You have not yet added any article to your bookmarks!

Join 10k+ people to get notified about new posts, news and tips.
Do not worry we don't spam!

Post by : Samjeet Ariff
Launching a business without validating the concept ranks among the most significant errors entrepreneurs can make. Many individuals face financial losses not due to a lack of dedication or effort, but from early investments in ideas that lack market interest. Validation isn’t about stifling dreams; it’s about preserving your resources.
This guide provides a detailed, step-by-step approach to appropriately validating a business idea using methods embraced by actual businesses. Emphasis is placed on clarity, evidence, and data-driven decision-making rather than mere speculation.
Validation of a business idea entails demonstra<|vq_6570|>the willingness of real customers to pay for your product or service. It addresses three fundamental questions:
Is there a genuine problem?
Is there a demand for a solution?
Will customers pay for it consistently?
Validation goes beyond friend opinions or social media likes; it focuses on observed behaviors, genuine demand, and willingness to spend.
Common errors bridge numerous failed ventures:
Building first, questioning later
Assuming demand without confirmation
Focusing on features over real issues
Prioritizing personal enthusiasm over market realities
Financial commitment exacerbates mistakes. The more you invest without validation, the harsher the failure.
Every solid business concept begins by identifying a specific, pressing issue.
Who experiences this issue?
How frequent is the occurrence?
How serious is the impact?
What are the consequences of inaction?
A vague problem undermines a business’s potential; clearly identified problems draw paying customers.
Many individuals become enamored with solutions prior to verifying the existence of the problem. Validation should always begin with understanding the problem, not jumping to product ideas.
Aiming to cater to everyone generally results in appealing to no one.
Age range
Occupation or lifestyle
Income bracket
Geographic location
Daily challenges they face
The more precise you are, the easier it becomes to validate need.
Diverse groups attribute varying values to problems. A concern that one group deems worthy of spending may be overlooked by another.
Absence of solutions might indicate lack of demand.
Similar offerings from competitors
Indirect alternatives that address the same issue
Free options that users currently prefer
Competition validates market demand.
Instead of wondering “Why are there competitors?”, consider:
Customer complaints in reviews
Missing features
Pricing issues
Gaps can illuminate opportunities for validation.
People search for what they desire.
Active searches reflect demand
Low search activity suggests weak urgency
Look for:
Searches related to problems
“How to” inquiries
Comparative searches
Price-related inquiries
Search intent represents a powerful validation signal.
Nothing substitutes for direct conversations.
How do you currently address this issue?
What aspects of current solutions frustrate you?
Have you previously paid for a solution?
What factors would provoke you to switch?
Resist the urge to pitch; listen more than you talk.
Genuine emotional responses
Specific feedback on frustrations
An account of previous failed solutions
Discussions about willingness to pay
Polite interest does not equal validation. Pain and urgency do.
Interest alone is insufficient.
Pre-orders
Paid waiting lists
Deposits
Limited-time offers
If customers are hesitant to invest even a small sum, demand might be weaker than anticipated.
Monetary involvement reveals honesty. Individuals may express enthusiasm yet hesitate when asked to pay.
A Minimum Viable Product (MVP) assesses value with minimal investment.
A landing page explaining the concept
A basic prototype
A manual version of the service
A demo or sample
The aim is learning, not achieving perfection.
Sign-up rates
Conversion rates
User engagement
Points of drop-off
Validation derives from actual actions, not surveys.
Pricing errors can devastate profitable concepts.
Propose varied price points
Experiment with bundles versus individual offers
Compare subscription models to one-time payments
If pricing feels uncomfortable, confidence in value may be lacking.
Even ideas with significant demand can falter financially.
Cost to acquire a single customer
Cost to deliver the service or product
Net margin per sale
Potential scalability restrictions
Validation involves financial viability, not merely demand.
Expensive customer reach can erode profits.
Organic content strategies
Engagement within communities
Referral strategies
Small-scale paid experiments
If marketing expenses eclipse lifetime value, the concept necessitates refinement.
Single-instance interest won’t sustain a business.
Frequent usage
Follow-up inquiries
Customer referrals
Continued engagement
Strong retention validates the long-term success of the business.
Some ideas falter not due to lack of demand, but because of feasibility issues.
Necessary skill sets
Time commitments required
Dependence on third-party vendors
Legal or regulatory hurdles
A concept must be feasible for consistent operation.
Often, excellent ideas falter if released too soon or late.
Is the problem pressing today?
Are consumers actively seeking solutions?
Are supporting technologies or behaviors sufficiently advanced?
Timing is a vital, albeit often unnoticed, factor.
Not every positive signal is genuine.
Likes without corresponding purchases
Compliments without true commitment
Encouragement from friends and family
Free trial usage without conversion rates
Authentic validation always entails sacrifice from customers.
Outcomes from validation lead to one of three paths:
Move forward with confidence
Adjust strategy based on insights
Pause to conserve financial resources
All three choices are victories as they promote informed investment.
Validation isn't about absolute certainty; it focuses on intelligent risk reduction. It's not about seeking guarantees, but striving for robust evidence.
Successful entrepreneurs prioritize problems over ideas. Ideas are mutable. Evidence will guide future actions. Validation fosters confidence based on reality.
Before committing funds to a business idea, validating it is not about delaying action—it accelerates the path to success. Avoiding costly errors, building what consumers genuinely desire, and investing with informed clarity rather than mere hope are all aspects of smart validation.
The content of this article serves informational and educational purposes only and does not constitute advice in financial, legal, or professional matters. Business results depend on various factors, including market dynamics, execution, and individual situations. Readers should perform independent research and consult with qualified experts prior to making investment choices.
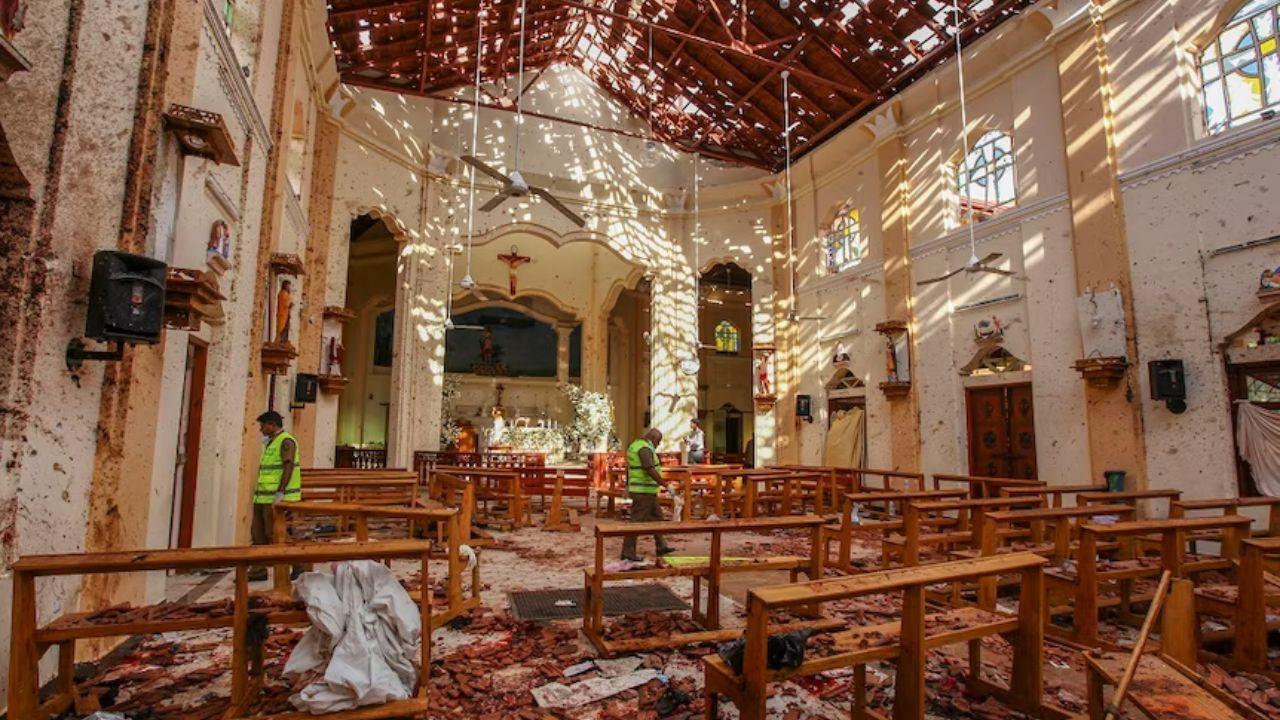









Sri Lanka Ex-Intel Chief Arrested Over Easter Attacks
Former SIS Chief Suresh Sallay arrested by CID in connection with the 2019 Easter Sunday bombings th

Japan Reports Spike in Measles Cases Authorities Issue Alert
Japan confirms 43 measles cases in early 2026, prompting health authorities to warn potential contac

Korea US Clash Over West Sea Drill Communication
Conflicting accounts emerge on prior notice briefing, and apology during Feb 18-19 US air exercise i

Richard Liu launches $690M eco-yacht brand Sea Expandary
JD.com founder Richard Liu invests $690M in Sea Expandary aiming to produce affordable green yachts

China imposes export curbs on 40 Japanese firms over military ties
Beijing restricts dual-use exports to Japanese companies, citing remilitarization concerns, promptin

Malaysia moves to protect Musang King durian amid China impostors
Authorities safeguard Malaysia’s Musang King brand as durians from Thailand and Vietnam are being fa