You have not yet added any article to your bookmarks!

Join 10k+ people to get notified about new posts, news and tips.
Do not worry we don't spam!
Post by : Anis Farhan
Technological revolutions rarely arrive with dramatic announcements. In most cases, they develop quietly inside research labs, startups, and experimental pilot programs long before they enter public awareness. While attention often focuses on familiar trends such as smartphones, social media, or generative AI, some of the most transformative breakthroughs remain largely unknown outside specialist circles. By 2030, several of these emerging technologies could redefine how humans live, work, heal, communicate, and interact with the planet.
These breakthroughs are not speculative science fiction. Many already exist in early or fragmented forms, progressing steadily rather than explosively. Their potential lies not in novelty alone, but in their capacity to merge with existing systems and solve problems that current technologies struggle to address.
One of the most promising but underreported advances is the development of self-healing materials. These materials can detect microscopic cracks or damage and repair themselves without human intervention. Inspired by biological systems such as skin and bone, self-healing composites could dramatically extend the lifespan of buildings, vehicles, bridges, and electronic devices.
By 2030, widespread adoption of such materials could reduce infrastructure maintenance costs, improve safety, and lower resource consumption. Entire industries may shift from reactive repair models to predictive resilience, fundamentally altering construction and manufacturing economics.
Programmable matter refers to materials that can change shape, density, or function when exposed to specific stimuli such as heat, light, or magnetic fields. Unlike traditional smart materials, programmable matter can be reconfigured repeatedly for different purposes.
This breakthrough could enable objects that adapt to their environment in real time, from clothing that adjusts insulation automatically to furniture that reshapes itself based on user needs. The implications extend into aerospace, medical devices, and disaster response equipment.
Conventional data storage technologies face physical and energy limitations as global data generation accelerates. DNA-based storage offers a radically different approach, encoding information into synthetic DNA strands. A single gram of DNA can theoretically store vast amounts of data while remaining stable for thousands of years.
By 2030, DNA storage could revolutionize archival systems, preserving cultural, scientific, and historical data in ways previously impossible. It may also significantly reduce the energy footprint of global data infrastructure.
Researchers are exploring biological systems that compute using living cells rather than electronic circuits. These systems can process information, respond to environmental signals, and adapt over time. Unlike silicon-based computers, biological computation operates efficiently at microscopic scales and consumes minimal energy.
Such systems could enable advanced biosensors, responsive medical implants, and adaptive environmental monitoring tools that operate seamlessly within natural ecosystems.
Artificial photosynthesis aims to replicate the natural process plants use to convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into energy-rich compounds. Unlike solar panels that produce electricity directly, artificial photosynthesis could generate storable fuels using sunlight alone.
If successfully scaled by 2030, this technology could provide clean, decentralized fuel production while actively reducing atmospheric carbon. Its potential impact on climate change mitigation and energy independence is enormous.
Beyond batteries, solid-state energy networks focus on distributing energy through advanced materials that minimize loss and maximize efficiency. These systems could enable buildings and cities to function as interconnected energy ecosystems, sharing power dynamically based on demand.
This approach could dramatically improve grid resilience and support the transition to renewable energy without requiring massive infrastructure overhauls.
While brain-computer interfaces are often discussed publicly, less attention is paid to the quiet breakthroughs in miniaturization and non-invasive neural interfaces. These advancements aim to read and influence neural activity without surgical implantation.
By 2030, such interfaces could support cognitive rehabilitation, enhanced learning, and new forms of communication for individuals with neurological impairments. Ethical oversight will be critical as boundaries between assistance and enhancement blur.
Modern prosthetics increasingly incorporate AI, but the next leap involves restoring sensory feedback to users. Adaptive prosthetics that communicate directly with the nervous system can provide real-time sensation, allowing users to feel pressure, temperature, and texture.
This breakthrough could redefine disability, shifting from compensation toward genuine restoration of function and experience.
Rather than relying on visible devices, ambient intelligence embeds computation into everyday surroundings. Walls, streets, and public spaces become responsive systems that adjust lighting, traffic flow, and environmental conditions automatically.
By 2030, cities may function as adaptive organisms, continuously learning from human behavior to improve efficiency, safety, and quality of life without constant user interaction.
Future cities may rely less on centralized control and more on autonomous coordination among distributed systems. Traffic, utilities, emergency services, and public transport could self-organize based on real-time conditions.
This shift could reduce congestion, lower emissions, and improve disaster response, particularly in rapidly growing urban regions.
Advances in data modeling and biological simulation are enabling predictive health systems that identify disease risk before symptoms appear. These models integrate genetics, lifestyle data, and environmental factors to forecast health trajectories.
By 2030, healthcare may shift decisively from treatment to prevention, reducing costs and improving quality of life through early intervention.
Emerging therapies aim not to treat symptoms but to repair damage at the cellular level. These approaches involve directing biological mechanisms to correct dysfunctions directly within cells.
If successful, targeted cellular repair could transform the management of chronic diseases and age-related degeneration.
Future communication technologies may interpret emotional context alongside words. By analyzing tone, facial expression, and physiological signals, systems could adjust responses dynamically to emotional states.
This capability could improve remote collaboration, mental health support, and conflict resolution by reducing miscommunication and enhancing empathy.
Research into transmitting information through non-traditional channels such as haptic feedback or neural signals could enable communication beyond speech and text. This may be especially impactful in high-risk environments or accessibility contexts.
Supply chains are becoming increasingly autonomous, capable of sensing disruptions and reconfiguring routes without human oversight. These systems rely on predictive analytics and distributed decision-making.
By 2030, autonomous supply chains could significantly reduce waste, improve resilience, and stabilize global trade under volatile conditions.
Traditional economic models struggle to account for automated labor and intangible digital value. Emerging systems aim to measure contribution and productivity in environments where machines perform much of the work.
These models could reshape taxation, employment, and wealth distribution frameworks.
Many of these breakthroughs operate invisibly, raising concerns about transparency and accountability. Systems that make decisions quietly can be difficult to audit or challenge.
Ensuring ethical deployment will require new governance models that prioritize explainability and public oversight.
As technology becomes more autonomous and embedded, humans may relinquish more decision-making authority. The challenge lies in preserving meaningful choice and responsibility while benefiting from technological efficiency.
The convergence of multiple quiet breakthroughs makes the period leading up to 2030 uniquely significant. Individually, these technologies are incremental. Together, they form interconnected systems capable of reshaping civilization-level structures.
Their impact will depend not only on technical success but on social readiness, policy alignment, and ethical foresight. The choices made in the coming years will determine whether these breakthroughs amplify human potential or deepen existing inequalities.
The technologies most likely to change everything by 2030 are not necessarily the ones dominating headlines today. They are the subtle, foundational innovations advancing steadily beneath public awareness. Understanding and preparing for their impact requires attention, adaptability, and thoughtful governance.
As history has shown, the most profound transformations often arrive quietly, becoming visible only once they are already woven into everyday life.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only and reflects current research trends and expert analysis. Technological outcomes may vary based on scientific, economic, and regulatory developments.








Japan Says Farewell to Last Giant Pandas Amid Rising China Tensions
Thousands bid goodbye to Japan’s last giant pandas before their return to China, as diplomatic tensi
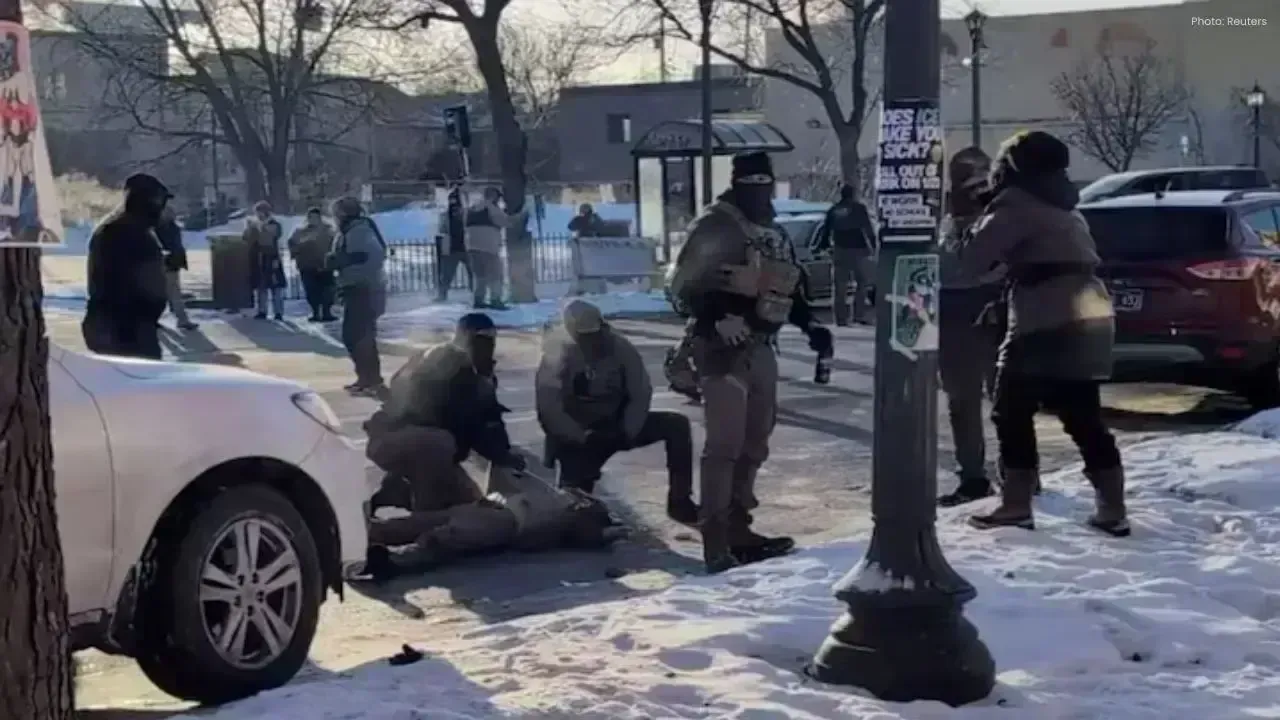

Doctor Tried to Save Man Shot by Immigration Agents in Minneapolis
A doctor tried to revive Alex Pretti after immigration agents shot him, but was initially stopped. T
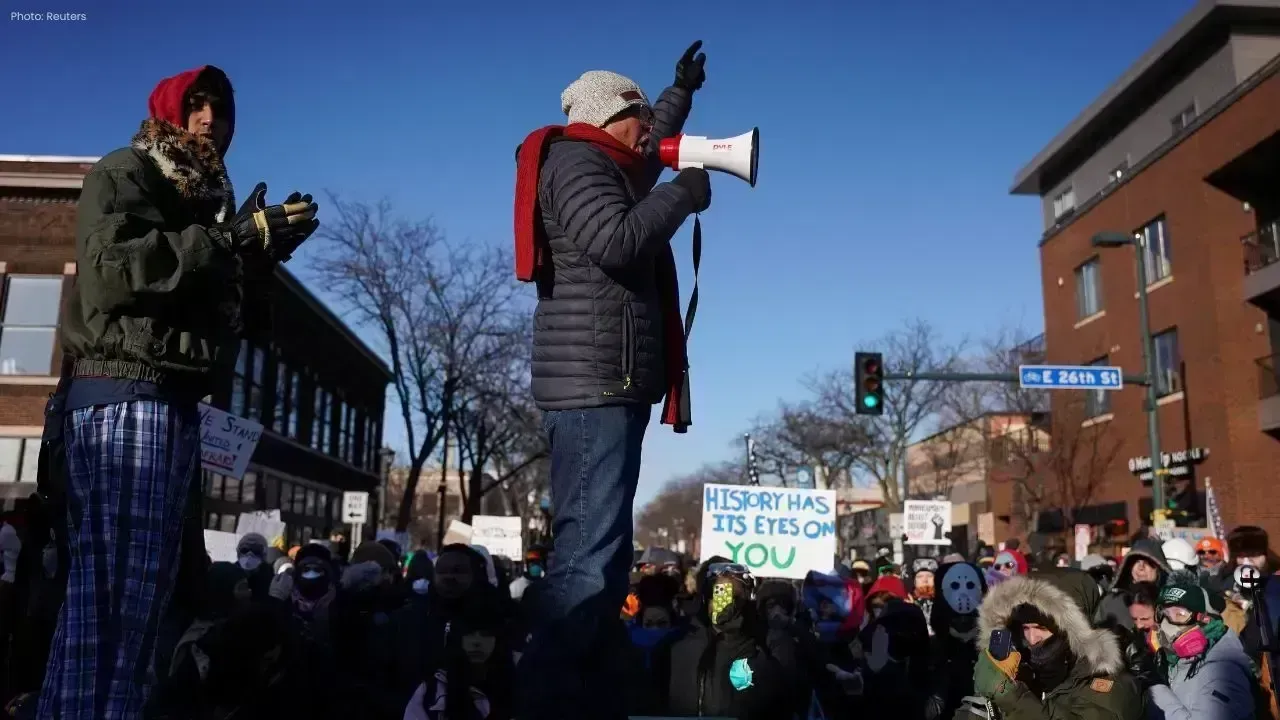

Minneapolis Tension After U.S. Citizen Shot by Federal Immigration Agents
A U.S. citizen was fatally shot by immigration agents in Minneapolis. Officials cite self-defense, b
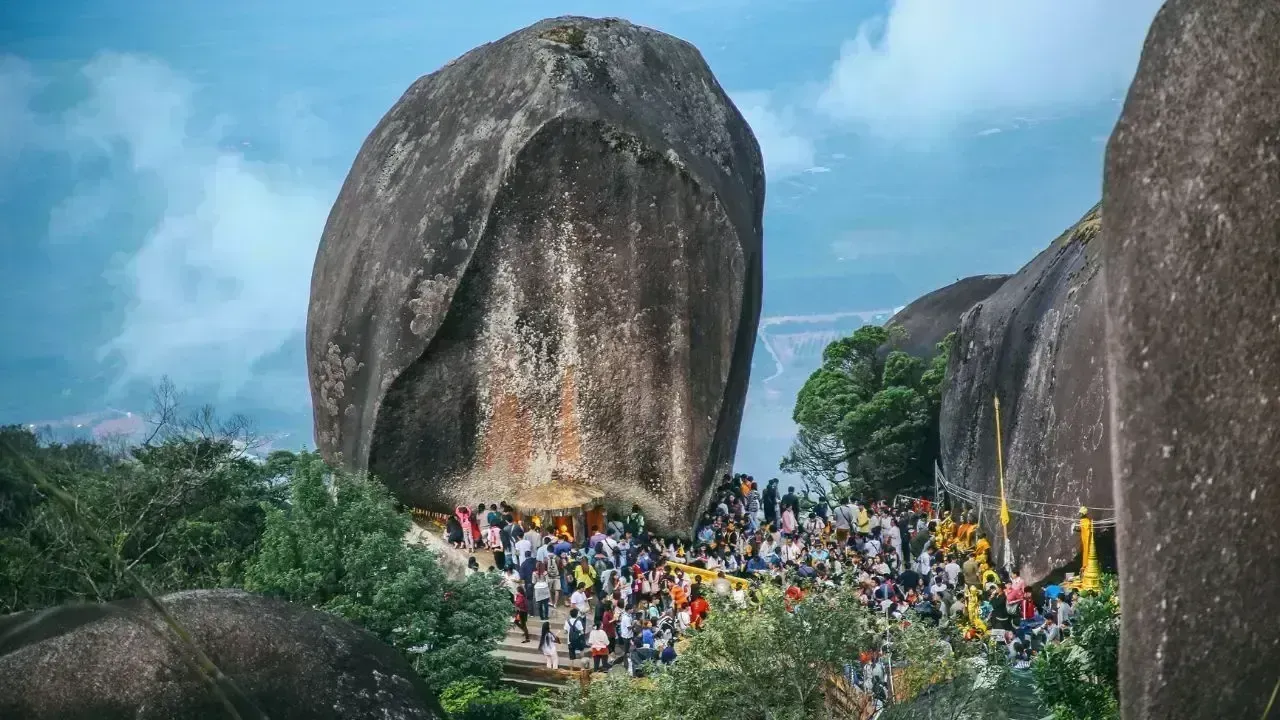

Devotees Flock to Khao Khitchakut for 2026 Buddha Footprint Pilgrimage
Hundreds visit Khao Khitchakut National Park to pray at the sacred Buddha footprint for blessings an

Indian National Among 4 Killed In Georgia Shooting, Suspect Held
An Indian national was among four people killed in a Georgia home shooting linked to a family disput

Trump Slams Canada Over “Golden Dome”, Warns China May Take Over Soon
Trump criticised Canada for rejecting the “Golden Dome” plan over Greenland and warned China could d