You have not yet added any article to your bookmarks!

Join 10k+ people to get notified about new posts, news and tips.
Do not worry we don't spam!

Post by : Anis Farhan
For decades, patient care relied heavily on paper-based records. Medical histories were scattered across hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic centres, often leading to delays, duplication of tests, and gaps in treatment. In emergencies, the absence of immediate access to accurate records could prove costly.
Digital health records have emerged as a solution to this long-standing problem. By storing medical information electronically and making it accessible across authorised platforms, healthcare providers can now view a patient’s history in real time. This transition marks one of the most important structural changes in modern healthcare.
At its core, digital health records are not just about technology; they are about continuity of care.
Digital health records, often referred to as electronic health records, are secure digital versions of a patient’s medical history. These records typically include diagnoses, prescriptions, lab reports, imaging results, treatment plans, and vaccination details.
Unlike traditional files that remain locked within a single institution, digital records are designed to be interoperable. This means information can move with the patient, ensuring that care is informed by complete and accurate data rather than assumptions or incomplete recollection.
One of the most immediate benefits of digital health records is the reduction of errors caused by illegible handwriting, missing files, or outdated information. Digital entries are standardised and easier to interpret, lowering the risk of misdiagnosis or incorrect medication.
Doctors and nurses can quickly verify allergies, past treatments, and ongoing conditions, reducing guesswork and improving clinical decision-making.
Many digital health record systems include built-in alerts that notify healthcare providers about potential drug interactions, abnormal test results, or overdue follow-ups. These features act as an additional layer of safety, supporting clinicians without replacing professional judgment.
Digital records eliminate the need for patients to repeatedly fill out forms or carry physical files from one facility to another. For doctors, this translates into less administrative burden and more time focused on patient care.
Appointments become more efficient when a patient’s complete medical history is available at the click of a button.
When lab reports and imaging results are instantly accessible, unnecessary repeat tests can be avoided. Referrals to specialists also become smoother, as relevant data can be shared securely in advance, enabling quicker and more informed consultations.
Patients today often consult multiple providers across different locations. Digital health records ensure that each provider is working with the same information, reducing fragmentation in care.
This continuity is particularly important for managing chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or respiratory illnesses, where long-term tracking is essential.
In emergency situations, access to accurate medical history can be life-saving. Information about blood groups, allergies, or existing conditions allows emergency teams to act quickly and confidently, even if the patient is unable to communicate.
Digital health records are changing the traditional doctor-patient dynamic. Patients can now access their own health data, track test results, and understand treatment plans more clearly.
This transparency encourages informed decision-making and greater engagement in personal health management.
With digital systems, health information is no longer tied to a single hospital. Patients can carry their records across cities, states, or even countries, ensuring continuity regardless of location.
In India, initiatives under the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission aim to create a unified digital health ecosystem that gives individuals greater control over their medical data while maintaining privacy safeguards.
When aggregated responsibly, digital health data can reveal trends that help doctors identify risks early. Patterns in blood pressure, glucose levels, or recurring symptoms can prompt timely interventions before conditions worsen.
This shift from reactive to preventive care is one of the most transformative aspects of digital health records.
At a broader level, anonymised health data helps policymakers and researchers understand disease trends, resource needs, and healthcare gaps. This enables better planning, targeted interventions, and more efficient use of healthcare resources.
Health data is deeply personal, making privacy and security critical. Digital health record systems are designed with encryption, access controls, and audit trails to prevent unauthorised use.
Trust is central to adoption. Patients are more willing to embrace digital records when they are confident that their information is protected and used responsibly.
While easy access improves care, it must be carefully balanced with strict consent mechanisms. Modern systems increasingly allow patients to decide who can view specific parts of their health records, reinforcing autonomy and confidence.
Not all healthcare facilities have equal access to digital infrastructure. Smaller clinics and rural centres may face challenges related to connectivity, training, and costs.
Bridging this gap is essential to ensure that digital health records benefit all sections of society, not just urban populations.
For digital health records to work seamlessly, different systems must be able to communicate effectively. Achieving standardisation across providers and platforms remains a work in progress in many regions.
Digital health records form the foundation for future innovations such as artificial intelligence–assisted diagnosis, remote monitoring, and personalised treatment plans. These advancements rely on accurate, comprehensive data to function effectively.
Healthcare is gradually shifting from treating isolated illnesses to managing long-term well-being. Digital health records support this transition by maintaining a continuous health narrative rather than disconnected episodes of care.
Digital health records are not merely a technological upgrade; they represent a fundamental change in how patient care is delivered and experienced. By improving accuracy, efficiency, continuity, and patient empowerment, they address some of the most persistent challenges in healthcare systems worldwide.
While challenges around infrastructure, privacy, and standardisation remain, the direction is clear. As digital health records become more integrated into everyday healthcare, patient care is set to become more informed, responsive, and human-centred than ever before.
Disclaimer:
This article is intended for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical, legal, or policy advice.









China Ousts Three Retired Generals from Top Political Advisory Body
CPPCC ousts retired PLA generals ahead of annual Two Sessions as broader anti‑corruption military sh

Japan Jobless Rate Rises to 2.7%
Japan sees first increase in jobless rate in five months as voluntary quits rise and job openings sl

Strong 6.1-Magnitude Earthquake Shakes Indonesia’s Sumatra Island
Tremors felt across region no immediate reports of damage or casualties as authorities monitor seism

Rizwan Sajan Reaffirms Trust in UAE’s Safety and Growth
Danube Group Chairman Rizwan Sajan assures residents and expatriates of safety in UAE, highlighting

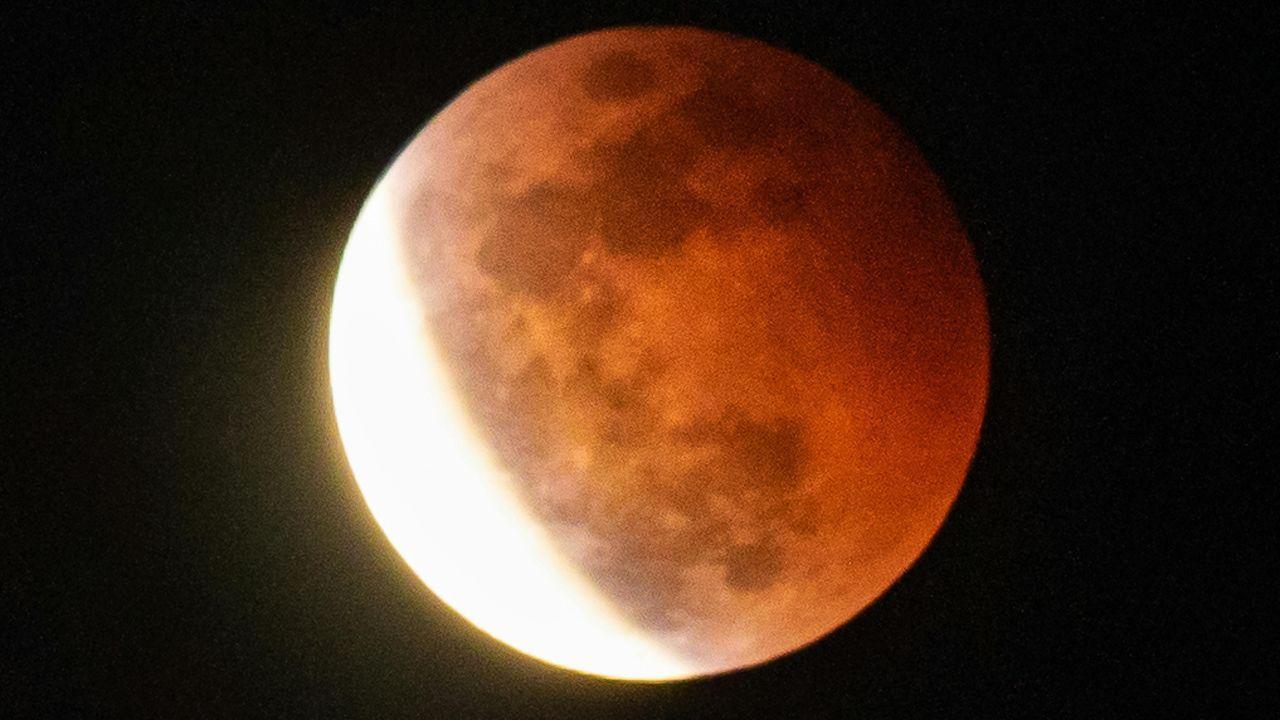
India Witnesses Chandra Grahan Blood Moon Visible in Parts of World
Skywatchers observe partial eclipse in India as total ‘Blood Moon’ visible across North America Aust
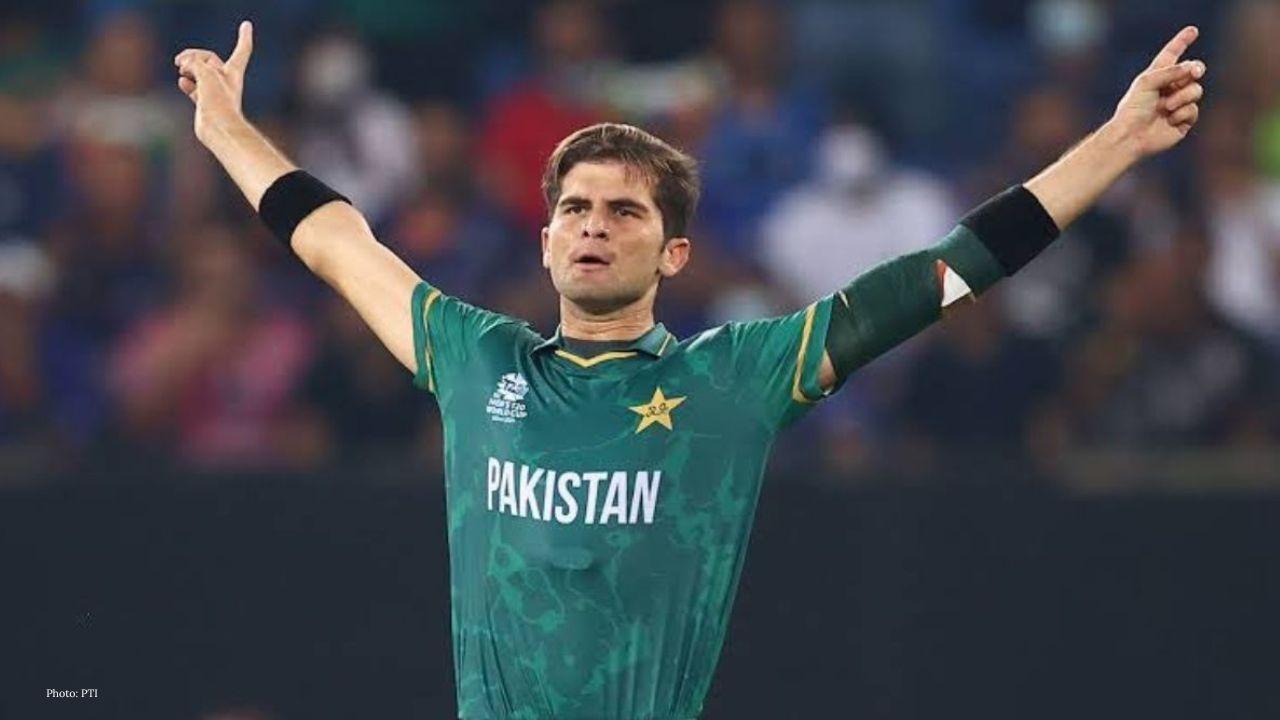

14 Pakistan Players Shortlisted for The Hundred 2026
ECB reiterates nationality will not influence selections as Haris Rauf and Shaheen Afridi headline P