You have not yet added any article to your bookmarks!

Join 10k+ people to get notified about new posts, news and tips.
Do not worry we don't spam!
Post by : Anis Farhan
The global landscape in 2026 feels fundamentally different from the relatively predictable order of previous decades. Long-standing assumptions about power, trade, and security have been challenged by overlapping crises—geopolitical tensions, economic fragmentation, technological competition, and climate stress. In this environment, the idea of nations acting independently has become increasingly unrealistic.
Strategic alliances have re-emerged as one of the most critical pillars of global politics. But unlike the rigid blocs of the past, today’s alliances are more flexible, issue-based, and pragmatic. Countries are not merely aligning for ideological reasons; they are cooperating out of necessity. In a fragmented and uncertain world, alliances are no longer symbols of shared values alone—they are survival strategies.
For years, globalisation encouraged deep interdependence among nations. Supply chains stretched across continents, trade barriers fell, and cooperation was driven largely by efficiency. However, repeated disruptions have exposed the vulnerabilities of this model.
Geopolitical conflicts, sanctions, and trade restrictions have made it clear that excessive dependence on single partners or regions can be dangerous. Strategic alliances now serve as a way to manage interdependence—allowing cooperation without overexposure.
In 2026, countries are increasingly favouring trusted networks over open-ended global integration. Alliances help nations identify reliable partners for trade, technology, and security. This shift reflects a move from maximum efficiency to maximum resilience.
Modern security threats do not respect borders. Cyberattacks, terrorism, misinformation campaigns, and regional conflicts have global consequences. No single country, regardless of strength, can address these challenges alone.
Strategic alliances allow countries to share intelligence, coordinate responses, and deter aggression. Collective security has become more relevant as threats grow more complex and less conventional.
Alliances amplify deterrence. When countries stand together, potential aggressors must consider the collective response rather than individual retaliation. In 2026, this shared strength acts as a stabilising force in an otherwise volatile environment.
Trade is no longer viewed as purely economic. It has become deeply strategic. Alliances influence trade agreements, supply chain decisions, and market access.
Countries use alliances to secure essential goods, protect critical industries, and reduce vulnerability to economic coercion. These partnerships shape not only who trades with whom, but on what terms.
Global economic shocks—whether from financial instability, commodity price swings, or supply disruptions—are easier to manage collectively. Strategic alliances allow countries to coordinate policy responses, stabilise markets, and support each other during crises.
Technological leadership is a defining factor of power in 2026. From artificial intelligence and semiconductors to digital infrastructure, control over technology shapes economic and military capabilities.
Developing and governing advanced technologies requires collaboration. Alliances help pool research, set standards, and ensure interoperability. Without coordination, fragmented systems can slow innovation and increase risk.
Who sets global technology standards often determines who benefits economically. Strategic alliances play a crucial role in shaping these standards, ensuring that members are not sidelined in emerging industries.
Climate change is the ultimate transnational challenge. Extreme weather, rising sea levels, and resource scarcity affect regions collectively, not individually.
Strategic alliances enable coordinated climate action—whether through shared technology, financing mechanisms, or policy alignment. In 2026, environmental cooperation is increasingly tied to alliance structures.
Alliances help translate climate commitments into action. By working together, countries can scale renewable energy, share best practices, and support vulnerable regions. Collective effort increases credibility and effectiveness.
As global institutions struggle to maintain consensus, regional alliances have gained importance. Countries find it easier to cooperate with neighbours who share geographic realities and immediate concerns.
These regional partnerships address issues such as trade facilitation, migration, and security more efficiently than distant global forums. In 2026, regionalism complements rather than replaces global cooperation.
Strategic alliances allow countries to balance global ambitions with regional priorities. This layered approach to diplomacy provides flexibility and reduces overreliance on any single framework.
Unlike Cold War-era alliances, modern partnerships are often issue-specific. Countries may cooperate on security, diverge on trade, and align again on climate or technology.
This flexibility reflects realism. Nations prioritise interests over ideology, making alliances more adaptable but also more complex to manage.
Alliances in 2026 are less about permanent alignment and more about ongoing negotiation. Trust remains important, but adaptability is key. This pragmatism allows countries to respond to changing circumstances without abandoning cooperation altogether.
Domestic audiences are more engaged with foreign policy than before. Economic impact, security concerns, and migration issues directly affect voters, influencing alliance decisions.
Governments must justify alliances not only on strategic grounds but also on tangible benefits for citizens. This accountability has made alliance-building more transparent and deliberate.
Trade access, investment flows, and job creation linked to alliances strengthen domestic support. In 2026, successful alliances are those that clearly deliver economic value at home.
From pandemics to financial crises, recent years have shown the importance of coordinated responses. Strategic alliances provide ready-made channels for cooperation during emergencies.
Shared resources, coordinated policies, and mutual support reduce response time and improve outcomes when crises strike.
Unified messaging and coordinated action help prevent panic in global markets and societies. Alliances contribute to stability by presenting a collective front during uncertain times.
Alliances are not without tension. Member countries may have conflicting priorities, economic competition, or political differences. Managing these internal contradictions requires constant diplomacy.
In 2026, alliance management is as important as alliance formation. Misalignment can weaken partnerships if left unaddressed.
While alliances reduce isolation, excessive reliance on partners can create new vulnerabilities. Countries must balance cooperation with maintaining independent capabilities.
As global institutions face credibility and efficiency challenges, alliances are stepping in to fill gaps. Smaller, focused groups often act faster than large multilateral bodies.
This does not signal the end of global institutions, but a rebalancing where alliances handle execution while institutions provide legitimacy.
Countries increasingly operate across multiple alliance frameworks simultaneously. Coordinating these overlapping commitments is complex but necessary in a fragmented world.
Alliances facilitate joint investment in infrastructure, research, and development. Shared projects reduce costs and spread risk, enhancing competitiveness.
This collaborative approach is especially important in capital-intensive sectors such as energy, technology, and defence.
Collective bargaining power improves access to markets, resources, and technology. Alliances amplify individual country influence on the global stage.
In an increasingly polarised environment, remaining neutral is more challenging. Economic interdependence and security risks force countries to align selectively.
Strategic alliances offer a way to navigate this pressure without full alignment, providing flexibility while maintaining protection.
Rather than full neutrality, many countries adopt selective engagement—joining alliances on specific issues while maintaining autonomy elsewhere.
In 2026, alliances are not temporary arrangements but long-term stabilising mechanisms. They provide predictability in an unpredictable world.
Countries that invest in building and maintaining alliances gain resilience against shocks and uncertainty.
Beyond military or economic strength, trust has become a valuable asset. Alliances built on reliability and transparency endure longer and perform better under stress.
Strategic alliances matter more than ever in 2026 because the challenges facing the world are too complex for unilateral solutions. Security threats, economic uncertainty, technological competition, and climate change demand collective responses.
In this fragmented global order, alliances act as power multipliers. They extend influence, reduce risk, and provide stability. While they require constant negotiation and compromise, their benefits far outweigh their limitations.
The countries that recognise this reality—and invest in smart, flexible partnerships—will be better positioned to navigate the uncertainties of the coming decade. In an era defined by disruption, cooperation has become the most valuable strategy of all.
Disclaimer:
This article is intended for informational and analytical purposes only. It does not constitute diplomatic, political, or strategic advice. International relations and alliance dynamics may evolve over time.









China Ousts Three Retired Generals from Top Political Advisory Body
CPPCC ousts retired PLA generals ahead of annual Two Sessions as broader anti‑corruption military sh

Japan Jobless Rate Rises to 2.7%
Japan sees first increase in jobless rate in five months as voluntary quits rise and job openings sl

Strong 6.1-Magnitude Earthquake Shakes Indonesia’s Sumatra Island
Tremors felt across region no immediate reports of damage or casualties as authorities monitor seism

Rizwan Sajan Reaffirms Trust in UAE’s Safety and Growth
Danube Group Chairman Rizwan Sajan assures residents and expatriates of safety in UAE, highlighting

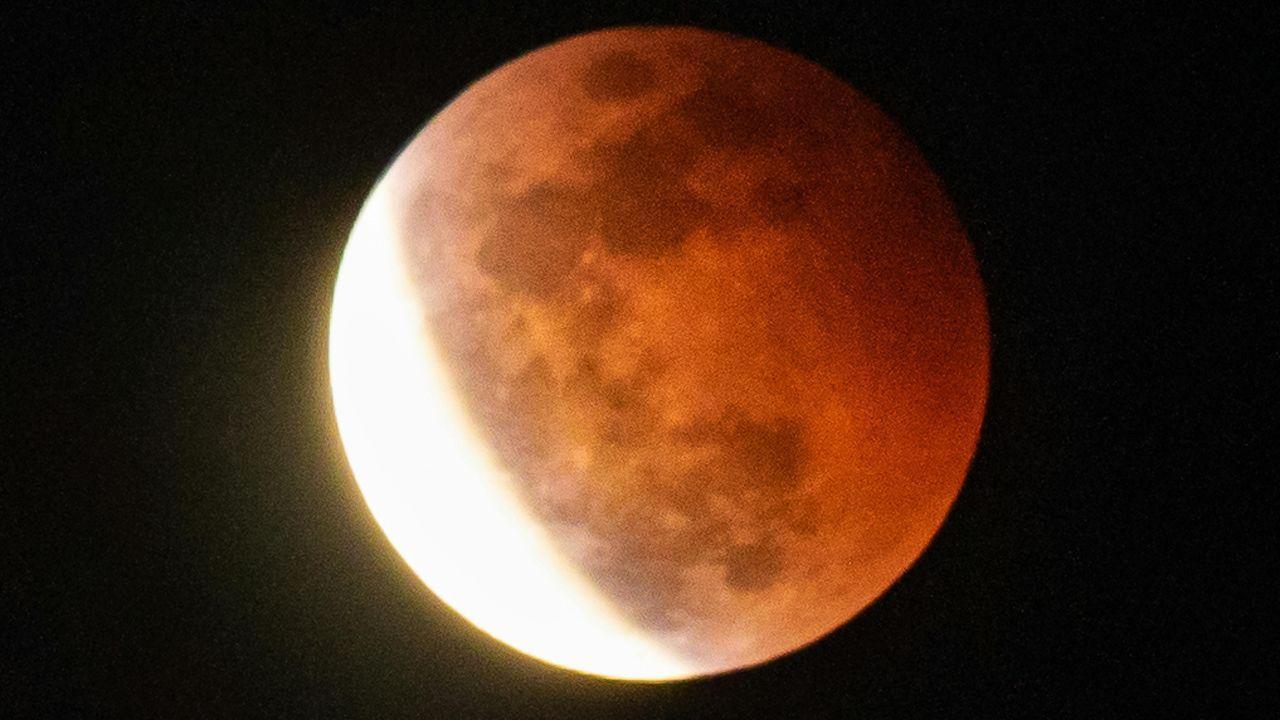
India Witnesses Chandra Grahan Blood Moon Visible in Parts of World
Skywatchers observe partial eclipse in India as total ‘Blood Moon’ visible across North America Aust
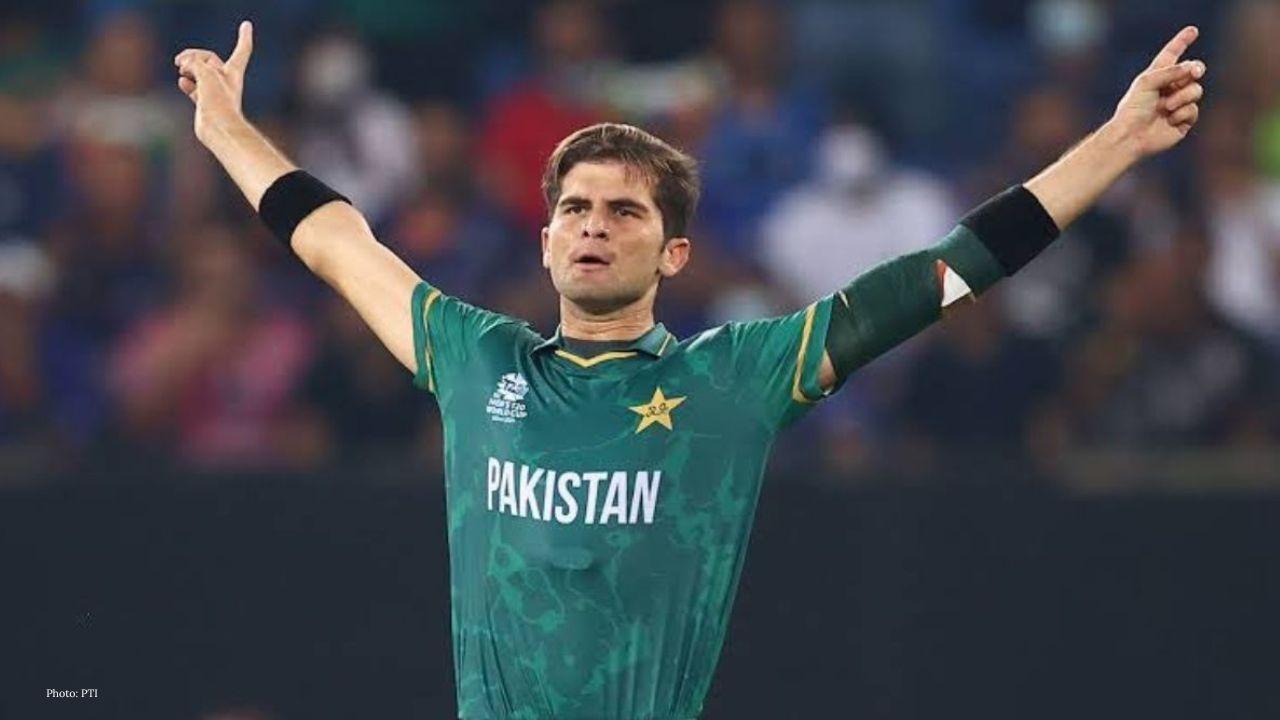

14 Pakistan Players Shortlisted for The Hundred 2026
ECB reiterates nationality will not influence selections as Haris Rauf and Shaheen Afridi headline P