
Join 10k+ people to get notified about new posts, news and tips.
Do not worry we don't spam!

Post by : Anis Farhan
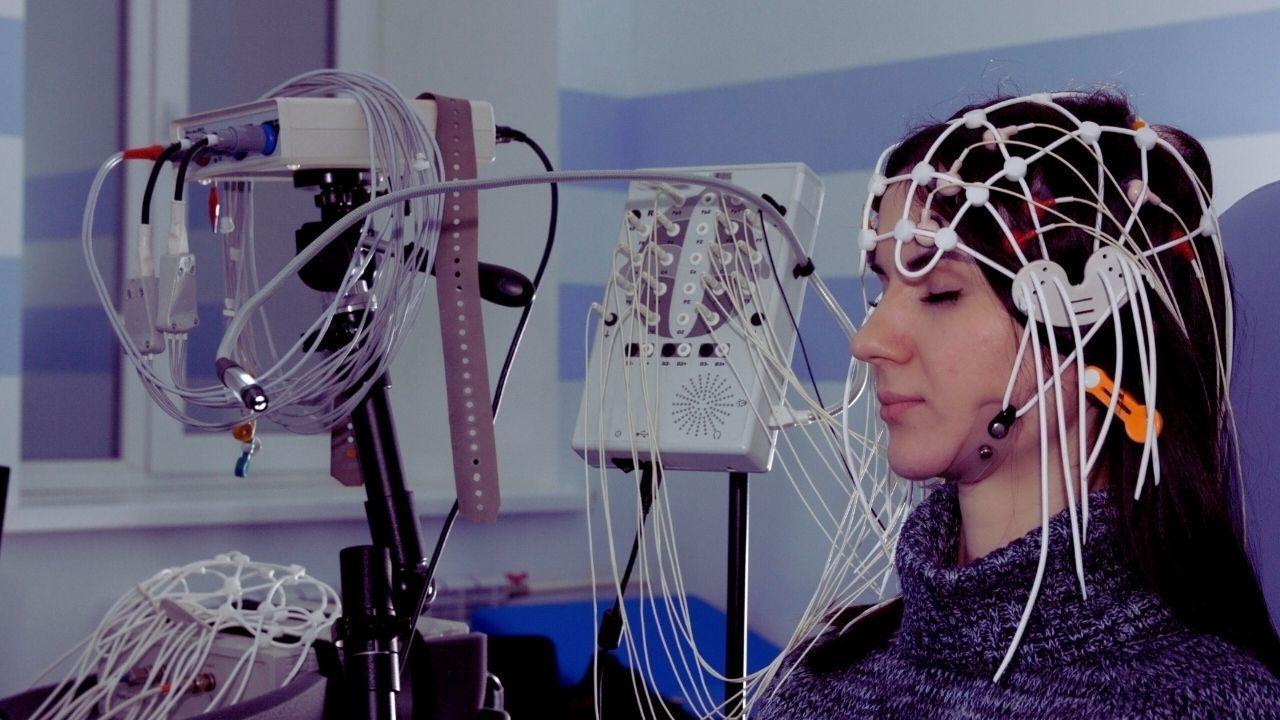
For decades, brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) were confined to research laboratories and specialized medical facilities. These devices, which allow direct communication between the brain and external systems, were primarily used to help patients with paralysis, neurological disorders, or sensory impairments.
Today, BCIs are becoming increasingly accessible for home use. Advances in hardware, software, and AI-driven signal interpretation have made it possible for consumers to integrate neurotechnology into their daily lives. From controlling computers and smart home devices to enhancing gaming experiences and monitoring mental health, BCIs promise to redefine the boundaries between humans and technology.
The shift toward home neurotechnology represents more than a technological trend—it reflects a fundamental change in how society interacts with the brain, blurring the lines between medical tools, lifestyle devices, and personal enhancement technologies.
Brain-computer interfaces work by detecting neural activity and translating it into commands that machines can understand. Non-invasive BCIs typically use electroencephalography (EEG) sensors placed on the scalp, while more advanced, invasive systems may involve implanted electrodes for precise control.
Signals from the brain are interpreted using algorithms that identify patterns corresponding to specific intentions or mental states. These signals can then be used to control devices, communicate text, or even influence virtual environments. The evolution of machine learning has significantly improved the accuracy and responsiveness of BCIs, making them viable for consumer use outside the laboratory.
The expanding capabilities of BCIs are opening doors to applications that were once considered science fiction, including real-time cognitive monitoring, immersive gaming, and mind-controlled smart homes.
One of the most impactful uses of home BCIs is in accessibility. Individuals with severe motor impairments can use BCIs to communicate, control wheelchairs, or operate assistive devices. Companies and research institutions are developing consumer-friendly devices that allow users to type text or control digital interfaces using only their thoughts.
Such technology has already transformed lives. For example, people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) or spinal cord injuries can regain independence and connect with the world in ways previously impossible. Home-use BCIs empower users to interact without relying on caregivers for simple tasks, promoting autonomy and improving quality of life.
As software becomes more intuitive and affordable, accessibility-driven BCIs are expected to expand to broader markets, benefiting both patients and caregivers.
Beyond medical and accessibility applications, BCIs are making waves in gaming and entertainment. Mind-controlled games, virtual reality experiences, and neurofeedback-based gaming are becoming increasingly popular. Players can control avatars, navigate virtual worlds, or trigger in-game actions using thought patterns detected by EEG sensors.
These experiences not only enhance engagement but also offer opportunities for cognitive training and mental wellness. Gamified neurofeedback exercises, for instance, can improve focus, memory, and stress management. As hardware becomes more affordable and wireless solutions proliferate, BCIs are poised to become a standard component of interactive entertainment systems.
The fusion of neurotechnology and entertainment opens up creative possibilities, where the brain becomes both the controller and the immersive medium.
Home BCIs are increasingly used for mental health and cognitive monitoring. Devices can track stress levels, attention, sleep patterns, and emotional states in real-time. By analyzing neural signals, users can gain insights into cognitive performance, mental fatigue, and emotional wellbeing.
This data can be integrated with mobile apps or smart home systems to suggest interventions such as relaxation exercises, guided meditation, or reminders to take breaks. Early adoption in wellness-focused markets suggests that BCIs could play a critical role in preventive mental healthcare, allowing individuals to manage cognitive health proactively.
As the technology matures, BCIs could become a valuable tool for psychologists, therapists, and neurocoaches to provide personalized guidance without requiring frequent in-person visits.
Despite their potential, home BCIs face several challenges. Accuracy and reliability remain major concerns. Non-invasive devices are susceptible to interference from muscle movement, environmental noise, or poor electrode contact. Achieving seamless control comparable to laboratory systems is still a technical hurdle.
Privacy and data security are also critical. Neural data is highly personal, and misuse could have profound ethical implications. Safeguarding brain data requires robust encryption, strict regulations, and transparent user consent.
Additionally, consumer adoption depends on affordability, comfort, and ease of use. Devices must be lightweight, unobtrusive, and simple to operate for everyday users. Companies are investing heavily in user-centered design to overcome these barriers and ensure widespread adoption.
The proliferation of BCIs in home environments raises ethical questions. Who owns the data generated by brain signals? How should it be stored, shared, or used? Could BCIs be exploited for surveillance or behavioral manipulation?
Ethical frameworks are being developed to address these concerns. Experts advocate for privacy-by-design, user control over data, and clear guidelines for acceptable applications. Governments and international bodies are also beginning to explore regulations for neurotechnology, emphasizing safety, transparency, and informed consent.
Public awareness and discourse are essential to ensure that the benefits of home BCIs do not come at the cost of individual autonomy, mental privacy, or societal trust.
Artificial intelligence is central to the functionality of home BCIs. Machine learning algorithms analyze raw neural signals, detect patterns, and translate them into actionable commands. AI also enables adaptive learning, where the device improves accuracy over time by understanding the unique neural signatures of each user.
Predictive algorithms can anticipate user intentions, reduce latency, and enhance user experience. Moreover, AI can support personalization, customizing feedback and recommendations for cognitive training, meditation, or gaming based on individual neural profiles.
The integration of AI with BCIs represents a synergistic advancement, combining human cognition with machine intelligence to create highly responsive and intelligent systems.
Looking ahead, the potential applications of home BCIs are vast. Imagine controlling lighting, temperature, or home appliances using thought alone. Integration with smart home ecosystems could make homes more accessible for individuals with mobility challenges or cognitive impairments.
Beyond utility, BCIs may enhance learning, creativity, and productivity. Neurofeedback can help users optimize focus, reduce stress, or practice mindfulness more effectively. Some researchers are exploring applications in artistic expression, where neural activity drives music, painting, or digital art.
As technology advances, home BCIs could blur the line between assistive tools, lifestyle devices, and cognitive enhancers, transforming how people interact with both technology and themselves.
The global consumer neurotechnology market is expanding rapidly. Companies in North America, Europe, and Asia are launching products targeting gamers, wellness enthusiasts, and accessibility users. Investment in BCI startups has grown exponentially, reflecting confidence in the technology’s commercial potential.
Market trends indicate a shift from clinical prototypes to wearable, user-friendly devices. Wireless headsets, dry electrodes, and integration with smartphones and VR/AR platforms are accelerating adoption. As awareness increases and costs decline, home BCIs are likely to become mainstream within the next decade.
International collaboration between tech companies, research institutions, and healthcare providers will be essential to standardize protocols, ensure safety, and drive innovation globally.
Home neurotechnology represents a paradigm shift in how people interact with machines, themselves, and their environment. Brain-computer interfaces, once confined to laboratories, are now enabling new forms of communication, entertainment, and cognitive enhancement in everyday life.
Challenges remain in terms of reliability, privacy, ethics, and accessibility. However, advances in AI, wearable sensors, and user-centered design are steadily overcoming these barriers. As BCIs become more affordable, intuitive, and integrated with daily routines, they will redefine the possibilities of human-machine interaction.
The rise of home neurotechnology signals not only a technological revolution but also a cultural transformation — one where the brain becomes both a source of control and insight, empowering individuals to navigate their lives in unprecedented ways.
This article is intended for informational purposes only. It does not provide medical, psychological, or investment advice. The content reflects current global trends in home neurotechnology and may evolve as research, regulatory frameworks, and market developments progress.









Zohran Mamdani Clinches NYC Mayoral Seat as Victory Speech Blends Politics and Bollywood
Zohran Mamdani won New York City's mayoral race, becoming the city's first Muslim and South Asian ma
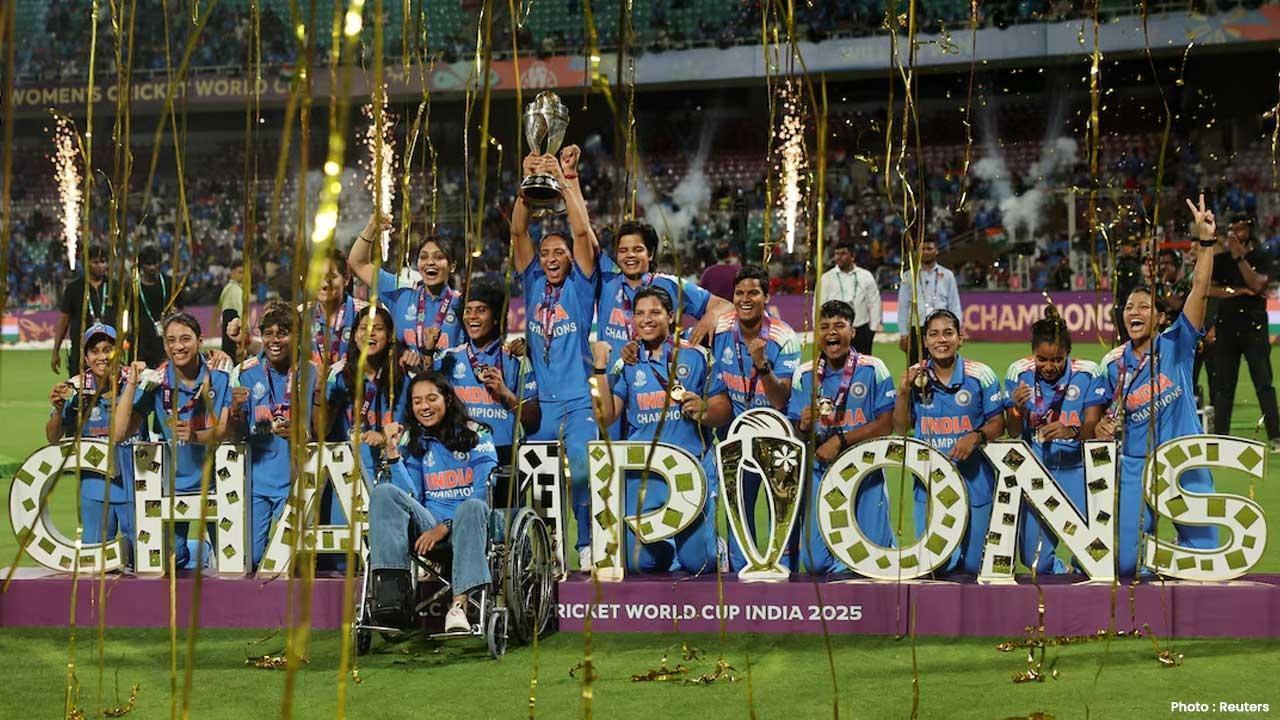
India Wins First Women’s World Cup 2025 Title
India lifts its maiden Women’s World Cup 2025 title! Harmanpreet Kaur’s team stuns South Africa in a
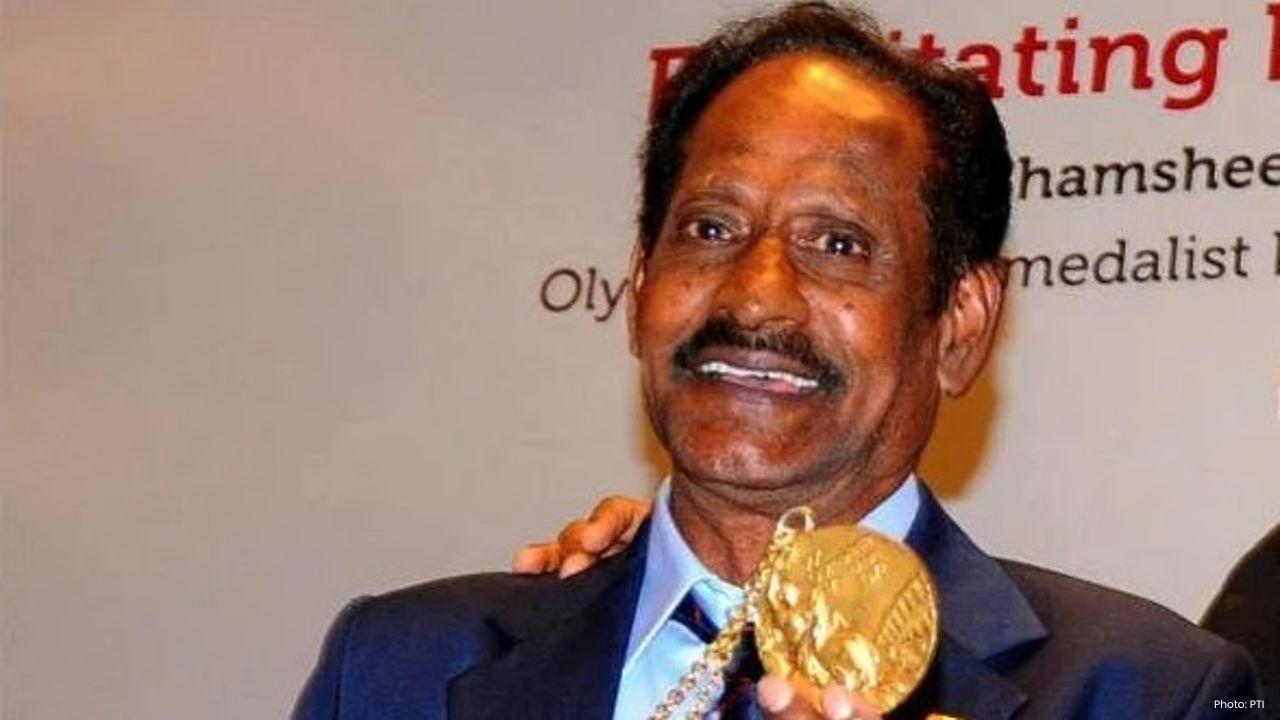

Manuel Frederick, 1972 Olympic Bronze Goalkeeper, Dies at 78
Manuel Frederick, a member of India’s 1972 Olympic bronze hockey team, has died in Bengaluru at 78 a
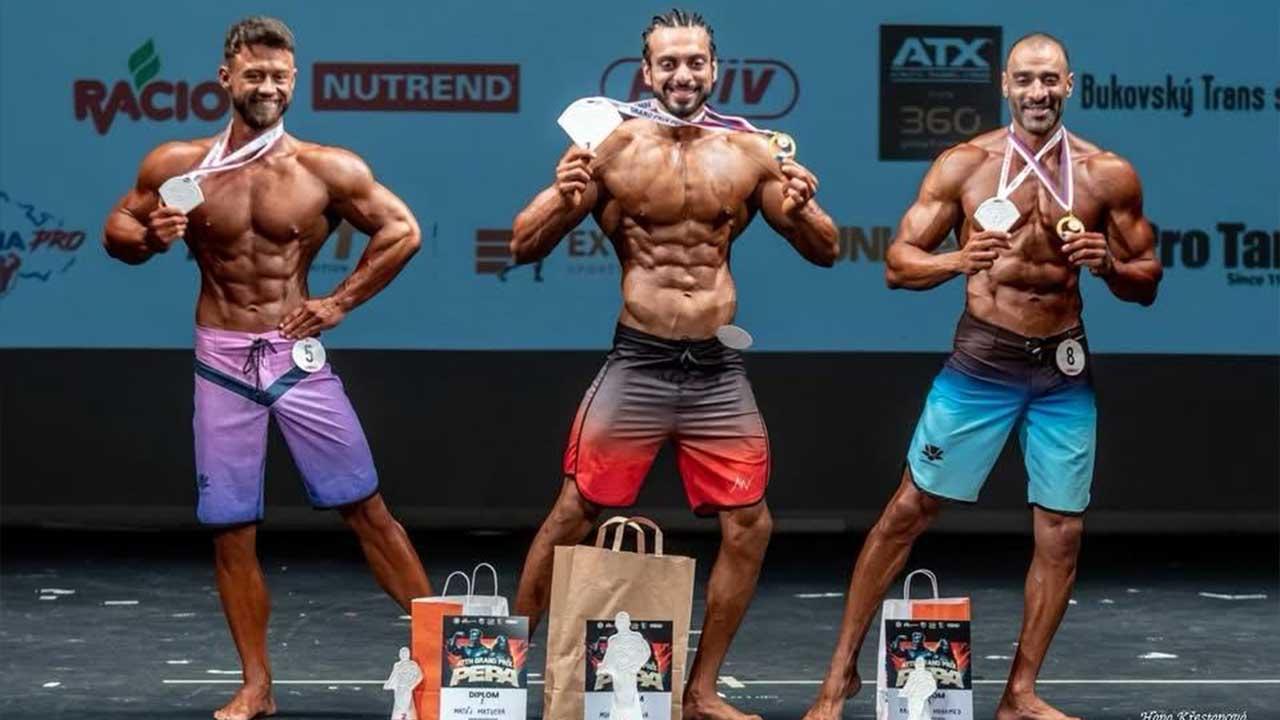

Muhammad Hamza Raja Wins IFBB Pro Card Puts Pakistan & UAE on Global Stage
Pakistani bodybuilder Muhammad Hamza Raja earns IFBB Pro Card in Czech Republic, showcasing Dubai’s
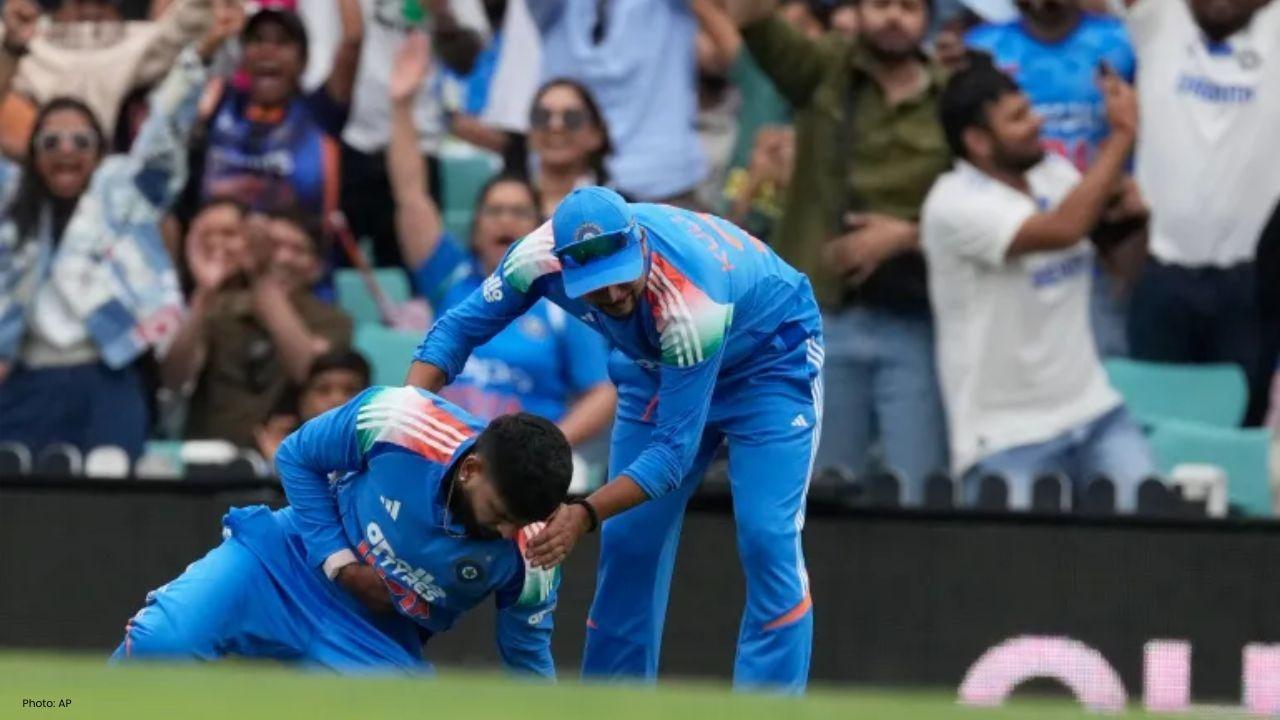

Shreyas Iyer’s Recovery Underway After Spleen Laceration in Sydney ODI
Shreyas Iyer is recovering after a spleen laceration sustained while taking a catch in the Sydney OD
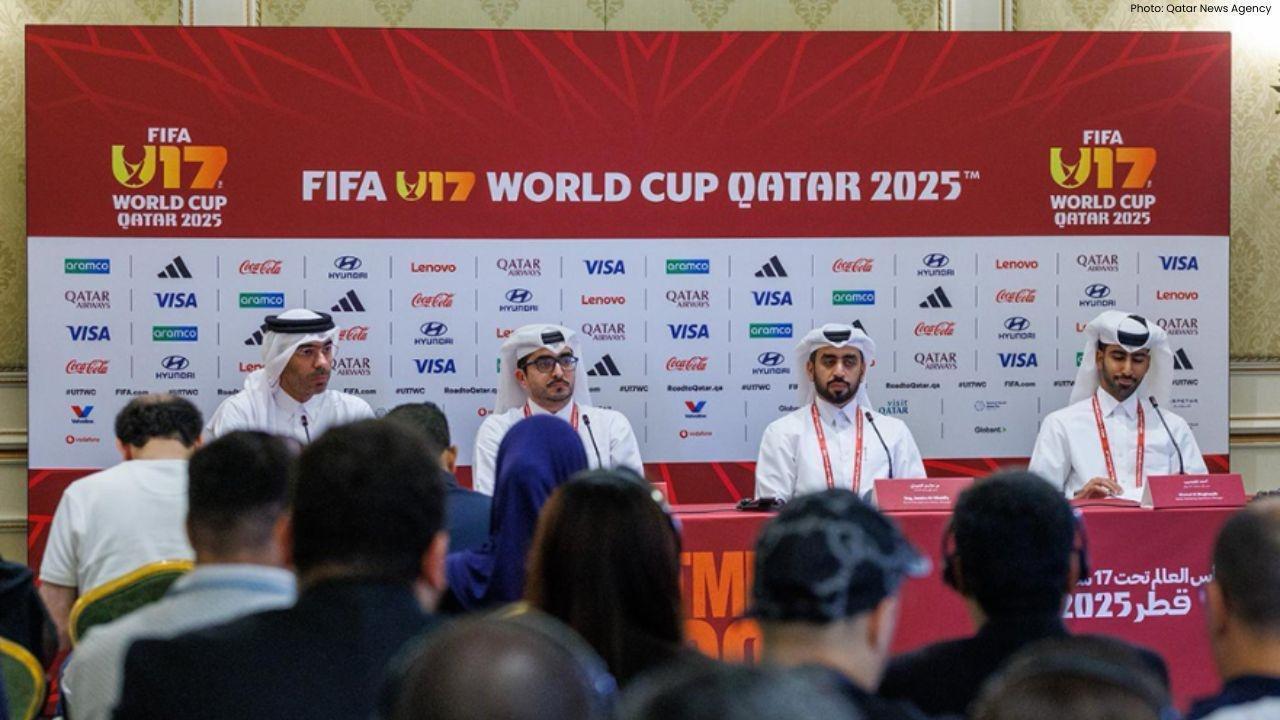

Qatar Ready to Host FIFA U-17 World Cup 2025 in Aspire
Qatar confirms full readiness to host the FIFA U-17 World Cup 2025 from November 3–27, with world-cl