ultimately helping reduce the burden of this chronic disease.
This article reflects current medical research and expert opinions on diabetes testing strategies. It is intended for informational purposes and should not replace professional medical advice. Individuals concerned about diabetes screening or monitoring should consult qualified healthcare providers.









Abhishek Sharma Hospitalised With Stomach Infection, Doubtful for India’s T20 World Cup Match Against Namibia
Indian opening batter Abhishek Sharma has been hospitalised with a stomach infection and is unlikely

Mass Shooting in British Columbia Leaves 10 Dead in One of Canada’s Deadliest Attacks
A tragic mass shooting at a high school and nearby residence in Tumbler Ridge, British Columbia, has

More Than a Ticket Out: How IPOs Are Redefining Value for Startups and Investors
In the evolving startup ecosystem, initial public offerings (IPOs) have emerged as far more than exi

Study Warns Using AI for Medical Advice Is ‘Dangerous’ as Users Get Inaccurate Health Guidance
A major new study reveals that artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots and tools may give misleading o

Top Sci-Fi Movies Streaming on Netflix This February: Must-Watch Picks for Genre Fans
A curated news-style guide to the best science fiction films currently available on Netflix in Febru

BCCI Central Contracts Shake-Up: Kohli, Rohit Moved to Grade B as Board Reshapes 2025–26 List
Virat Kohli and Rohit Sharma have been placed in Grade B in the BCCI’s 2025–26 central contract list