You have not yet added any article to your bookmarks!

Join 10k+ people to get notified about new posts, news and tips.
Do not worry we don't spam!
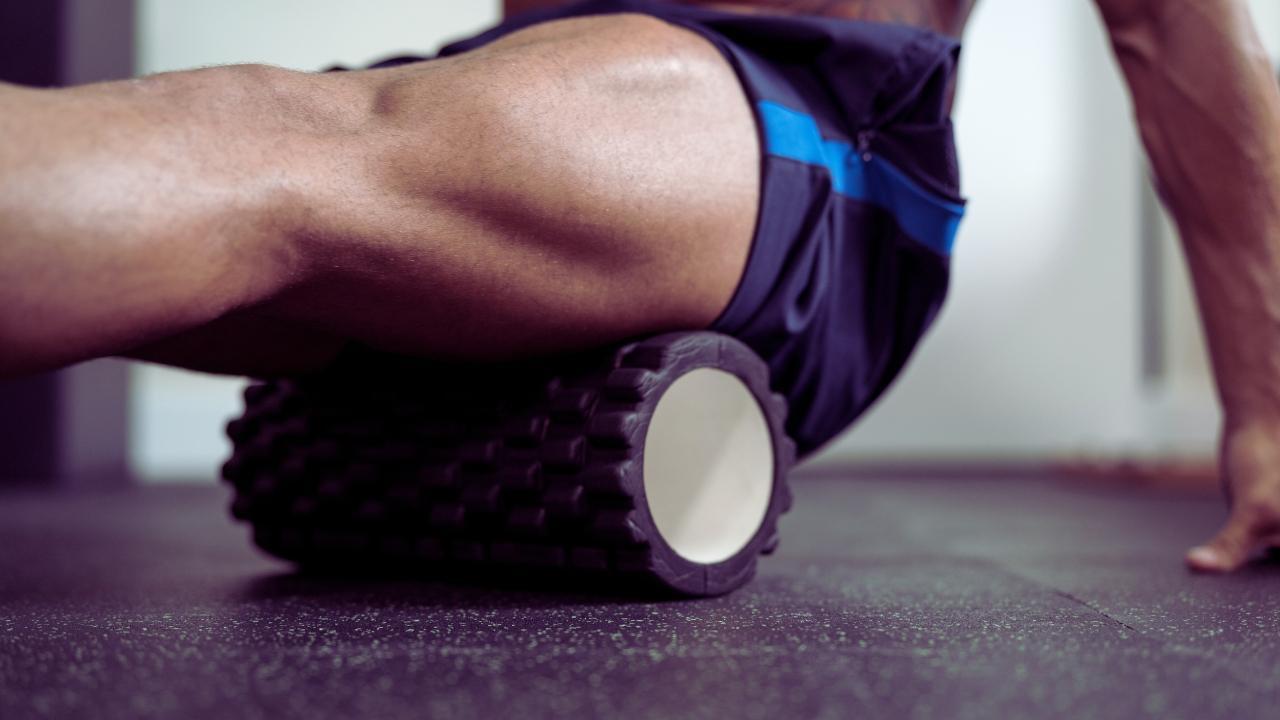

Post by : Anis Farhan
When most people think about athlete recovery, they imagine a few days of rest or a quick massage before the next big game. But in professional sports, recovery is an intricate, science-driven process that can determine whether an athlete stays at the top of their game or falls behind. It’s a blend of biology, technology, nutrition, psychology, and personalized strategies designed to repair the body, optimize performance, and prevent long-term injury.
From ice baths to cutting-edge wearable trackers, the modern athlete’s recovery toolkit is far more advanced than the average gym-goer might imagine. The difference between a gold medal and a silver one can come down to how well an athlete’s body bounces back after training or competition. This is why recovery has now become as important — if not more important — than training itself.
Recovery is not just a matter of feeling rested — it’s a biological necessity. When an athlete trains, tiny microtears form in their muscle fibers, glycogen stores deplete, and inflammation rises. Recovery is the process where these muscles repair, energy is restored, and the body adapts to become stronger and faster.
Key stages of recovery include:
Muscle Repair – The body activates satellite cells to rebuild damaged muscle fibers, making them thicker and stronger.
Inflammation Reduction – Controlled inflammation is part of healing, but excessive inflammation can slow recovery.
Energy Replenishment – Athletes need to restore glycogen stores in muscles and liver through precise nutrition.
Hormonal Rebalancing – High-intensity exercise can cause spikes in stress hormones; recovery helps return them to normal.
Understanding these processes helps sports scientists and trainers create targeted recovery plans for each athlete.
If there’s one recovery method that beats them all, it’s sleep. Deep sleep is when the body releases growth hormone, repairs tissue, and consolidates motor learning — all critical for athletes.
Elite athletes like LeBron James and Roger Federer famously sleep 10–12 hours a day. Poor sleep, on the other hand, leads to slower reaction times, reduced accuracy, and increased injury risk.
Advanced teams now track players’ sleep cycles with wearable devices to ensure they’re getting enough deep and REM sleep. Strategies include:
Creating a consistent bedtime routine
Avoiding screens before bed
Keeping the sleeping environment cool and dark
Napping strategically between training sessions
Nutrition plays a direct role in how quickly the body bounces back. The right mix of carbohydrates, protein, fats, vitamins, and minerals can speed up healing and reduce soreness.
Protein helps repair muscle fibers — sources include lean meats, fish, dairy, and plant-based proteins.
Carbohydrates restore glycogen levels, with whole grains, fruits, and starchy vegetables as key sources.
Healthy fats (like omega-3s) reduce inflammation and support cell repair.
Hydration aids nutrient transport, joint lubrication, and temperature regulation.
Some athletes also use nutrient timing, consuming high-protein and carb meals within 30 minutes of training to maximize recovery.
Contrary to popular belief, recovery doesn’t always mean lying on the couch. Active recovery — light, low-intensity activity — helps keep blood flowing, flushes out metabolic waste, and maintains joint mobility.
Examples include:
Gentle cycling or swimming
Stretching and yoga
Mobility drills targeting hips, shoulders, and spine
Athletes often use active recovery on “off days” to stay in rhythm while giving their bodies time to heal.
The science behind recovery tools is constantly evolving.
Ice baths reduce muscle soreness and inflammation by constricting blood vessels and numbing nerve endings.
Heat therapy improves circulation, which brings nutrients and oxygen to tired muscles.
Compression garments help push fluid out of muscles, reducing swelling and soreness.
Some teams now use contrast therapy, alternating between cold and hot treatments to improve blood flow and reduce fatigue.
In the last decade, technology has transformed sports recovery. Wearables like WHOOP, Oura Ring, and GPS trackers monitor heart rate variability (HRV), sleep quality, and training load. These metrics allow coaches to adjust training intensity based on recovery status.
Other advanced tech includes:
Cryotherapy chambers for whole-body cooling
Infrared saunas to stimulate blood circulation
Percussion massage guns for muscle relaxation
Electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) to activate recovery without heavy exertion
Athlete recovery isn’t just physical — the mind plays a critical role. Competitive sports can be mentally exhausting, and chronic stress can hinder physical healing.
Mental recovery strategies include:
Meditation and mindfulness
Visualization techniques
Breathing exercises to lower heart rate and promote calm
Structured downtime away from sport
Sports psychologists work with athletes to ensure they’re mentally recharged, focused, and ready to perform under pressure.
Every athlete’s body responds differently to training and recovery. Factors like age, genetics, training history, and even personality can influence recovery speed.
Sports scientists now design personalized recovery plans using biometrics, injury history, and sport-specific demands. This tailored approach ensures each athlete gets exactly what their body needs to perform at its peak.
Looking ahead, the recovery field is moving toward predictive analytics — using AI and big data to forecast when an athlete will need more rest. Genetic testing could reveal how individuals respond to certain recovery methods, making interventions even more precise.
We may also see more bio-regenerative therapies like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections and stem cell treatments becoming mainstream to speed up healing.
The hidden science of athlete recovery goes far beyond simple rest. It’s a highly strategic process that blends biology, technology, nutrition, and psychology. As sports science advances, recovery will continue to be one of the most important performance tools in an athlete’s career. For the average person, understanding these principles can also lead to better workouts, fewer injuries, and improved health.
The information presented in this article is for general informational purposes only and is based on publicly available sources at the time of writing. While every effort has been made to ensure accuracy and relevance, the author and publisher do not guarantee the completeness, timeliness, or reliability of the information. Readers are encouraged to verify facts independently and consult qualified professionals before making any business, financial, or investment decisions. The views expressed in the article are solely those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the opinions of the publisher.








Thai Baht Falls as Dollar Gains on War Tensions
Currency slips to 31.77 per dollar as investors seek safe-haven assets and watch US economic data an

Japan and Canada Boost Defense Energy Ties
Tokyo summit between leaders expected to strengthen security economic ties and support for a Free an

Indonesia May Exit US Peace Board Over Palestine
President Prabowo Subianto says Indonesia will withdraw from the initiative if it does not benefit P

Judge’s Wife Found Dead in Train Toilet During Journey
Usha Chauhan wife of Additional District Judge found lifeless in washroom of Kanchiguda–Bhagat Ki Ko

Bangladesh Government Declares Seven-Day Eid-ul-Fitr Holiday
Extra public holiday on 18 March approved by cabinet to create week-long break from 17–23 March

Pakistanis Return Home via Taftan Border
Hundreds cross from Iran into Balochistan as US-Israel strikes intensify FIA ensures 24-hour immigra