You have not yet added any article to your bookmarks!

Join 10k+ people to get notified about new posts, news and tips.
Do not worry we don't spam!

Post by : Samjeet Ariff
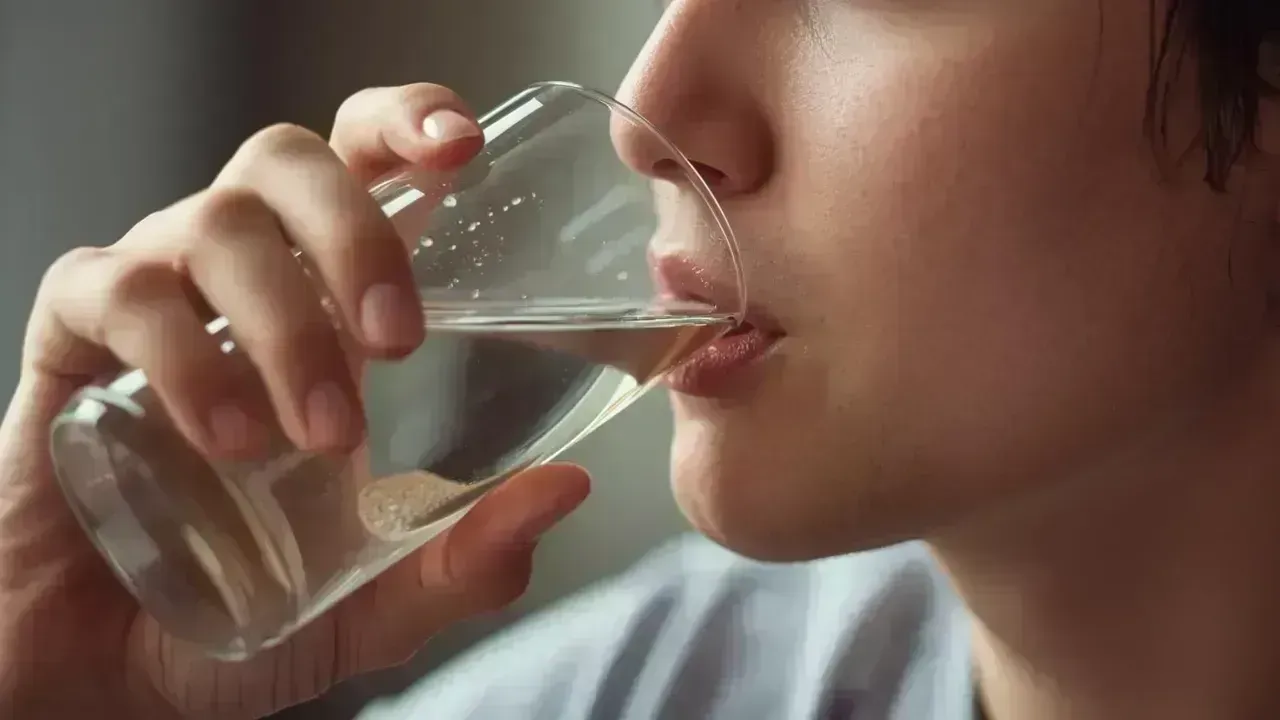
While sleep, diet, and stress are often cited as culprits for fatigue, hydration is a frequently overlooked factor that significantly influences daily energy. Mild dehydration can sap physical energy, mental clarity, and emotional stability long before thirst signals arise. Many individuals cope with feelings of fatigue, irritability, and sluggishness, often unaware that their bodies may be in need of more fluids.
Hydration goes beyond quenching thirst; it involves maintaining optimal fluid balance to ensure all bodily functions operate smoothly. Water is crucial for everything from cognitive functions and muscle performance to hormone activity and metabolic processes that dictate how energized you feel.
This article delves into how hydration levels impact energy, the reasons behind fatigue linked to dehydration, the actual water requirements for your body, and methods to cultivate hydration habits that can sustain energy levels throughout your day.
Water constitutes nearly 60% of the human body, affecting all significant physiological functions.
At the cell level, hydration is vital for generating adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the molecule responsible for energy storage and transfer. When hydration falls short, ATP production becomes inefficient, leading to diminished energy levels.
Water facilitates the transport of oxygen, glucose, vitamins, and minerals to cells, while also aiding in metabolic waste removal. Dehydration hampers these processes, causing stress within cells and escalating fatigue.
Water is crucial for temperature control through sweating and blood circulation. Inadequate hydration causes the body to work harder to cool itself, fostering increased fatigue and physical exertion.
When hydration is low, the body shifts into conservation mode, prioritizing survival over performance.
A mere 1–2% reduction in body water can drastically affect energy and cognitive performance.
A lack of hydration leads to decreased blood volume, compelling the heart to exert more effort to circulate oxygen and nutrients. This can induce physical fatigue even with regular tasks.
The brain is highly sensitive to hydration levels. Mild dehydration can trigger:
Decreased concentration
Cognitive fog
Sluggish reaction times
Irritability
Mental fatigue often manifests before physical exhaustion.
Water teams up with electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and magnesium. Dehydration disrupts this balance, impairing nerve signals and muscle function, resulting in weakness and decreased energy.
Mental fatigue signals dehydration at its earliest stages.
Research consistently indicates that dehydration diminishes short-term memory, alertness, and attention span. Tasks that require creativity or problem-solving become increasingly challenging.
Low hydration correlates with heightened feelings of:
Stress
Anxiety
Poor motivation
Mental burnout
These occurrences can happen without noticeable thirst, making dehydration a subtle contributor to emotional fatigue.
The brain uses considerable water to maintain electrical signals. If hydration decreases, decision-making becomes slower and more prone to errors, amplifying perceived workloads and fatigue.
Hydration is crucial for enhancing physical performance, even outside athletic activities.
Muscles consist of about 75% water. Dehydration undermines muscle strength, endurance, and recovery time.
Under dehydration, everyday activities may feel disproportionately arduous. Simple tasks like walking or climbing stairs could induce unexpected fatigue.
Reduced oxygen delivery to muscles during dehydration quickens fatigue and prolongs recovery.
Energy levels are also affected by digestive efficiency.
Water aids in enzyme function and food breakdown. Dehydration dampens digestion, leading to sensations of heaviness and sluggishness post-meal.
Poor hydration can result in fluctuations in blood sugar levels, causing energy crashes, especially after carbs-heavy meals.
Even with a well-rounded diet, dehydration hampers the absorption of vital nutrients like B vitamins and minerals that facilitate energy metabolism.
Hydration needs differ based on individual factors such as body size, activity level, climate, and diet.
A commonly suggested intake is:
Men: about 3.5 liters daily
Women: roughly 2.5 liters daily
This encompasses water from drinks and food.
Hot or humid climates
Exercise
High-protein or high-fiber diets
Caffeine or alcohol intake
Illness or fever
Ignoring these aspects often leads to chronic low-level dehydration.
frequent misinterpretation of dehydration signs as stress or sleep deprivation.
Common indicators include:
Persistent fatigue despite adequate rest
Cognitive fog or difficulty in concentration
Headaches
Dry mouth or lips
Dark-colored urine
Frequent cravings for sugar or caffeine
Addressing hydration often alleviates these symptoms faster than altering diet.
The timing of your water intake is as crucial as the quantity.
After 6–8 hours of sleep, the body experiences mild dehydration. Consuming water in the morning:
Boosts metabolism
Heightens mental clarity
Mitigates morning fatigue
Drinking water between meals enhances digestion and helps avoid energy dips without impairing digestive enzymes.
Many individuals cease water intake in the evening, resulting in overnight dehydration that hinders next-day energy levels.
Not all liquids offer the same hydration benefits.
The most effective and calorie-free method of hydration.
Beneficial during intense exercise or excessive sweating but unnecessary for those leading a sedentary lifestyle.
Caffeine provides a fleeting boost but can lead to increased fluid loss and contribute to energy crashes.
They can cause rapid blood sugar spikes followed by fatigue, exacerbating dehydration effects.
Chronic dehydration contributes not only to daily fatigue but also long-lasting health issues.
Water is critical for the transport and balance of hormones. Dehydration can disrupt cortisol, insulin, and thyroid levels, complicating energy management.
Poor hydration can lead to nighttime cramping, dry mouth, and an elevated heart rate, detracting from sleep quality and energy revival.
Hydration supports fat metabolism and thermogenic processes. Dehydration slows these metabolic functions, resulting in persistent low energy.
Consume 1–2 glasses of water within 30 minutes of waking for an energy boost.
Thirst is a delayed signal; make it a habit to sip water consistently throughout the day.
Drink water:
Post restroom visits
Before meals
During breaks at work
More consistency trumps volume at once.
Fruits and vegetables like cucumber, watermelon, oranges, and spinach aid in hydration.
A light yellow color indicates good hydration, while dark yellow suggests dehydration.
Unlike stimulants or supplements, consistent hydration fosters energy without side effects. It operates in harmony with the body’s natural mechanisms instead of artificially inducing alertness.
Maintaining hydration:
Boosts physical endurance
Accentuates mental clarity
Stabilizes mood
Lessens dependence on caffeine
Promotes long-term well-being
Energy derived from hydration is stable, not contrived.
Low energy is often misdiagnosed as a productivity issue, a sleep problem, or a nutritional shortfall. In fact, hydration is one of the simplest yet most potent means to regulate energy. Making small adjustments to your daily water intake can lead to significant improvements in focus, endurance, and overall health.
While hydration shouldn’t replace good rest or nutrition, it is essential for their effective functioning.
This article serves informational purposes and is not a substitute for medical or nutritional consultation. Individual hydration needs can vary widely based on personal health and lifestyle. For tailored advice, consult a healthcare professional.
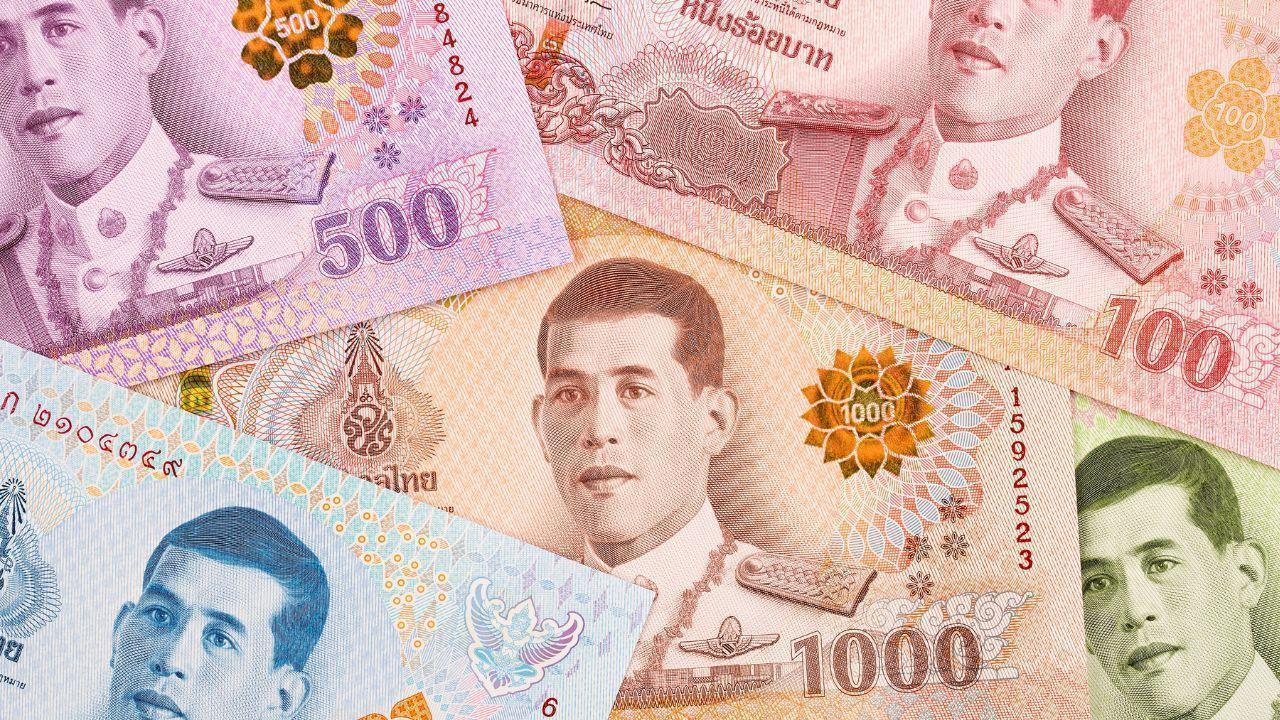








Thai Baht Falls as Dollar Gains on War Tensions
Currency slips to 31.77 per dollar as investors seek safe-haven assets and watch US economic data an
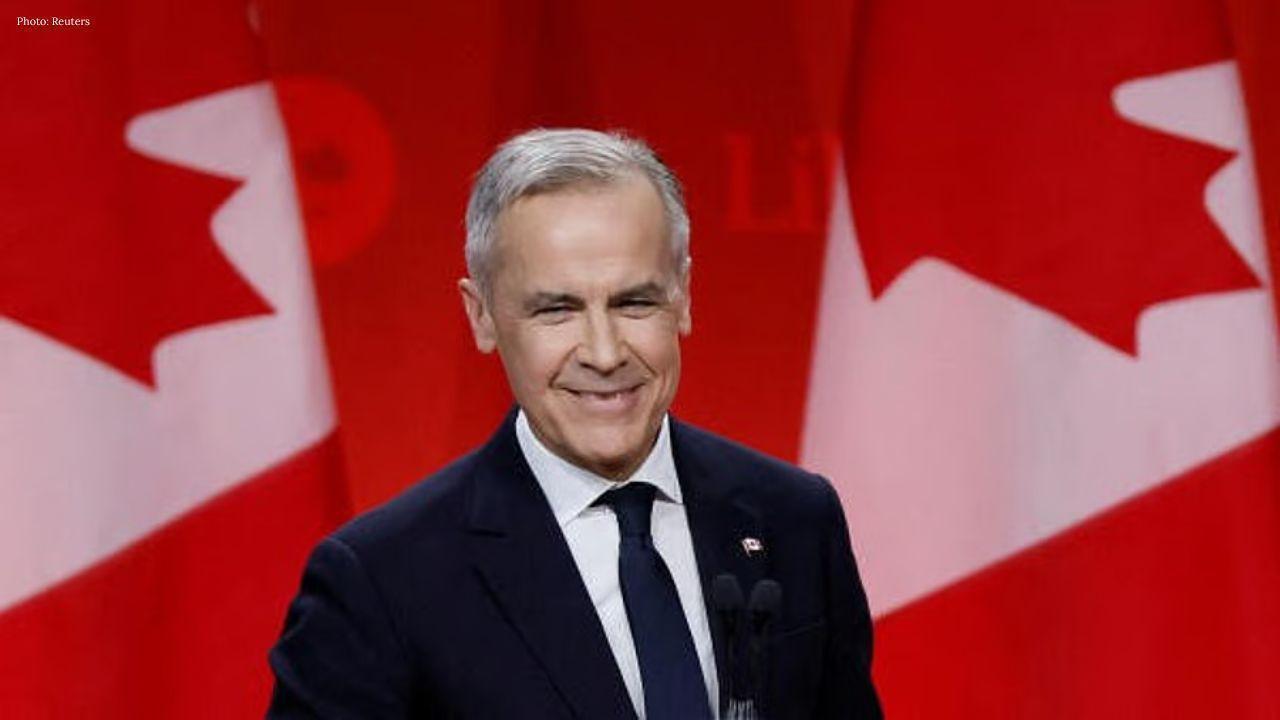

Japan and Canada Boost Defense Energy Ties
Tokyo summit between leaders expected to strengthen security economic ties and support for a Free an

Indonesia May Exit US Peace Board Over Palestine
President Prabowo Subianto says Indonesia will withdraw from the initiative if it does not benefit P

Judge’s Wife Found Dead in Train Toilet During Journey
Usha Chauhan wife of Additional District Judge found lifeless in washroom of Kanchiguda–Bhagat Ki Ko

Bangladesh Government Declares Seven-Day Eid-ul-Fitr Holiday
Extra public holiday on 18 March approved by cabinet to create week-long break from 17–23 March

Pakistanis Return Home via Taftan Border
Hundreds cross from Iran into Balochistan as US-Israel strikes intensify FIA ensures 24-hour immigra