You have not yet added any article to your bookmarks!

Join 10k+ people to get notified about new posts, news and tips.
Do not worry we don't spam!
Post by : Badri Ariffin
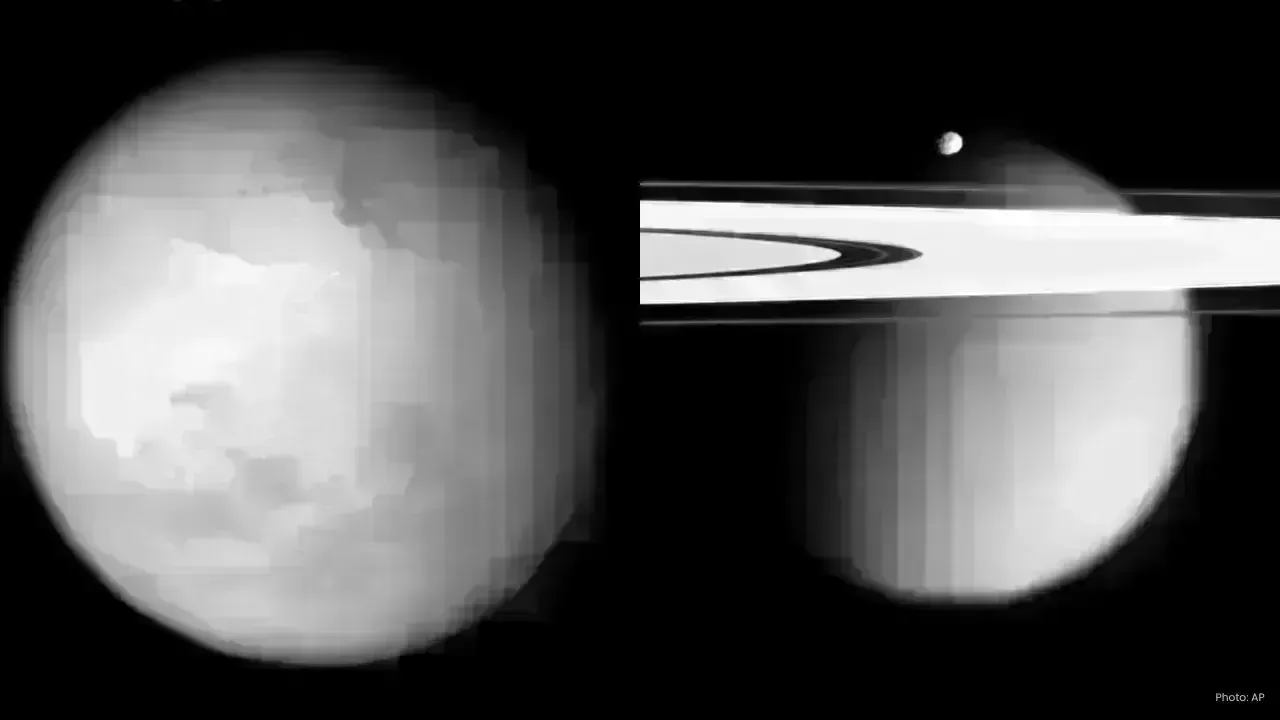
Scientists are reevaluating what exists beneath the icy surface of Titan, Saturn's largest moon. For over a decade, many experts assumed Titan had a massive underground ocean akin to those theorized on moons like Europa, but recent research from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) disputes this prevailing theory.
Instead of a significant ocean, the findings suggest that Titan may harbor dense layers of ice intermixed with slushy materials and pockets of liquid water. This accumulation may resemble semi-melted ice found in Earth's polar areas rather than an expansive ocean. Remarkably, these discoveries could enhance the prospects for life, despite no direct evidence of life yet identified.
The Significance of Titan in the Quest for Life
As the second-largest moon in the solar system, Titan spans approximately 3,200 miles (5,150 kilometers) wide, making it slightly smaller than Ganymede of Jupiter. Its surface is frigid, covered with lakes and rivers of liquid methane, and its rich atmosphere and intricate chemical processes have long marked it as a prime locale in the hunt for extraterrestrial life.
The new analysis does not outright dismiss the potential for life on Titan. It proposes a contrasting environment that might still sustain small, microscopic organisms. Baptiste Journaux, a researcher from the University of Washington involved in the study, mentioned that conditions potentially nearing melting could make Titan more hospitable for life than earlier assumed. He emphasized that nature often surprises us, and life could exist in ways beyond our current comprehension.
Discoveries from the Research
The research team delved into historical data gathered by NASA's Cassini spacecraft, which reached Saturn in 2004 and provided extensive observations for over ten years before concluding its mission in 2017 by diving into Saturn's atmosphere.
Advanced modeling and data analysis allowed scientists to reassess Cassini's contributions and found that Titan's interior responds to Saturn's gravitational influence in a manner suggesting that the ground isn't entirely fluid. If a significant ocean existed, the surface would promptly adjust to gravitational changes. However, researchers noted a 15-hour delay.
This delay indicates that Titan's interior consists of multiple layers:
A robust outer ice crust about 100 miles (170 kilometers) thick
Substantial slushy ice layers beneath
And deeper pools of liquid water
Altogether, these layers could extend to over 340 miles (550 kilometers) deep, with the deepest water pockets possibly reaching temperatures around 68°F (20°C)—unexpectedly warm for such a distant world.
Surface Dynamics
Being tidally locked to Saturn, one side of Titan always faces the planet, similarly to how the Moon consistently presents one face to Earth. This positioning allows Saturn's gravity to consistently affect Titan, causing its surface to flex and bulge.
Near its closest orbital point, Titan's surface can rise by as much as 30 feet (10 meters). The timing of this movement is crucial for the researchers' latest insights. The delayed response signifies a slushy interior rather than a free-flowing ocean.
Ongoing Debates
This study does not signal the end of discussion. Some scientists, like Luciano Iess from Sapienza University of Rome, who previously utilized Cassini data to advocate for the underground ocean theory, remain skeptical. He finds the new results intriguing but believes they don’t adequately dismiss the ocean hypothesis.
The complexities of Titan illustrate the challenges of direct exploration, compelling scientists to depend on indirect evidence, which can be subject to varying interpretations.
Implications for Future Missions
NASA's forthcoming Dragonfly mission aims to yield more definitive answers. Scheduled for launch in the upcoming decade, Dragonfly will serve as a helicopter-like robotic vehicle to probe Titan's surface and atmosphere, gather samples, and investigate the hidden dynamics below.
This mission may clarify several critical questions:
Is the majority of Titan's interior frozen?
Are liquid water pockets prevalent?
Could life inhabit those areas?
What changes has Titan's interior undergone over time?
Insights into these aspects may transform our understanding of potentially habitable worlds beyond Earth.
Titan in the Context of the Cosmos
Titan represents just one of many frigid bodies believed to harbor water—and perhaps life.
Others include:
Ganymede, Jupiter’s largest moon
Europa, noted for its underground ocean
Enceladus, celebrated for its space-bound geysers
With 274 confirmed moons, Saturn serves as a crucial region for exploring environments that may harbor life.
The Importance of Water in Astrobiology
Finding liquid water equates to contemplating the existence of life. Earth's most inhospitable areas—such as polar ice, deep ocean vents, and boiling springs—are home to microorganisms. If Titan contains warm water pockets, cocooned by ice and methane, it could create conditions suitable for life.
Scientists stress that any potential life on Titan would likely be microscopic and vastly different from terrestrial life. Nonetheless, the notion of life thriving in such a remote and chilling world highlights nature's remarkable adaptability and resilience.
What Lies Ahead?
As data is continually reexamined and new missions launch, our understanding of Titan advances. This latest study does not negate the possibility of an underground ocean; rather, it presents fresh opportunities—indicating that even in the absence of a massive ocean, Titan could remain one of the solar system's most promising locales for the quest for extraterrestrial life.









Study Warns Using AI for Medical Advice Is ‘Dangerous’ as Users Get Inaccurate Health Guidance
A major new study reveals that artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots and tools may give misleading o

Top Sci-Fi Movies Streaming on Netflix This February: Must-Watch Picks for Genre Fans
A curated news-style guide to the best science fiction films currently available on Netflix in Febru

BCCI Central Contracts Shake-Up: Kohli, Rohit Moved to Grade B as Board Reshapes 2025–26 List
Virat Kohli and Rohit Sharma have been placed in Grade B in the BCCI’s 2025–26 central contract list

Dalal Street Spotlight: Top 10 Stocks Investors Are Watching as Markets Open on a High
Indian stock markets begin the week with strong momentum, and several blue-chip and mid-cap stocks a

Market Movers Today: Key Stocks Set To Watch In Indian Markets
Indian equity markets are poised for active trading as several major companies, including Bharti Air

Milan Welcomes the World: Inside the Grand Opening Ceremony of the 2026 Winter Olympics
The 2026 Winter Olympics opening ceremony in Milan marked a defining moment for global sport, blendi