You have not yet added any article to your bookmarks!

Join 10k+ people to get notified about new posts, news and tips.
Do not worry we don't spam!

Post by : Anis Farhan
The political influence of youth voters has been discussed for years, often framed as a future possibility rather than a present reality. In 2026, that narrative has changed decisively. Young voters are no longer just a demographic category mentioned in election speeches or campaign manifestos; they have become a decisive force capable of altering policy priorities and electoral outcomes. Governments that once underestimated this group are now adapting their strategies to address youth-driven concerns more directly.
What makes this shift remarkable is not just the size of the youth electorate, but the nature of its engagement. Young voters today are informed, connected, and increasingly pragmatic. Their political participation extends beyond voting booths into digital advocacy, issue-based movements, and sustained public pressure. As a result, national policies in areas such as employment, education, climate action, technology regulation, and social welfare are being reshaped in response to youth expectations.
The definition of a youth voter has evolved over time. In 2026, it broadly includes individuals in their late teens through early thirties. This group spans students, first-time job seekers, gig workers, young professionals, and early-stage entrepreneurs. Despite diverse backgrounds, they share common concerns rooted in economic security, social mobility, and long-term stability.
Unlike previous generations, today’s youth voters have grown up amid economic uncertainty, rapid technological change, and recurring global crises. These shared experiences have shaped a political mindset that values practical solutions over ideological promises. Understanding this context is key to understanding their growing influence.
Youth voters are deeply aware of how policy decisions affect their daily lives. Issues like housing affordability, student debt, job insecurity, and climate risks are not abstract concepts but lived realities. This awareness has translated into clearer expectations from political leadership, pushing governments to address structural issues rather than rely on short-term populism.
One of the defining features of youth political influence in 2026 is digital mobilisation. Social platforms have become spaces where political narratives are debated, challenged, and amplified. Young voters use these platforms not only to consume political content but to actively shape it, calling out inconsistencies and demanding accountability.
This digital presence has forced political actors to engage more transparently. Policies are scrutinised in real time, and public backlash can emerge within hours. As a result, governments are increasingly cautious, knowing that youth-led digital discourse can quickly influence public opinion.
Digital engagement does not remain confined to screens. Online discussions often translate into coordinated campaigns, petitions, and issue-based voting patterns. Youth voters may not always align with traditional party loyalties, but they consistently rally around causes. This has shifted the focus of politics from personality-driven campaigns to issue-driven accountability.
Economic stability tops the list of youth priorities in 2026. Young voters are pressing governments to address unemployment, underemployment, and the lack of long-term career pathways. Traditional job creation narratives are being challenged by demands for skill development, fair wages, and workplace protections in emerging sectors.
In response, policymakers are placing greater emphasis on vocational training, digital skills programs, and employment-linked education reforms. Youth pressure has made it politically risky to ignore the quality of jobs being created, not just their quantity.
Housing affordability, transportation costs, and access to basic services have become political flashpoints. Youth voters are questioning policies that favour asset accumulation for older generations while leaving younger citizens priced out. This has led to renewed debates on rental regulations, urban planning, and public infrastructure investment.
Young voters in 2026 are vocal about the gap between education and employment. Degrees alone are no longer seen as guarantees of opportunity. As a result, education policy is being reshaped to focus on skill relevance, adaptability, and lifelong learning.
Governments are under pressure to modernise curricula, integrate practical training, and make education more accessible. Youth-led discussions have reframed education as an ongoing process rather than a one-time phase of life.
Rising education costs have turned affordability into a major political concern. Youth voters are pushing for policies that reduce financial barriers, whether through subsidies, loan reforms, or public investment. Education is no longer viewed purely as a social sector issue, but as a cornerstone of economic policy.
Climate change remains one of the most defining issues for young voters. Unlike older generations, youth voters see environmental risks as immediate threats to their future livelihoods and well-being. This sense of urgency has translated into sustained political pressure.
In 2026, climate policy is increasingly framed through the lens of intergenerational responsibility. Governments are being challenged to justify decisions that prioritise short-term gains over long-term sustainability.
Youth-driven advocacy has influenced national approaches to renewable energy, environmental regulation, and urban sustainability. While progress varies, the political cost of ignoring climate concerns has risen sharply. Leaders are now expected to present measurable plans rather than symbolic commitments.
Youth voters respond poorly to conventional political rhetoric. Grand speeches and vague promises fail to resonate with a generation accustomed to data, transparency, and instant feedback. In 2026, political communication has shifted toward clarity, specificity, and engagement.
Governments and political parties are adopting more conversational tones, using digital platforms to explain policies and respond to criticism. This shift reflects a recognition that youth voters value honesty over perfection.
Young voters expect continuous accountability, not just election-time engagement. Policy decisions are monitored, questioned, and debated throughout a government’s term. This has made governance more exposed but also more responsive.
Unlike older voting blocs, youth voters are less tied to traditional party loyalties. They are more willing to switch allegiances based on performance and policy alignment. This makes them a powerful swing demographic capable of influencing tight electoral contests.
Political parties are adjusting by crafting targeted policy platforms rather than relying on historical support bases. Youth voters, in effect, have increased electoral competition.
Contrary to long-standing assumptions, youth voter turnout in several regions has shown steady improvement. Issue-driven mobilisation and digital awareness campaigns have played a role in making voting feel relevant and impactful.
While youth voters share some common concerns, they are far from uniform. Differences in geography, education, and economic background shape priorities. Policymakers must navigate this diversity to avoid oversimplifying youth expectations.
If youth-driven demands are acknowledged rhetorically but ignored in practice, disillusionment can grow quickly. Sustaining youth engagement requires tangible outcomes, not just symbolic gestures.
The influence of youth voters in 2026 is not a temporary trend but a structural change in how politics operates. By combining digital engagement, issue-based voting, and sustained advocacy, young citizens have reshaped the relationship between governments and the governed. National policies are increasingly being evaluated through the lens of long-term impact rather than short-term gain.
As this generation continues to mature politically, its influence is likely to deepen rather than fade. Governments that adapt to this reality will find greater legitimacy and stability, while those that resist risk losing relevance. In this sense, youth voters are not just influencing policies—they are redefining the future of governance itself.
Disclaimer:
This article is intended for informational purposes only and reflects a broad analysis of global political trends. It does not endorse any political party, ideology, or policy position.
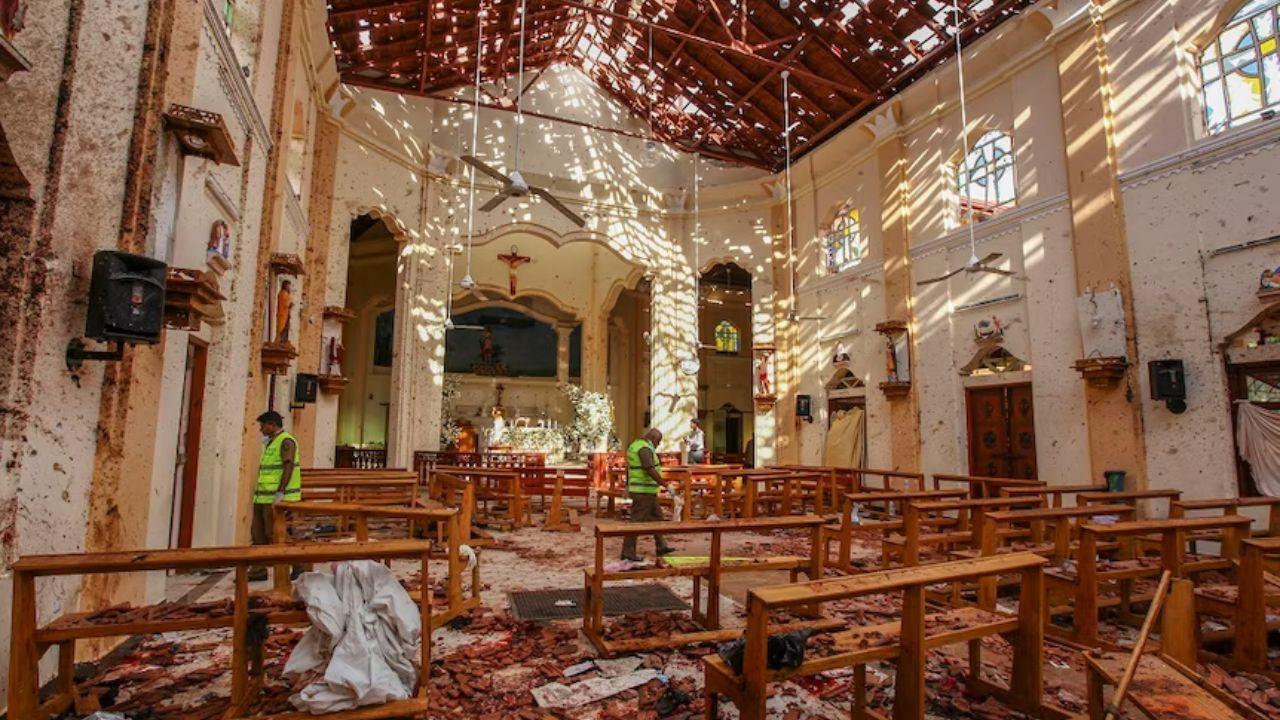









Sri Lanka Ex-Intel Chief Arrested Over Easter Attacks
Former SIS Chief Suresh Sallay arrested by CID in connection with the 2019 Easter Sunday bombings th

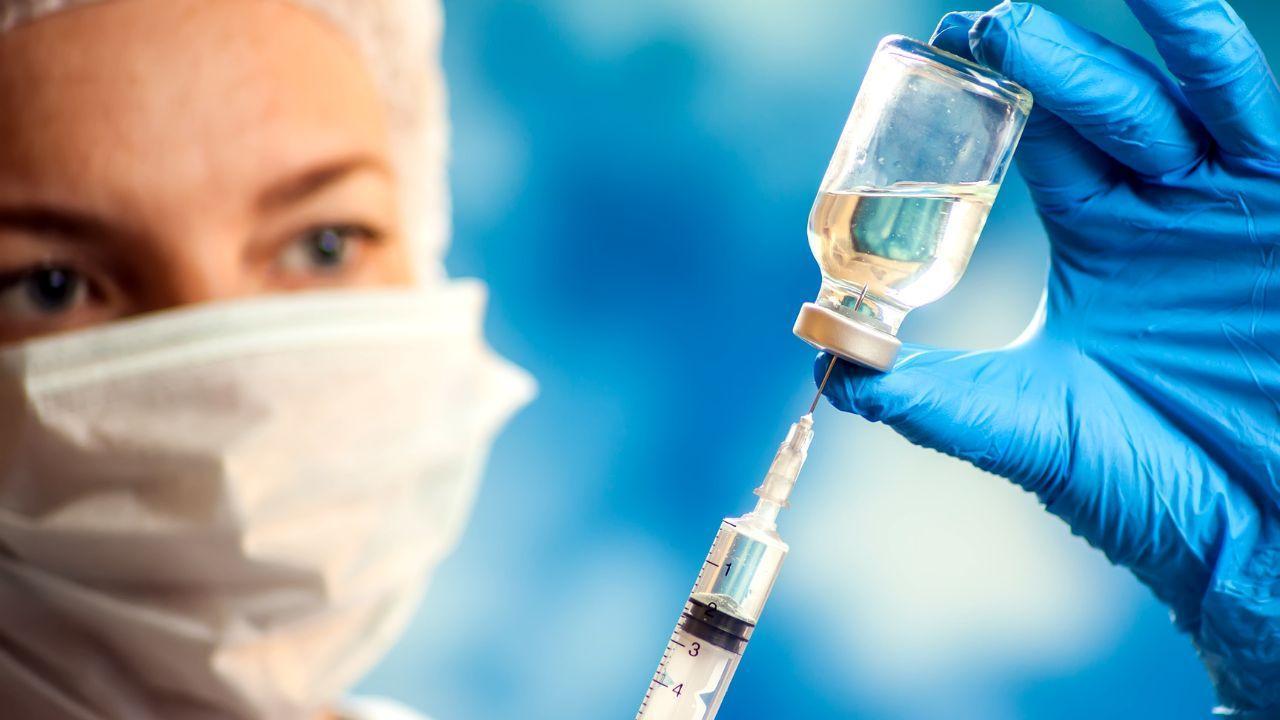
Japan Reports Spike in Measles Cases Authorities Issue Alert
Japan confirms 43 measles cases in early 2026, prompting health authorities to warn potential contac

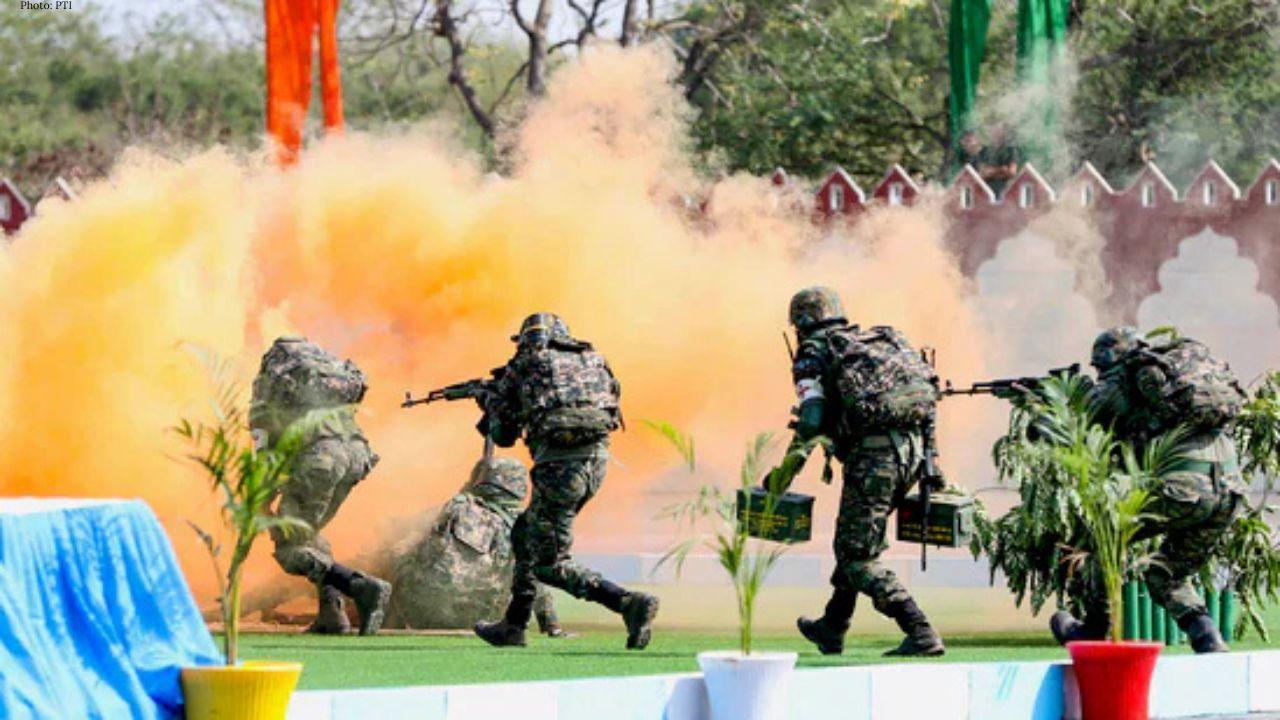
Korea US Clash Over West Sea Drill Communication
Conflicting accounts emerge on prior notice briefing, and apology during Feb 18-19 US air exercise i

Richard Liu launches $690M eco-yacht brand Sea Expandary
JD.com founder Richard Liu invests $690M in Sea Expandary aiming to produce affordable green yachts

China imposes export curbs on 40 Japanese firms over military ties
Beijing restricts dual-use exports to Japanese companies, citing remilitarization concerns, promptin

Malaysia moves to protect Musang King durian amid China impostors
Authorities safeguard Malaysia’s Musang King brand as durians from Thailand and Vietnam are being fa