You have not yet added any article to your bookmarks!

Join 10k+ people to get notified about new posts, news and tips.
Do not worry we don't spam!

Post by : Anis Farhan
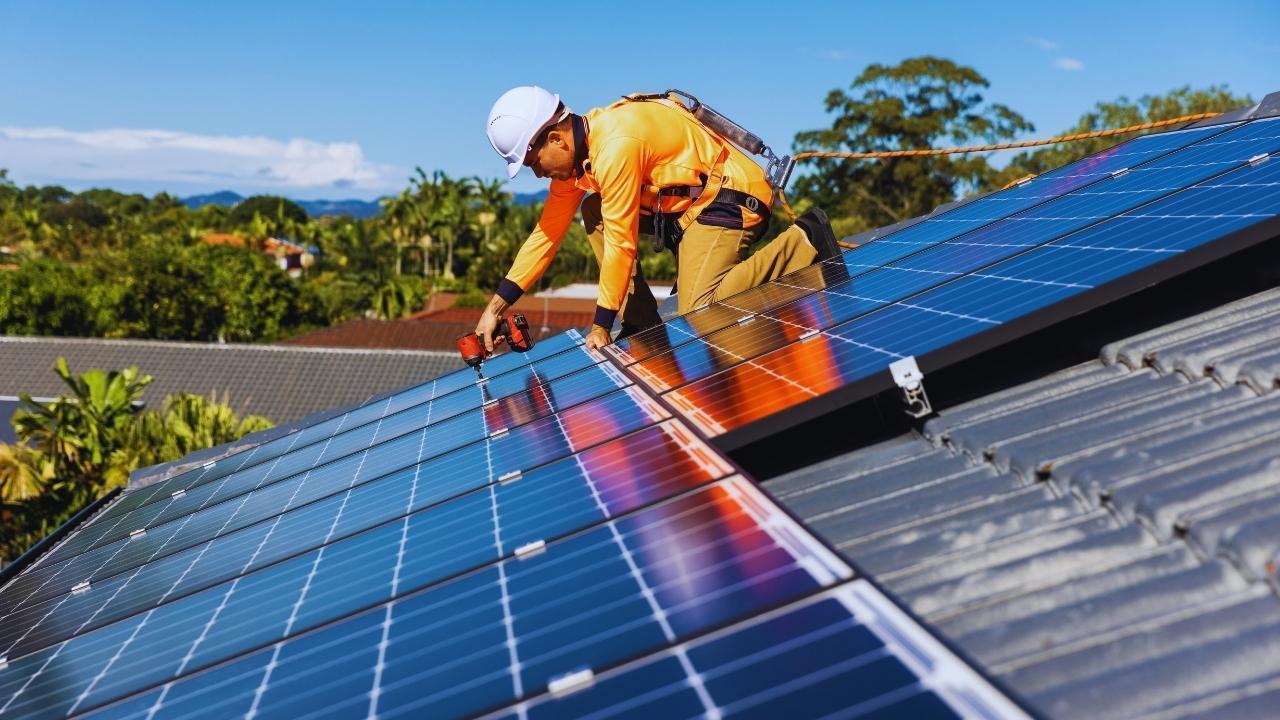
The sun is the most abundant source of energy available to humankind. Every hour, it sends more energy to Earth than the world consumes in an entire year. Harnessing this limitless power has been a human dream for centuries, but only in recent decades have solar panels—technically known as photovoltaic (PV) systems—turned that dream into a reality. Today, from rooftops to deserts, fields to spacecraft, solar panels are capturing sunlight and transforming it into usable electricity.
Solar panels have become a global symbol of sustainability. They not only reduce dependence on fossil fuels but also empower households, communities, and industries with renewable power. But how exactly does this transformation from sunshine to electricity occur? The answer lies in the combination of physics, engineering, and the natural behavior of light itself.
The idea that sunlight could generate electricity is not new. In 1839, French physicist Edmond Becquerel discovered the photovoltaic effect, the principle behind solar panels. He observed that certain materials produced small electric currents when exposed to light. Over the following century, scientists built on his discovery, leading to the creation of the first practical solar cell in the 1950s.
Initially, solar panels were used mainly in space exploration, powering satellites where traditional fuel-based systems were impractical. As technology improved and costs decreased, solar panels gradually entered civilian use. Today, they are one of the fastest-growing energy sources worldwide, shaping the future of power generation.
At the heart of solar panels lies the photovoltaic effect. This phenomenon explains how sunlight, composed of tiny particles called photons, interacts with certain materials to release electrons.
Here’s the process in simple terms:
Sunlight hits the solar panel. Photons, which carry energy, strike the surface.
Electrons are knocked loose. In specially designed materials, these photons transfer their energy to electrons, freeing them from their atomic bonds.
An electric current forms. The freed electrons flow through the material in a directed path, creating an electrical current.
Power is harnessed. Wires capture this current and channel it into usable electricity for homes, businesses, and grids.
This process is clean, efficient, and continuous as long as sunlight is available.
A solar panel is not just a flat piece of glass. It is a carefully engineered system made up of several layers:
Silicon Cells: The core of the panel, usually made from crystalline silicon, where the photovoltaic effect occurs.
Glass Layer: Protects the cells from weather while allowing sunlight to pass through.
Anti-Reflective Coating: Ensures maximum absorption of sunlight instead of reflection.
Conducting Wires: Capture and direct the flow of electrons.
Encapsulation Layers: Hold everything together and shield sensitive components from moisture and dust.
Each panel is a collection of dozens or even hundreds of these cells, working together to produce significant amounts of electricity.
Silicon is the most common material used in solar panels because of its properties as a semiconductor. Unlike metals that freely conduct electricity or insulators that resist it, semiconductors can control the flow of electrons.
When silicon is “doped” with other elements, such as phosphorus or boron, it creates an electric field within the solar cell. This field pushes electrons in a specific direction when sunlight frees them, ensuring the current flows consistently instead of randomly. This controlled movement is what allows solar panels to produce usable electricity.
The electricity generated by solar panels is in the form of direct current (DC), where electrons flow in one direction. However, most homes, appliances, and power grids use alternating current (AC), where electrons switch directions many times per second.
To bridge this gap, solar systems include a device called an inverter. The inverter converts DC electricity into AC, making it compatible with everyday use. Without this step, the energy produced by solar panels would remain largely unusable for modern living.
Not all solar panels are equally effective. Their ability to convert sunlight into electricity depends on several factors:
Material Quality: High-purity silicon and advanced designs yield higher efficiency.
Angle and Positioning: Panels produce the most energy when angled toward the sun’s path.
Temperature: Ironically, too much heat reduces efficiency, as extreme heat affects semiconductor performance.
Shading: Even small shadows from trees or buildings can significantly cut output.
Dust and Dirt: Layers of dust reduce sunlight penetration, which is why cleaning is essential.
Modern innovations like bifacial panels, tracking systems, and advanced coatings are improving efficiency and output year by year.
Not all solar panels are the same. The main types include:
Monocrystalline Panels: Made from single-crystal silicon, they offer high efficiency but are costlier.
Polycrystalline Panels: Made from multiple silicon crystals, they are more affordable but slightly less efficient.
Thin-Film Panels: Lightweight and flexible, made from materials like cadmium telluride, suitable for certain applications.
Each type has its advantages, making solar energy adaptable to diverse needs, from powering satellites to supplying household electricity.
The electricity generated from solar panels has countless uses:
Residential Power: Rooftop panels reduce dependency on conventional grids and lower electricity bills.
Commercial and Industrial Use: Factories, offices, and malls harness solar power to cut operational costs.
Rural Electrification: Solar panels bring electricity to remote areas without reliable grid connections.
Transportation: Solar-powered cars, buses, and even boats are being developed.
Space Exploration: Satellites, space stations, and rovers rely on solar panels for long-term energy needs.
This versatility makes solar energy a key driver in global renewable strategies.
Sustainability: Sunlight is inexhaustible, unlike fossil fuels.
Low Operating Costs: Once installed, maintenance is minimal compared to traditional energy systems.
Environmentally Friendly: No greenhouse gas emissions during operation.
Energy Independence: Nations and households reduce reliance on imported fuels.
Despite their promise, solar panels face hurdles:
Intermittency: Energy production stops at night and drops during cloudy weather.
Storage Costs: Storing solar energy in batteries can be expensive.
Space Requirements: Large-scale solar farms need significant land area.
Initial Investment: Though prices are falling, installation can still be costly for many households.
Innovations in battery technology, efficiency improvements, and government incentives are gradually overcoming these obstacles.
Solar panels are more than just devices; they are part of a broader shift toward clean energy. Governments around the world are investing heavily in solar infrastructure to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. Countries like China, India, Germany, and the United States lead in large-scale solar projects, while smaller nations harness solar power to achieve energy independence.
The International Energy Agency predicts that solar power will be the single largest source of electricity by 2050. This signals not just a technological revolution but also a cultural one, as humanity learns to rely more on nature’s gifts than on finite resources.
The solar industry is rapidly advancing. New frontiers include:
Perovskite Solar Cells: Offering higher efficiency and lower costs than silicon.
Solar Windows: Transparent panels that can turn glass buildings into energy producers.
Space-Based Solar Power: Concepts of collecting solar energy in space and transmitting it to Earth via microwaves.
Integration with Smart Grids: Solar panels linked to intelligent systems for efficient distribution.
These innovations suggest that solar panels will not remain confined to rooftops and fields but will become part of daily life, embedded in clothing, cars, and infrastructure.
This article is intended for informational and educational purposes. Technical explanations are simplified for general understanding. Regional practices and applications may vary.









China Ousts Three Retired Generals from Top Political Advisory Body
CPPCC ousts retired PLA generals ahead of annual Two Sessions as broader anti‑corruption military sh

Japan Jobless Rate Rises to 2.7%
Japan sees first increase in jobless rate in five months as voluntary quits rise and job openings sl

Strong 6.1-Magnitude Earthquake Shakes Indonesia’s Sumatra Island
Tremors felt across region no immediate reports of damage or casualties as authorities monitor seism

Rizwan Sajan Reaffirms Trust in UAE’s Safety and Growth
Danube Group Chairman Rizwan Sajan assures residents and expatriates of safety in UAE, highlighting

India Witnesses Chandra Grahan Blood Moon Visible in Parts of World
Skywatchers observe partial eclipse in India as total ‘Blood Moon’ visible across North America Aust

14 Pakistan Players Shortlisted for The Hundred 2026
ECB reiterates nationality will not influence selections as Haris Rauf and Shaheen Afridi headline P