You have not yet added any article to your bookmarks!

Join 10k+ people to get notified about new posts, news and tips.
Do not worry we don't spam!

Post by : Anis Farhan
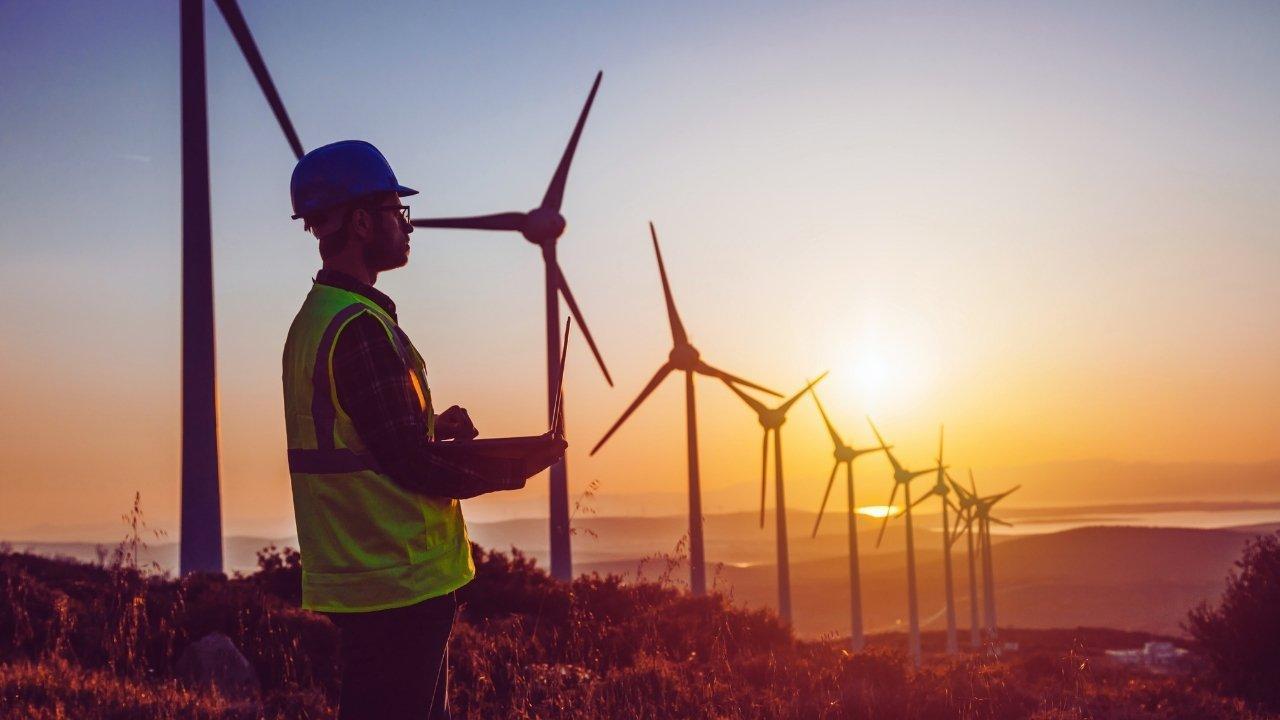
Energy is at the heart of human progress. From powering homes and industries to fueling transport and innovation, the demand for energy has shaped economies and societies. For over a century, fossil fuels—coal, oil, and natural gas—have dominated the global energy landscape. They built modern cities, drove industrial revolutions, and created unprecedented growth. But they also brought environmental destruction, rising carbon emissions, and volatile global markets. Today, the story is changing. Renewable energy sources—like solar, wind, hydropower, and geothermal—are becoming cheaper, more reliable, and more widely adopted than ever before. The world is living through a historic energy transition, where renewables are no longer an alternative but increasingly the default.
Just a decade ago, renewable energy was seen as costly, experimental, and dependent on government subsidies. Today, the opposite is true. The price of solar panels has dropped by nearly 90% in the last 15 years, while the cost of wind energy has fallen by over 60%. Large-scale solar farms now produce electricity at a fraction of the cost of coal and natural gas plants. Even offshore wind, once prohibitively expensive, has seen dramatic cost reductions thanks to technological advances and scaled-up production.
This economic transformation is not just about cheaper technology—it’s about predictability. Unlike fossil fuels, which are subject to global price shocks, renewable energy relies on free natural resources: sunlight, wind, and water. Once infrastructure is in place, the cost of generating power becomes stable and predictable, insulating economies from the turbulence of oil markets and geopolitical conflicts.
Fossil fuels are facing challenges on multiple fronts. Economically, they are no longer competitive. Environmentally, they are unsustainable. Politically, they are divisive. Socially, they are losing public support. These four dimensions make it clear why fossil fuels are steadily losing ground.
Economic Decline: Oil and gas companies are finding it harder to justify new investments. As renewable projects offer better returns and faster deployment, investors are shifting money away from fossil fuels.
Environmental Pressure: Climate change policies, carbon taxes, and emission restrictions are pushing fossil fuel industries to cut back. The Paris Agreement and national net-zero pledges have made clear that fossil fuels are incompatible with long-term goals.
Political Instability: Energy security has become a pressing issue, especially during global conflicts. Countries relying heavily on imported oil and gas face major risks. Renewable energy, by contrast, enhances energy independence.
Social Awareness: Citizens worldwide are demanding cleaner air, sustainable living, and responsible governance. Public protests, climate activism, and consumer preferences are all putting fossil fuels in an unfavorable light.
Solar energy is at the center of this transition. It is versatile, scalable, and increasingly affordable. From rooftop solar panels on private homes to mega solar farms powering entire cities, the adaptability of solar is unmatched. Countries in sunny regions, from India to the Middle East, are harnessing solar power at record levels. Even nations with less sunlight are investing heavily in advanced photovoltaic technology and battery storage to make solar viable year-round.
Solar’s biggest advantage lies in its accessibility. Individuals can become energy producers by installing panels on their rooftops, reducing reliance on central grids. This democratization of energy is reshaping economies and empowering communities.
Wind power is another pillar of the renewable revolution. Onshore wind farms have been expanding rapidly in Europe, North America, and Asia, while offshore wind—especially in coastal regions—is becoming a game changer. Technological improvements, such as larger turbines and smarter grid integration, have made wind energy more efficient and cost-competitive.
Wind farms also bring economic opportunities to rural areas, creating jobs and generating local revenue. For governments, wind energy offers a clear path to decarbonization while boosting energy resilience.
While solar and wind dominate headlines, hydropower and geothermal energy provide consistent, reliable baseload power. Hydropower has been a backbone of renewable electricity for decades, while geothermal—though geographically limited—offers an untapped potential for countries with volcanic activity. Together, these steady sources complement variable solar and wind, ensuring stable energy supply throughout the year.
One of the criticisms often aimed at renewables is intermittency—what happens when the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing? This is where energy storage and smart technology come in. Advances in battery technology, particularly lithium-ion and emerging solid-state batteries, are making it possible to store surplus renewable energy for later use. Smart grids, artificial intelligence, and digital monitoring are enhancing efficiency, balancing supply and demand, and preventing blackouts.
In the near future, hydrogen energy storage and advanced grid systems will further eliminate the intermittency issue, making renewables not only affordable but also completely reliable.
Countries around the world are rewriting their energy playbooks. China has become the largest investor in solar and wind energy, while the European Union is pushing aggressive climate policies. The United States, after years of mixed policies, is now investing heavily in clean energy infrastructure. In the Middle East, traditionally reliant on oil exports, nations like Saudi Arabia and the UAE are diversifying into massive solar projects.
This global competition is driving innovation. Nations that lead in renewable technology are positioning themselves as future energy superpowers. Meanwhile, countries clinging to fossil fuels risk economic stagnation and environmental damage.
Beyond economics, the shift to renewables has profound human and environmental benefits. Cleaner energy means cleaner air, fewer health issues, and reduced healthcare costs. Communities near coal plants or oil fields often suffer from pollution, respiratory diseases, and environmental degradation. Transitioning to renewables reduces these risks and creates healthier societies.
Environmentally, renewables drastically cut greenhouse gas emissions. They help slow global warming, protect biodiversity, and preserve natural ecosystems. Unlike fossil fuel extraction, renewable projects generally have smaller land and water footprints, reducing environmental destruction.
Another critical factor is employment. The renewable energy sector is one of the fastest-growing job markets in the world. From engineers and technicians to construction workers and researchers, millions of new jobs are being created. This “green economy” is not only about producing clean energy but also about building sustainable infrastructure, electric vehicles, and energy-efficient technologies.
For countries struggling with unemployment, the renewable sector offers opportunities for growth, skill development, and economic stability.
While renewables are on the rise, challenges remain. Fossil fuel industries still wield political influence in many countries. Transitioning entire economies requires massive investments, policy support, and long-term commitment. Developing countries, in particular, face financial and technological hurdles in adopting large-scale renewable solutions.
There is also the issue of just transition—ensuring that communities and workers dependent on fossil fuel industries are not left behind. Retraining programs, government support, and community-driven policies will be essential to make the transition fair and inclusive.
The writing is on the wall: fossil fuels are on borrowed time. While they will not disappear overnight, their dominance is ending. The future of energy belongs to renewables—not because they are fashionable, but because they are cheaper, cleaner, and more sustainable.
The world is entering an era where energy is not only abundant and affordable but also aligned with environmental and social well-being. The fossil fuel age may have powered humanity’s past, but renewables will shape its future.
This article is for informational and educational purposes only. It is based on current trends, research, and industry insights related to renewable energy and fossil fuels. Readers are encouraged to consult official reports, energy experts, and government sources for policy decisions or investment guidance.










Meta Shuts Down 150,000 Scam Accounts Worldwide
Joint international operation involving Singapore police and global agencies targets scam networks o

Singapore–Batam Ferries Add Fuel Surcharge
Ferry operators introduce S$6 surcharge on Singapore–Batam routes as rising global fuel prices incre
SC Orders Policy for COVID Vaccine Side Effects
Landmark ruling asks Centre to frame a no-fault compensation scheme for people who suffered severe a

Japan Marks 15 Years Since Earthquake and Tsunami
Nation observes moment of silence as thousands remember victims of the 2011 triple disaster that res

Six Dead After Bus Fire Near Bern in Switzerland
Regional PostBus vehicle catches fire near Kerzers, triggering investigation by Swiss authorities

China Exports Surge Despite Trump Tariffs
Strong global demand for electronics and manufactured goods pushes China’s exports higher despite ri