You have not yet added any article to your bookmarks!

Join 10k+ people to get notified about new posts, news and tips.
Do not worry we don't spam!
Post by : Rameen Ariff
Asia, the world’s largest continent, is home to more than 4.7 billion people, diverse cultures, and rich historical legacies. Spanning thousands of years, the history of Asia is a tapestry of civilizations, empires, religions, trade, colonization, revolutions, and modern development. Understanding Asia’s history provides insight into the global influence it holds today and highlights its cultural, social, and economic contributions to humanity.
Asia is the cradle of some of the earliest known human civilizations. These civilizations developed sophisticated social, political, and technological systems that influenced human history.
Known as the “Cradle of Civilization,” Mesopotamia was home to the Sumerians, Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians. The region developed:
Cuneiform writing, one of the first known writing systems.
The Code of Hammurabi, one of the earliest legal codes.
Advanced agriculture and irrigation techniques.
Early cities like Ur, Uruk, and Babylon.
The Indus Valley Civilization is famous for:
Planned cities like Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro with well-organized streets and drainage systems.
Early trade networks with Mesopotamia and Central Asia.
Development of weights, measures, and standardized bricks, showing remarkable urban planning.
The Yellow River civilization saw the rise of:
The Xia, Shang, and Zhou dynasties.
Development of bronze casting, silk production, and early Chinese writing.
Philosophical foundations in Confucianism and Taoism, guiding governance, ethics, and society.
The Persian Empire introduced:
Advanced administrative systems and the Royal Road for trade and communication.
Respect for local cultures and religions.
Architectural marvels and cities like Persepolis.
These civilizations collectively laid the groundwork for global governance, trade, and culture.
Asia is the birthplace of most of the world’s major religions, which continue to shape societies globally:
Hinduism (India): Focuses on dharma (duty), karma, and reincarnation.
Buddhism (India/Nepal, 5th century BCE): Advocates mindfulness, meditation, and compassion, spreading to East and Southeast Asia.
Confucianism & Taoism (China): Philosophies emphasizing ethics, harmony, and social responsibility.
Islam (Arabian Peninsula, 7th century CE): Spread across West, South, and Southeast Asia, influencing law, architecture, and education.
Judaism & Zoroastrianism: Originated in the Middle East and shaped religious traditions worldwide.
Religious movements influenced laws, governance, art, and cultural practices across Asia.
Asia has witnessed the emergence of empires that changed the course of history:
Mongol Empire (1206 – 1368): Under Genghis Khan, it became the largest contiguous empire, connecting East and West, facilitating trade and cultural exchange.
Ottoman Empire (1299 – 1922): Spanning Asia, Europe, and Africa, it impacted art, governance, and trade.
Mughal Empire (1526 – 1857, India): Known for architectural achievements like the Taj Mahal, promotion of art, and economic prosperity.
Chinese Dynasties (Han, Tang, Ming): Expanded territory, developed technology, and enhanced trade along the Silk Road.
These empires influenced languages, art, religion, and political systems in Asia and beyond.
Trade was central to Asia’s development and connected civilizations across continents:
Silk Road: Linked China, India, Persia, and Europe. Silk, spices, and ideas traveled along this route.
Maritime Trade Routes: Southeast Asian kingdoms traded with India, China, and the Middle East.
Cultural Diffusion: Languages, art, literature, and technology spread across regions.
Trade contributed to economic growth, diplomatic relationships, and cultural richness.
During the medieval period, regional kingdoms and states flourished:
Japan (12th – 19th century): Shogunates ruled, samurai influenced society, and Zen Buddhism shaped art and culture.
Southeast Asia: Kingdoms like Srivijaya, Majapahit, and Ayutthaya became trade hubs connecting India, China, and the Middle East.
Mongol Influence: Yuan dynasty in China and Ilkhanate in Persia promoted political unity and cultural exchange.
These regional kingdoms were centers of commerce, governance, and cultural innovation.
From the 16th century, European powers colonized many parts of Asia, bringing significant changes:
India: British colonization introduced railways, legal systems, and English education, but exploited resources and people.
Indonesia & Malaysia: Dutch and British control altered trade, governance, and society.
China: Suffered foreign influence and the Opium Wars, weakening Qing authority.
Middle East: Post-World War I European mandates reshaped borders and governance.
Colonialism left a lasting impact on Asia’s political, social, and economic structures.
The 20th century was a period of independence, conflict, and rapid modernization:
Independence Movements: Countries like India, Indonesia, and Vietnam gained freedom from colonial powers.
Wars and Conflicts: World War II, Korean War, Vietnam War, and regional conflicts shaped modern Asia.
Economic Growth: Japan’s post-war recovery, China’s industrialization, and India’s economic expansion transformed Asia into a global powerhouse.
Global Influence: Asian nations emerged as leaders in technology, trade, and diplomacy.
Today, Asia is a blend of ancient traditions and modern development:
Cultural Diversity: Thousands of ethnic groups, languages, and religions coexist.
Economic Powerhouses: China, India, Japan, South Korea, and Singapore drive global economics.
Technological Innovation: Asia leads in technology, manufacturing, and scientific research.
Tourism: Millions visit Asia to explore historical sites, natural wonders, and cultural experiences.
Asia continues to play a vital role in shaping global culture, politics, and economy.
Asia’s historical contributions include:
Inventions: Paper, printing, gunpowder, compass, silk, and mathematics from China and India.
Architecture: Taj Mahal (India), Great Wall (China), Angkor Wat (Cambodia), and Pagodas in Japan.
Literature & Arts: Epic literature like Mahabharata, Chinese classics, Persian poetry, and Japanese Noh theatre.
Philosophy & Religion: Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism, Islam, and Hinduism shaping ethics and governance.
These contributions have influenced civilizations worldwide.
The history of Asia is vast, complex, and incredibly rich. From ancient civilizations in Mesopotamia and the Indus Valley to empires, trade networks, religions, colonial struggles, and modern development, Asia has continuously shaped human civilization. Studying Asia’s history allows us to appreciate its cultural diversity, global influence, and enduring legacy. Understanding the past helps travelers, students, and enthusiasts connect with the continent in a meaningful and educational way.
The content in this article is for informational and educational purposes only. Newsible Asia strives to provide accurate and reliable information, but we do not guarantee completeness or suitability for individual needs. Readers should consult official sources or experts before making decisions based on this content. Newsible Asia is not responsible for any outcomes resulting from the use of this article.
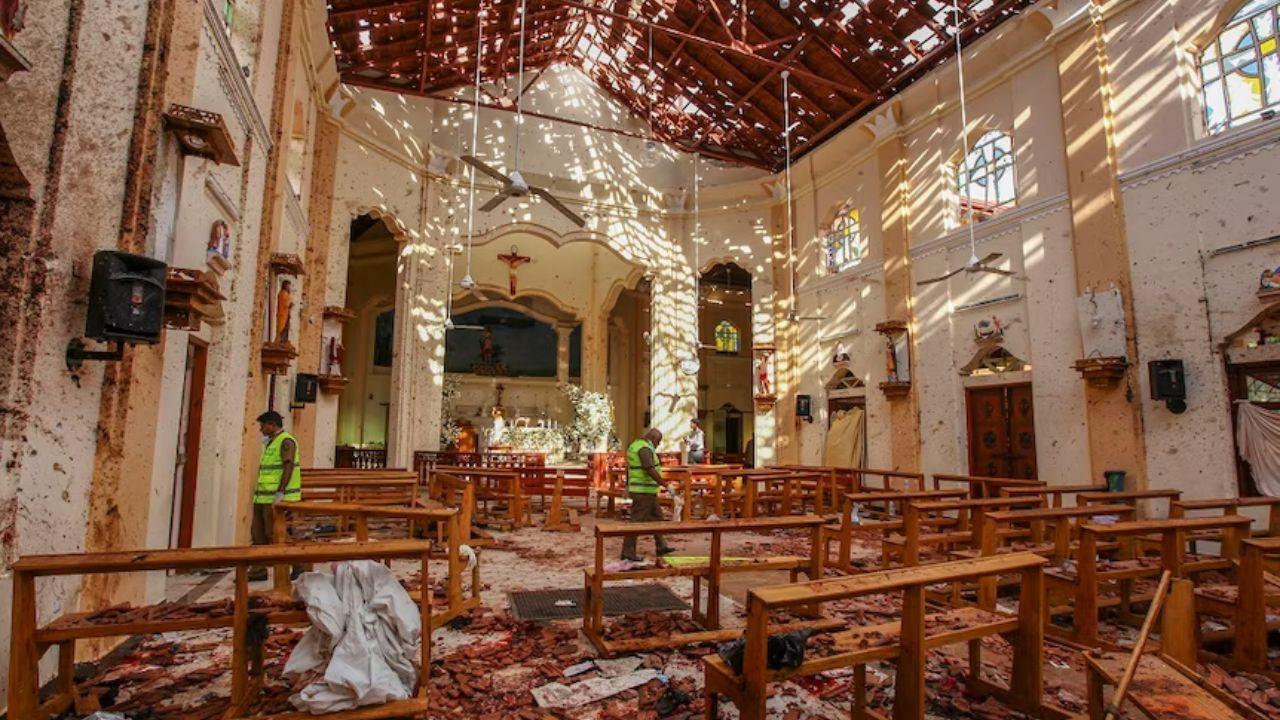









Sri Lanka Ex-Intel Chief Arrested Over Easter Attacks
Former SIS Chief Suresh Sallay arrested by CID in connection with the 2019 Easter Sunday bombings th

Japan Reports Spike in Measles Cases Authorities Issue Alert
Japan confirms 43 measles cases in early 2026, prompting health authorities to warn potential contac

Korea US Clash Over West Sea Drill Communication
Conflicting accounts emerge on prior notice briefing, and apology during Feb 18-19 US air exercise i

Richard Liu launches $690M eco-yacht brand Sea Expandary
JD.com founder Richard Liu invests $690M in Sea Expandary aiming to produce affordable green yachts

China imposes export curbs on 40 Japanese firms over military ties
Beijing restricts dual-use exports to Japanese companies, citing remilitarization concerns, promptin

Malaysia moves to protect Musang King durian amid China impostors
Authorities safeguard Malaysia’s Musang King brand as durians from Thailand and Vietnam are being fa