You have not yet added any article to your bookmarks!

Join 10k+ people to get notified about new posts, news and tips.
Do not worry we don't spam!
Post by : Anis Farhan
Space exploration in 2025 marked a turning point in modern astronomy and planetary science. Unlike years dominated by incremental findings, this period delivered discoveries that were both surprising and deeply transformative. Advanced telescopes, refined data analysis, and ambitious space missions converged to reveal a universe far more complex, dynamic, and alive with possibility than previously imagined.
What made 2025 particularly extraordinary was not just the volume of discoveries, but their nature. Scientists uncovered evidence that challenged existing models of planetary formation, stellar evolution, and even the potential conditions required for life. These breakthroughs did more than expand scientific databases; they reshaped the questions researchers now ask about our place in the cosmos.
The foundation of 2025’s discoveries lay in technological maturity. Space observatories launched in earlier years reached peak operational efficiency, while data from long-running missions was re-examined with more powerful analytical tools. Improved spectroscopy, machine-learning-assisted data filtering, and deeper sky surveys allowed astronomers to spot patterns and anomalies that were previously invisible.
This combination of patience and precision proved crucial. Many of the year’s most astonishing revelations came not from brand-new missions, but from fresh interpretations of existing data, reinforcing the idea that the universe still holds secrets even in places we thought we understood well.
Mars has long been at the center of scientific curiosity, but 2025 added a new layer of intrigue. Subsurface radar analysis revealed extensive and stable ice deposits far closer to the Martian equator than expected. This discovery suggested that Mars may have retained accessible water resources much later into its geological history than previously believed.
More surprising was the chemical composition associated with these ice layers. Scientists identified organic compounds embedded within mineral formations, hinting at processes that could preserve signs of ancient microbial activity. While this does not confirm past life, it significantly strengthens the case that Mars once had environments capable of sustaining it.
These findings are reshaping future mission priorities. Human exploration plans and robotic lander targets are now being reconsidered, with an emphasis on regions once dismissed as too dry or geologically inactive.
Perhaps the most headline-grabbing discoveries of 2025 came from the study of exoplanets. Astronomers detected atmospheric compositions that defied conventional expectations, including planets with thick cloud layers reflecting extreme radiation while maintaining stable surface temperatures.
One of the most surprising revelations was the detection of complex molecules in the atmospheres of planets previously thought to be inhospitable. These chemical signatures suggested active atmospheric cycles and unexpected energy balance mechanisms. Such findings challenged the traditional definition of the “habitable zone,” expanding the range of worlds that could potentially support life.
These discoveries underscore a growing realization: life-friendly conditions may exist in far more diverse environments than scientists once imagined, altering the direction of future exoplanet research.
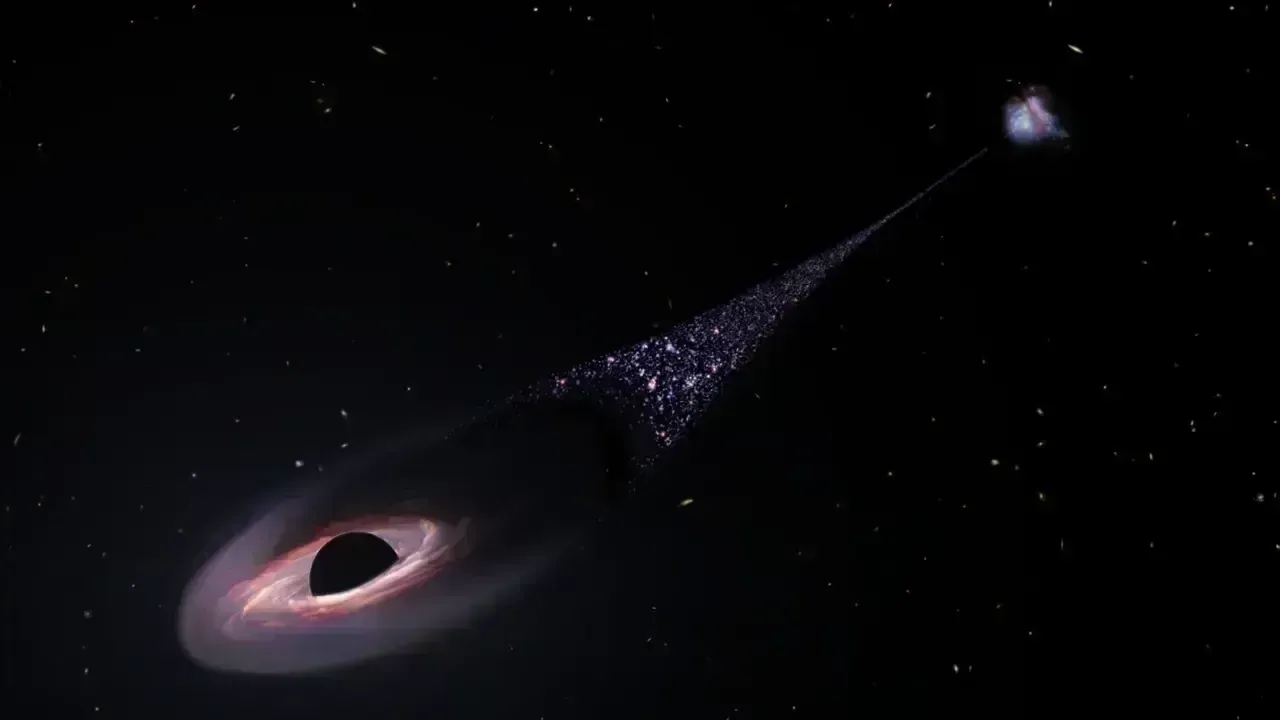
Black holes are often portrayed as cosmic destroyers, but 2025 revealed a more nuanced reality. Observations showed that some supermassive black holes emit energy in highly organized jets that influence star formation across entire galaxies. Rather than suppressing growth, these jets can trigger the birth of new stars by compressing surrounding gas.
Even more surprising was evidence suggesting that black holes can experience cycles of activity and dormancy, similar to natural systems on Earth. These patterns imply a feedback loop between black holes and their host galaxies, reinforcing the idea that black holes are not merely destructive endpoints but essential architects of cosmic structure.
This evolving understanding is forcing astronomers to revisit long-standing models of galaxy evolution.
Sample analysis from asteroid missions in 2025 provided fresh insight into the early solar system. Scientists identified complex organic molecules and water-bearing minerals that closely resemble those found on Earth. These findings strengthened the theory that asteroids may have played a critical role in delivering water and organic material to our planet.
What surprised researchers most was the diversity of chemical compositions within a single asteroid sample. This complexity suggests that early solar system bodies were far more dynamic and interactive than previously believed, constantly exchanging material during their formation.
These results deepen our understanding of how Earth became habitable and highlight asteroids as valuable archives of planetary history.
For decades, the Moon was considered geologically dormant. In 2025, that assumption was challenged. High-resolution imaging and seismic data revealed subtle tectonic movements and heat signatures beneath the lunar surface. These findings suggest that the Moon still retains internal energy, albeit at much lower levels than Earth.
This discovery has practical implications. Understanding lunar geological activity is essential for future long-term human presence, as it affects habitat stability and resource extraction planning. It also reshapes theories about how long rocky bodies can remain internally active after formation.
Gamma-ray bursts are among the most powerful events in the universe, and 2025 brought new clarity to their origins. Scientists identified previously unknown precursor signals that occur moments before these explosions. This breakthrough allows astronomers to predict such events with greater accuracy and study their environments in unprecedented detail.
The discovery revealed that these bursts are not isolated phenomena but part of a larger chain of stellar evolution events. This insight is helping scientists map the life cycles of massive stars with far greater precision than before.
The space between stars was once thought to be relatively empty. In 2025, researchers found evidence of complex chemical reactions occurring in interstellar clouds. These reactions produce molecules essential for star and planet formation, suggesting that the building blocks of life are more widespread than previously assumed.
This revelation reinforces the idea that the universe is not a static backdrop but a constantly evolving environment where chemistry and physics interact on vast scales.
A silent yet transformative factor behind many 2025 discoveries was the use of artificial intelligence in data analysis. Machine learning systems processed enormous volumes of astronomical data, identifying subtle patterns that human researchers might overlook.
AI-assisted analysis enabled faster identification of rare phenomena, from unusual stellar behavior to faint signals in deep-space observations. This partnership between human intuition and computational power is rapidly becoming essential to modern space science.
The implications of 2025’s space discoveries extend beyond academic circles. They influence how humanity plans future exploration, allocates resources, and even perceives its place in the universe. Each revelation brings us closer to answering fundamental questions about life, origins, and destiny.
These findings also inspire technological innovation, from advanced materials developed for space missions to improved data analysis techniques with applications on Earth.
As remarkable as 2025 was, it also set the stage for future breakthroughs. Upcoming missions are now being redesigned based on these discoveries, targeting locations and phenomena that were previously underestimated or overlooked.
Scientists expect that the next decade will further blur the line between science fiction and reality, with discoveries that challenge even the most imaginative theories.
The most surprising space discoveries of 2025 share a common theme: the universe is far more dynamic, interconnected, and complex than we once believed. From Mars and the Moon to distant exoplanets and black holes, each revelation expanded the boundaries of human knowledge.
Rather than providing final answers, these discoveries opened new questions, ensuring that curiosity remains the driving force of exploration. As humanity looks ahead, one truth stands clear — the cosmos still has many secrets waiting to be uncovered.
Disclaimer: This article is a general science overview based on publicly discussed space research trends and discoveries reported throughout 2025. Interpretations may evolve as further scientific data becomes available.










Bengaluru Matrimony Scam: Engineer Loses Rs 1.52 Crore to Fake Groom
A Bengaluru software engineer was cheated of Rs 1.52 crore by a man she met on a matrimony site, who

Vietnam Party Congress Begins, To Lam’s Power in Focus
Vietnam’s Communist Party meets to choose its top leader and set economic goals, as To Lam looks set

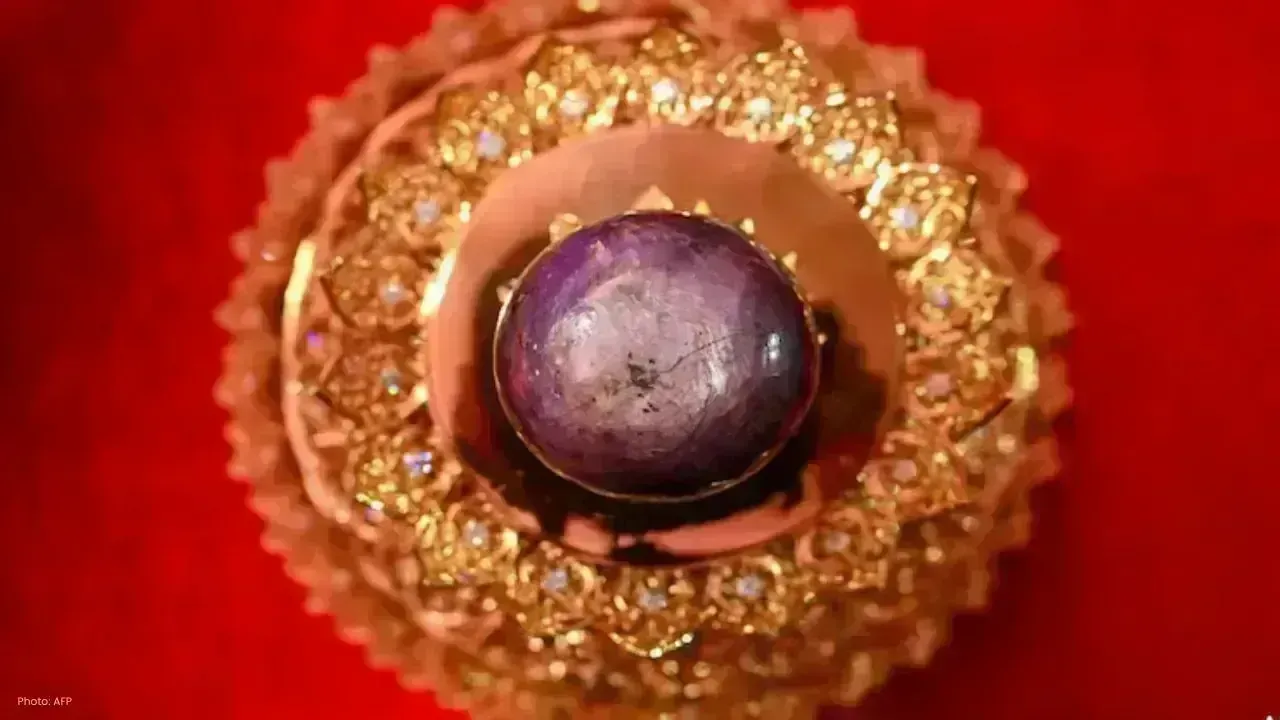
World’s Largest Purple Star Sapphire ‘Star of Pure Land’ Unveiled
A 3,563-carat Purple Star Sapphire, the world’s largest of its kind, was revealed in Sri Lanka, valu

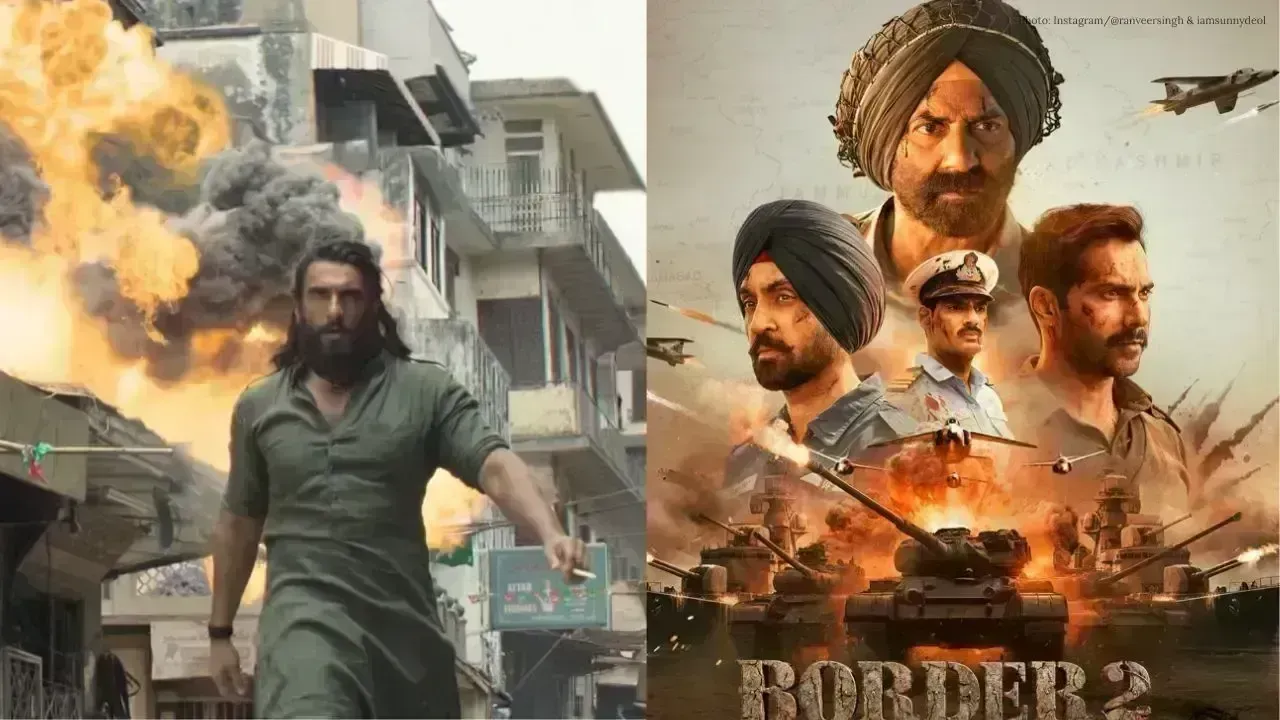
Dhurandhar 2 Confirmed for Eid 2026, Teaser to Premiere with Border 2
Dhurandhar 2 will release on March 19, 2026. Its teaser will premiere with Border 2 on January 23 to
The Raja Saab Box Office Flop: Prabhas’ Film Struggles to Hit ₹200 Crore
Prabhas' The Raja Saab becomes one of his slowest films, crossing ₹200 crore worldwide only after 10

Tragic Incident: Software Engineer Drowns After Car Plunges Into Waterlogged Pit in Greater Noida
Yuvraj Mehta, 27, drowned when his car fell into a 50-feet deep pit in Greater Noida. Rescue efforts