You have not yet added any article to your bookmarks!

Join 10k+ people to get notified about new posts, news and tips.
Do not worry we don't spam!

Post by : Anis Farhan
Despite living in the most connected era in human history, most people only see a narrow slice of what is actually happening in the world. Algorithms prioritize familiarity, headlines reward simplicity, and attention spans shape narratives. Beneath the surface of daily news cycles, however, quiet developments are reshaping how humans live, think, work, and even perceive reality.
The year 2026 is revealing truths that feel almost unbelievable—not because they are fictional, but because they rarely make it into mainstream conversations. These are not viral trivia facts. They are subtle realities with profound implications, hiding in plain sight.
Here are ten little-known facts in 2026 that may fundamentally change how you view the modern world.
By 2026, behavioral science has confirmed something unsettling: the majority of digital decisions are influenced before conscious thought kicks in. Recommendation systems, interface design, timing, color cues, and content sequencing subtly shape user behavior milliseconds before awareness occurs.
What feels like free choice online is often a guided outcome. This does not mean people are controlled, but it does mean autonomy is more fragile than assumed. Platforms optimize for engagement by predicting emotional states rather than interests, influencing what users read, buy, or believe without explicit persuasion.
The surprising part is not that this happens, but how consistently it works across cultures, age groups, and education levels.
In 2026, data models built from everyday digital behavior—scroll speed, pause duration, typing rhythm, and content interaction—can predict preferences, stress levels, and future decisions more accurately than traditional personality assessments.
These models do not rely on what people say about themselves, but on what they do unconsciously. This means identity is increasingly inferred rather than declared.
While this enables personalization and efficiency, it also raises questions about consent, transparency, and who truly controls personal narratives in a data-driven world.
Most people in 2026 believe they interact with artificial intelligence only occasionally. In reality, AI systems influence daily life constantly—often invisibly.
From traffic routing and content moderation to pricing, fraud detection, and automated decision-making, AI shapes outcomes without direct interaction. Many systems no longer announce themselves as AI-driven because their presence is normalized.
The mind-blowing part is not AI’s intelligence, but how seamlessly it has blended into the background of everyday life.
Despite advanced tools, automation, and AI assistance, individual human productivity has plateaued in many sectors. Systems are faster, but people are not necessarily producing more meaningful output.
In 2026, studies show that cognitive overload, constant context switching, and information saturation counteract technological gains. People spend more time managing systems than benefiting from them.
The paradox is that while tools have improved, attention has become the scarcest resource. The limiting factor is no longer capability, but focus.
Humans have always outsourced memory to tools, but by 2026, reliance on digital memory has crossed a psychological threshold. People increasingly remember where information is stored rather than the information itself.
This shift changes how knowledge is structured in the brain. Memory becomes navigational rather than internalized. While this frees cognitive space, it also weakens long-term retention and deep understanding.
The mind adapts, but the nature of learning itself is changing—quietly and irreversibly.
In an unexpected reversal, many people in 2026 maintain more consistent identities online than offline. Digital profiles, writing history, content creation, and interaction patterns form stable representations of belief and personality.
Offline identities shift based on context—work, family, social circles—while online expression often reflects sustained interests and values over time.
This challenges the assumption that online personas are less authentic. In many cases, they are more coherent and persistent than real-world behavior.
Culture was once shaped by editors, institutions, and shared experiences. In 2026, algorithms decide which ideas surface, which fade, and which never appear.
This does not mean culture is controlled, but it is filtered. Visibility determines relevance, and relevance shapes norms. Ideas that align with algorithmic incentives spread faster than those that challenge them.
The surprising truth is that cultural influence now depends less on merit and more on compatibility with digital distribution systems.
In a world of constant output, silence is gaining unexpected value. By 2026, individuals and organizations that pause strategically—posting less, speaking selectively, and avoiding constant visibility—often gain more credibility and influence.
Overexposure has created fatigue. Audiences increasingly associate restraint with confidence and noise with insecurity.
The most powerful voices are no longer the loudest, but the most deliberate.
People once trusted institutions, credentials, and authority figures. In 2026, trust is increasingly built through patterns: consistency, transparency, and behavioral history.
Individuals trust creators, brands, and platforms not because of formal authority, but because of predictable behavior over time. Trust has become algorithmic in nature—earned through repetition rather than reputation.
This subtle shift explains why traditional authority struggles to maintain influence in digital environments.
Contrary to popular belief, the future is not more chaotic than before. It feels that way because information is fragmented. People see different versions of reality shaped by personalized feeds, communities, and narratives.
In 2026, two people can inhabit the same society but experience entirely different informational worlds. This fragmentation creates uncertainty, anxiety, and misunderstanding—not because reality is unstable, but because shared context is disappearing.
The most mind-blowing realization is that confusion is not a lack of information, but an excess without alignment.
Taken together, these facts reveal a world that is quieter, subtler, and more complex than headlines suggest. Change is no longer announced—it accumulates. Influence no longer commands—it nudges. Power no longer declares—it embeds.
The systems shaping daily life in 2026 operate through design, behavior, and repetition rather than force or visibility. Understanding them requires attention, not outrage.
These facts remain little-known because they do not feel dramatic. They do not arrive as breaking news. They unfold gradually, blending into routines until they feel normal.
Human perception is tuned to sudden change, not slow transformation. By the time shifts are recognized, they are already embedded.
Awareness does not mean rejection. Technology, automation, and data-driven systems offer enormous benefits. But awareness restores agency.
Understanding how influence works allows people to engage intentionally rather than reactively. It enables better choices—not by resisting change, but by navigating it consciously.
These facts are not endpoints. They are early signals. As systems grow more intelligent and interconnected, the gap between surface understanding and underlying reality may widen further.
The future will reward those who observe patterns, question assumptions, and remain adaptable rather than those who chase certainty.
The most mind-blowing truths in 2026 are not hidden because they are secret. They are hidden because they are subtle.
The world is not changing loudly. It is changing quietly, through behavior, design, and systems that feel invisible until you learn how to see them.
Once you do, it is impossible to unsee.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only and reflects current observations, research trends, and expert analysis. Interpretations may evolve as new data emerges.








Japan Says Farewell to Last Giant Pandas Amid Rising China Tensions
Thousands bid goodbye to Japan’s last giant pandas before their return to China, as diplomatic tensi
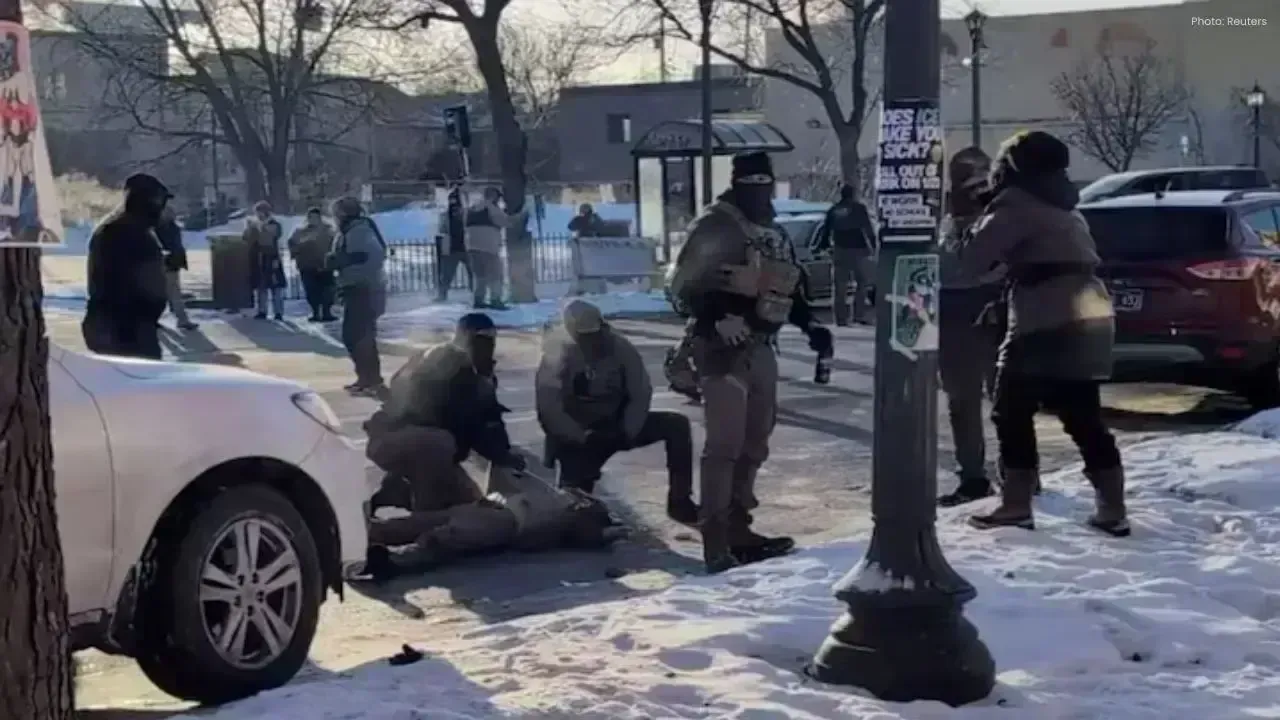

Doctor Tried to Save Man Shot by Immigration Agents in Minneapolis
A doctor tried to revive Alex Pretti after immigration agents shot him, but was initially stopped. T
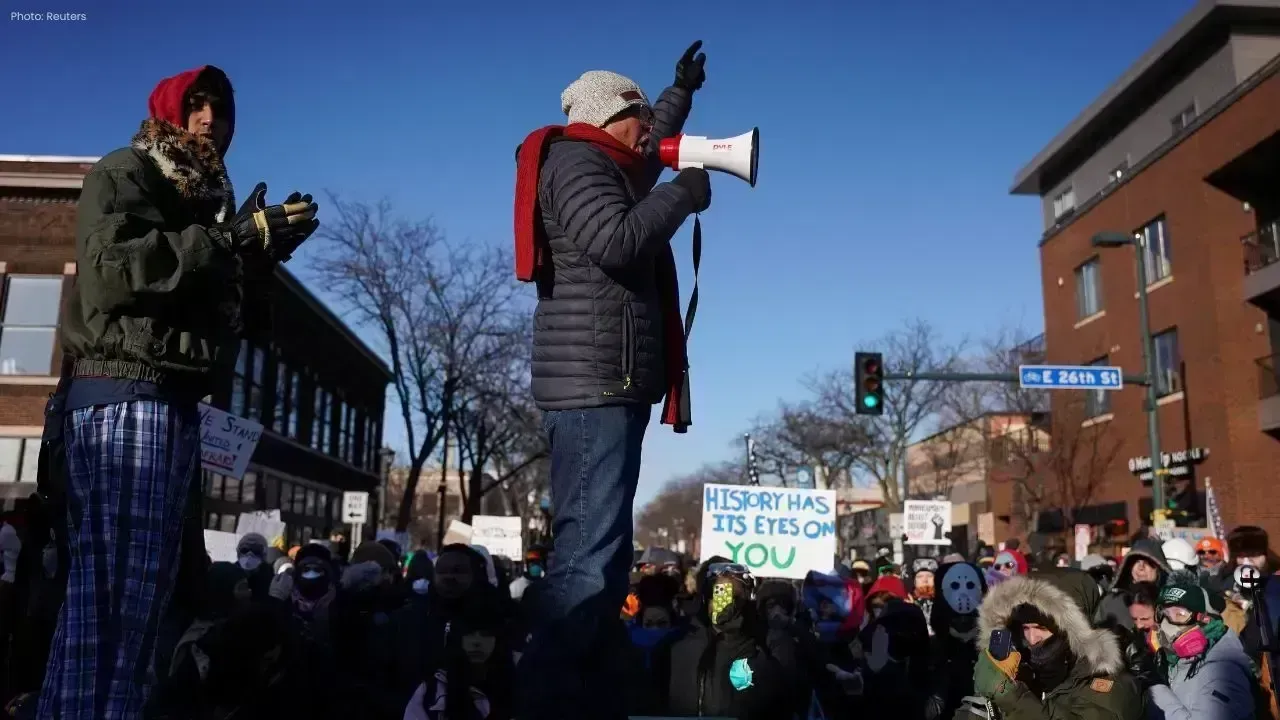

Minneapolis Tension After U.S. Citizen Shot by Federal Immigration Agents
A U.S. citizen was fatally shot by immigration agents in Minneapolis. Officials cite self-defense, b
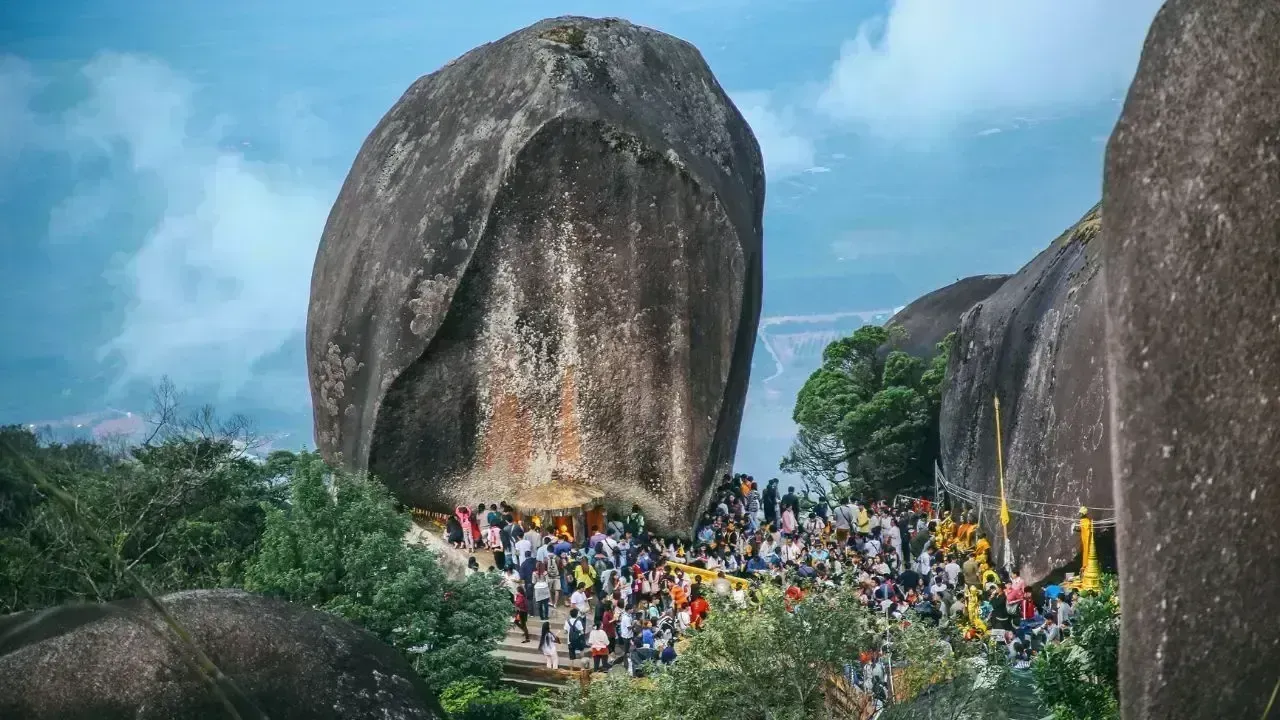

Devotees Flock to Khao Khitchakut for 2026 Buddha Footprint Pilgrimage
Hundreds visit Khao Khitchakut National Park to pray at the sacred Buddha footprint for blessings an

Indian National Among 4 Killed In Georgia Shooting, Suspect Held
An Indian national was among four people killed in a Georgia home shooting linked to a family disput

Trump Slams Canada Over “Golden Dome”, Warns China May Take Over Soon
Trump criticised Canada for rejecting the “Golden Dome” plan over Greenland and warned China could d