You have not yet added any article to your bookmarks!

Join 10k+ people to get notified about new posts, news and tips.
Do not worry we don't spam!
Post by : Samjeet Ariff
The Vitamin D Paradox Explained
Originally dubbed the “sunshine vitamin,” vitamin D deficiency remains common in countries blessed with sunlight. Experts now view this issue as stemming from modern living habits rather than inadequate sun exposure. Despite enjoying bright skies, many individuals aren't producing or absorbing enough vitamin D to satisfy their bodily needs.
Vitamin D is synthesized when UVB rays from sunlight touch the skin, with smaller proportions obtained through diet and supplements. Once generated, vitamin D serves key functions such as
• Enhancing bone and dental health
• Supporting the immune system
• Regulating mood and emotional health
• Boosting muscle strength
• Promoting heart and metabolic wellness
Deficiencies can affect various body systems, often silently.
One primary cause of deficiency is limited exposure to direct sunlight. Many modern daily routines keep individuals indoors for extended periods. Jobs in offices, work-from-home arrangements, and lengthy commutes significantly reduce natural light intake, even in sunny locales.
Most people tend to venture out only during early morning or late evening hours, when the UVB rays are weaker, thereby diminishing vitamin D production.
While the application of sunscreen is crucial for preventing skin cancer, it also obstructs UVB rays necessary for synthesizing vitamin D. Continuous use of high-SPF sunscreen, along with full-coverage garments and shade options, can drastically limit vitamin D creation, particularly during brief outdoor activities.
Experts recommend seeking a balance between sun protection and exposure.
In numerous sunny countries, traditional and religious garments that cover most of the body limit skin exposure to sunlight. Though this provides respite from heat, it significantly restricts vitamin D production even when people are outside.
Air pollution contributes to the diminished receipt of UVB rays at ground level. Urban areas with elevated pollution levels see a decrease in sunlight penetration, directly influencing vitamin D synthesis even on sunny days.
This issue is increasingly acknowledged in city populations.
Individuals with darker skin possess elevated melanin levels, which naturally filter UVB rays. Consequently,
• Prolonged sun exposure is required to generate equivalent amounts of vitamin D
• There is a heightened risk of deficiency even in sunny regions
This is a biological aspect rather than a health shortcoming, but it necessitates awareness and potential lifestyle modifications.
Vitamin D is naturally found in very few foods. Notably, prevalent diets in many sunny regions lack adequate amounts of vitamin D sources, including
• Fatty fish
• Egg yolks
• Fortified dairy options
Vegetarian or restrictive eating patterns may further escalate deficiency risks.
Given that vitamin D is fat-soluble, it becomes sequestered in fat tissue. Individuals with increased body fat may find vitamin D less bioavailable in the bloodstream. Thus, deficiency rates rise among overweight and obese individuals despite having ample sun exposure.
With age, the skin's capacity to generate vitamin D dwindles. Senior adults residing in sunny locales often presume they acquire sufficient sunlight, but physiological changes result in significantly reduced vitamin D production.
The growing reliance on screens, air-conditioned living, and indoor entertainment has markedly diminished natural sun exposure. Both children and adults spend less outdoor time compared to prior generations, exacerbating widespread deficiency.
Symptoms of vitamin D deficiency are often subtle and misattributed to general fatigue or stress. Common indicators include
• Persistent tiredness
• Joint or bone discomfort
• Muscle weakness
• Frequent illnesses
• Low spirits or mild depression
• Back pain
Due to the gradual emergence of symptoms, many individuals remain undiagnosed for years.
Health evaluations show surprisingly elevated deficiency levels in sunny locales, primarily due to
• Lifestyle shifts
• Urban living arrangements
• Cultural practices
• Dietary habits
• Environmental conditions
Merely having sunlight is no longer sufficient to guarantee sufficient vitamin D levels.
Experts propose:
• 15–30 minutes of midday sunlight
• Exposing arms and legs whenever feasible
• 3–4 times weekly
Individual needs vary significantly based on skin type, age, and geographic location. Excessive sun exposure is not advisable.
Supplements can often be essential when natural sources fall short. Healthcare professionals may recommend supplementary vitamin D based on blood test findings, particularly for
• Office workers
• Seniors
• Those with darker skin
• Individuals with limited sun exposure
Dosage should always be tailored based on medical expertise.
Effective measures include:
• Regular short durations in direct sunlight
• Incorporating vitamin D-rich foods into daily dining
• Balancing sun protection with brief, safe exposure
• Maintaining a healthy body weight
• Periodic vitamin D level assessments
Consistency is key, as opposed to sporadic sun exposure.
Insufficient vitamin D levels correlate with an elevated risk of infections. Adequate vitamin D promotes immune health, proving especially crucial for those who experience frequent colds or take longer to recover from illness.
Untreated deficiency can result in
• Fragile bones and heightened fracture risks
• Osteoporosis
• Chronic muscle pain
• Increased vulnerability to lifestyle diseases
• Weakened immune response
Early recognition can help avert long-term health issues.
Vitamin D deficiency in sun-rich countries underscores the impact of contemporary lifestyles, overshadowing natural advantages. Merely relying on sunlight is insufficient. Awareness, balanced practices, and timely evaluations are crucial for maintaining healthy vitamin D levels and overall wellness.
This article serves an informative purpose only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for diagnosis, evaluations, and treatment of vitamin D deficiency.









Indian Man Dies Mysteriously at Phuket Music Festival, Cause Unknown
remove news channal name give me rewrit in this news and full detaike news.news like orignal and tre
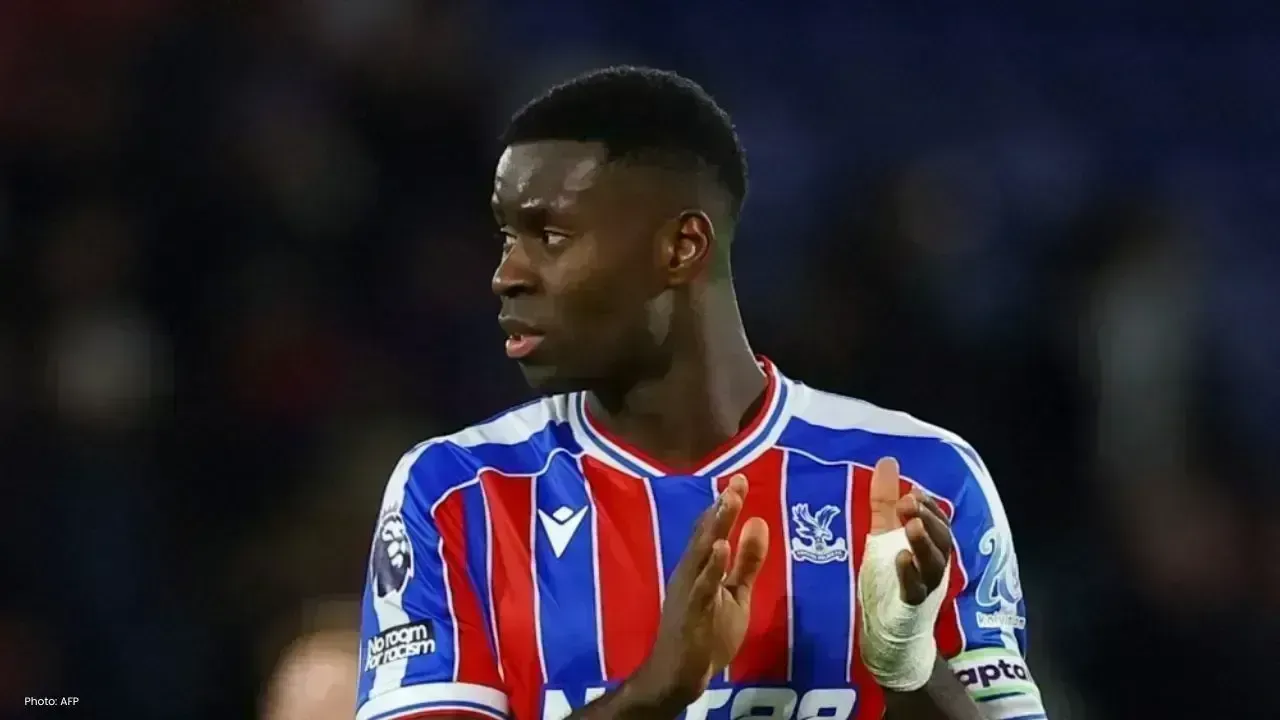

Manchester City Signs England Defender Marc Guehi From Crystal Palace
Manchester City signs 25-year-old England defender Marc Guehi from Crystal Palace for £20m, boosting

Japan Snap Election Sparks Bond Surge Amid Finance Concerns
Japan’s PM calls early election to back reflation plan. Bond yields hit decades-high as voters weigh
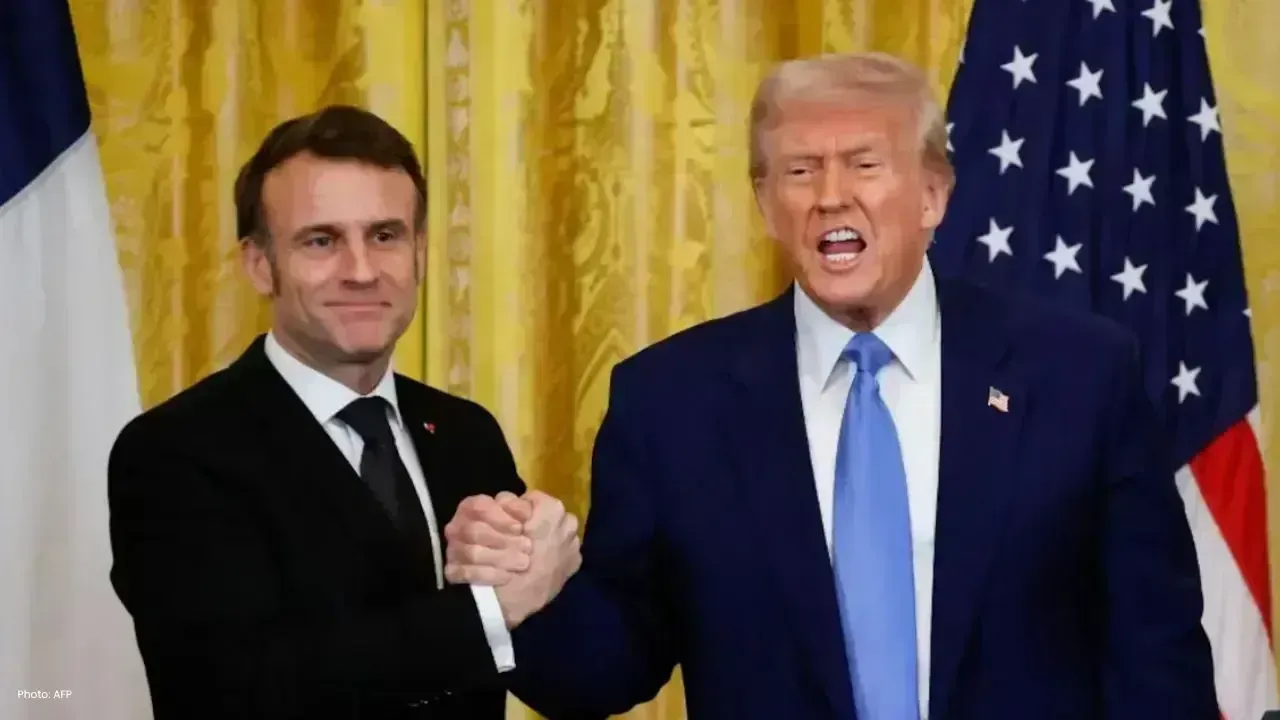

Trump Threatens Huge Tariffs on French Wine Over Peace Board Snub
Donald Trump warned of 200% tariffs on French wine after France rejected his Peace Board plan and mo
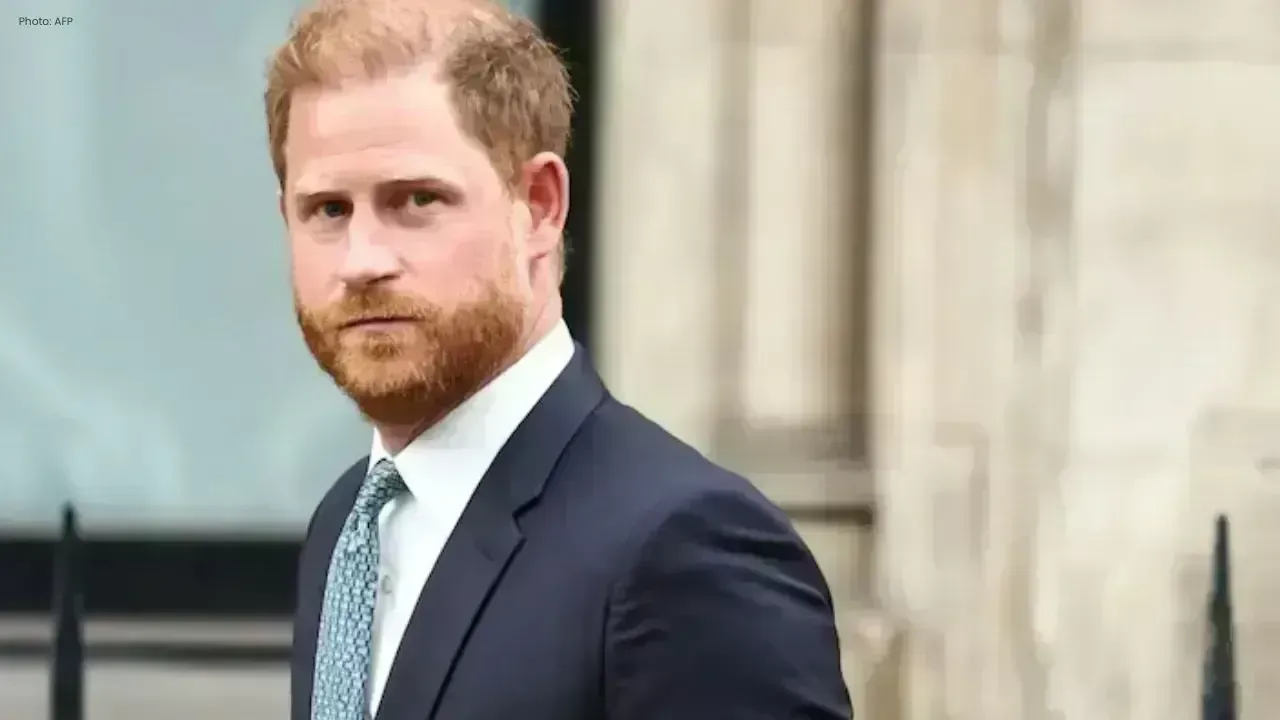

Prince Harry, Elton John Sue UK Tabloids Over Privacy Breaches
Prince Harry and Elton John accuse UK tabloids of phone hacking and stealing private info, calling i
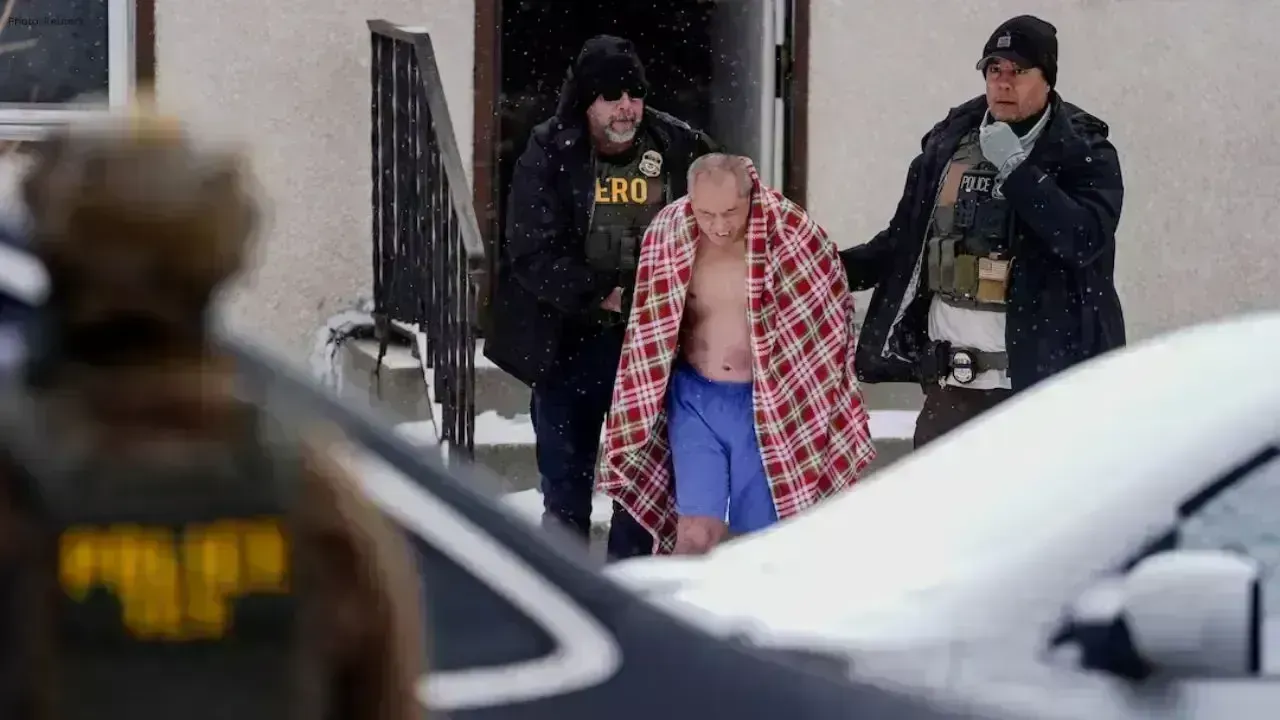

Minnesota Man Says ICE Broke In, Handcuffed Him, Dragged Him Into Snow
A U.S. citizen in Minnesota says ICE officers broke down his door, handcuffed him in shorts and Croc