You have not yet added any article to your bookmarks!

Join 10k+ people to get notified about new posts, news and tips.
Do not worry we don't spam!

Post by : Anis Farhan
The world faces an unprecedented electronic waste crisis. Millions of tons of discarded devices, from smartphones to medical sensors, end up in landfills each year, releasing toxic chemicals into the environment. Traditional electronics rely heavily on non-renewable resources and materials that are difficult to recycle. As cities grow and technology becomes more pervasive, this environmental challenge is only escalating.
In response, scientists and engineers are turning toward biodegradable electronics and solar-powered sensors. Unlike conventional devices, these solutions are designed to reduce environmental impact without compromising performance. Biodegradable electronics are made from materials that naturally decompose, while solar sensors harness renewable energy, reducing dependence on traditional power sources. Together, these technologies represent a paradigm shift in how society approaches electronics and sustainability.
Biodegradable electronics represent a major step toward addressing electronic waste. They are designed to perform their functions during their lifespan and safely degrade afterward, leaving minimal environmental footprint.
The success of biodegradable electronics depends largely on the materials used. Researchers have identified several promising options:
Polylactic Acid (PLA): Derived from renewable sources such as corn starch or sugarcane, PLA is compostable and widely used in biodegradable circuit substrates. Its flexibility and ease of processing make it ideal for lightweight electronic components.
Cellulose-Based Materials: Extracted from plant fibers, cellulose offers both biodegradability and structural integrity. It is particularly suitable for wearable electronics, where comfort and adaptability are crucial.
Silk Proteins: Silk-based electronics are known as transient devices because they can dissolve safely in water. This property is particularly valuable for medical implants or environmental sensors where retrieval may not be feasible.
Magnesium and Zinc: These metals are biocompatible and corrode naturally, making them suitable for temporary components like circuit traces or electrodes. They provide reliable performance while avoiding long-term environmental hazards.
The versatility of biodegradable electronics allows them to be applied across multiple sectors:
Medical Devices: One of the most promising applications is in temporary medical implants and biosensors. Devices can monitor patient health or deliver therapy for a set period before safely dissolving, eliminating the need for invasive removal procedures.
Environmental Monitoring: Biodegradable sensors can collect data on soil quality, water pollution, or atmospheric conditions and degrade afterward. This reduces the environmental burden of deploying large numbers of sensors in natural settings.
Consumer Electronics: Everyday devices, including packaging-integrated sensors, smart cards, and disposable gadgets, can be manufactured to decompose after their useful life, reducing the growing problem of e-waste.
Military and Industrial Uses: Temporary electronics for monitoring equipment or personnel can degrade safely after use, minimizing both logistical challenges and environmental impact.
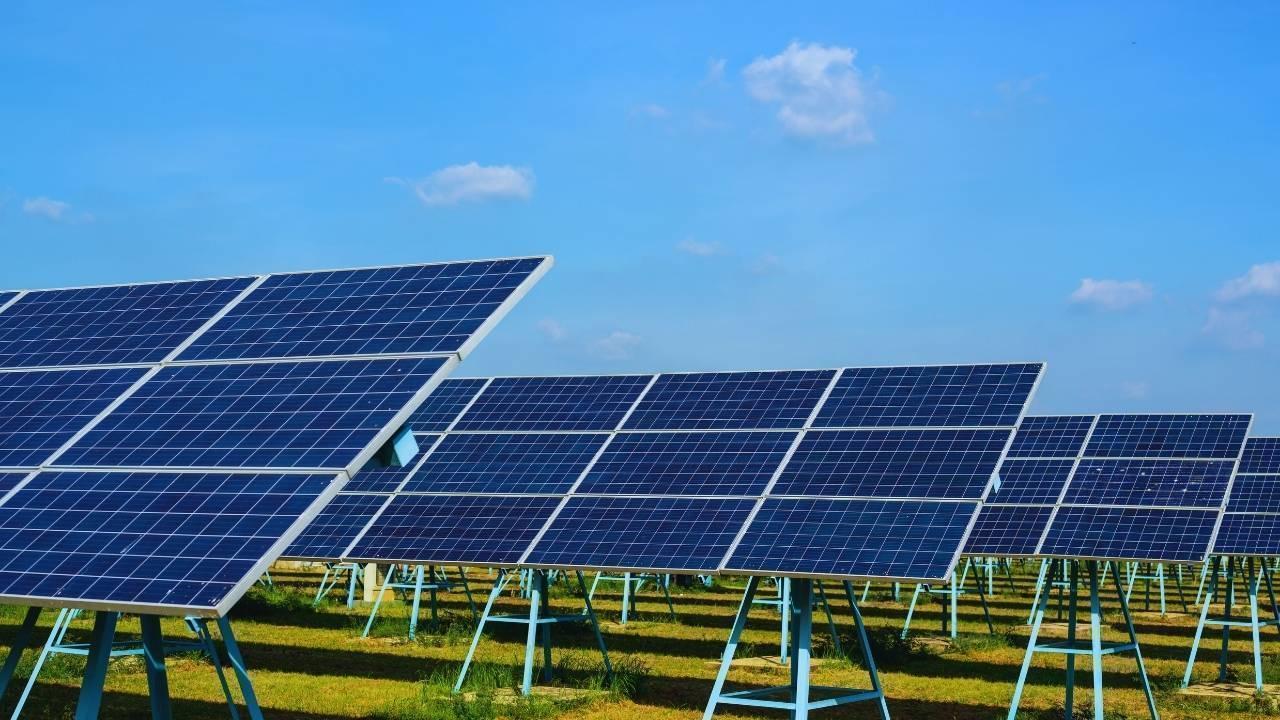
While biodegradable electronics address end-of-life concerns, solar-powered sensors tackle the energy consumption aspect of sustainability. By harnessing sunlight, these sensors operate independently of conventional power grids, making them ideal for remote or inaccessible locations.
Solar-powered sensors offer multiple advantages that make them attractive for a range of applications:
Energy Independence: They can function autonomously, reducing reliance on batteries or grid electricity. This is especially useful in remote environmental monitoring stations or disaster-affected areas.
Sustainability: Using solar energy reduces the carbon footprint associated with powering devices. Combined with biodegradable materials, solar-powered electronics represent a fully sustainable technology solution.
Cost-Effectiveness: Over time, operational costs are minimized as devices rely on freely available sunlight instead of consumable batteries or fuel.
Continuous Monitoring: Solar energy ensures longer operational lifespans for sensors in the field, enabling uninterrupted data collection.
The versatility of solar-powered sensors allows their use in a wide range of industries:
Agriculture: Farmers can use these sensors to monitor soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels, enabling precision irrigation and fertilizer management. This reduces water waste and enhances crop yields.
Environmental Monitoring: Solar sensors can track air quality, water pollution, or wildlife movement in real time, often in locations far from traditional power sources.
Smart Cities: Integrated into urban infrastructure, these sensors can monitor traffic flow, public utilities, and waste management, helping municipalities operate more efficiently.
Disaster Management: Deployed in disaster-prone areas, solar sensors can provide early warnings for floods, fires, or earthquakes without the need for constant human maintenance.
Despite their potential, both biodegradable electronics and solar-powered sensors face significant challenges that must be addressed before widespread adoption.
A primary concern is ensuring these devices remain functional for their intended lifespan. Biodegradable materials must resist degradation during use but decompose afterward. Similarly, solar-powered sensors must withstand varying environmental conditions, such as rain, wind, and temperature fluctuations, without performance loss. Researchers are working on coatings, protective layers, and hybrid materials to enhance durability while maintaining eco-friendly characteristics.
Currently, biodegradable and solar-powered electronics are more expensive than conventional alternatives. The cost of sourcing raw materials, developing specialized production techniques, and integrating solar technologies contributes to higher initial prices. Scaling production to meet global demand is a major hurdle, requiring collaboration between manufacturers, governments, and research institutions.
As these technologies are relatively new, regulatory frameworks are still evolving. Standardized guidelines for performance, biodegradability, and safety are essential to ensure devices are reliable and environmentally safe. Governments and international bodies are beginning to address these issues, but further coordination is needed to streamline approval processes.
Consumer education is crucial. Misunderstanding about the functionality and benefits of biodegradable electronics and solar-powered sensors can lead to misuse or improper disposal, undermining sustainability goals. Public awareness campaigns and clear labeling can help maximize environmental impact while encouraging responsible adoption.
The convergence of biodegradable electronics and solar-powered sensors represents the future of clean-tech hardware. Advances in material science, nanotechnology, and photovoltaic efficiency are steadily overcoming current limitations, enabling devices that are both functional and environmentally responsible.
In the next decade, we may see widespread deployment of smart cities equipped with solar-powered monitoring networks, medical devices that safely degrade after use, and consumer electronics designed with the environment in mind. These technologies have the potential to significantly reduce electronic waste, cut carbon emissions, and create a more sustainable technological ecosystem.
The combination of renewable energy integration, biodegradable materials, and innovative sensor technology will likely redefine the electronics industry. Companies investing in sustainable production practices and governments incentivizing eco-friendly innovations will play a crucial role in accelerating adoption.
Implementing biodegradable electronics and solar-powered sensors can have substantial environmental and economic benefits:
Reduction of E-Waste: By replacing conventional electronics with biodegradable alternatives, landfill accumulation of electronic waste will decrease significantly.
Energy Savings: Solar-powered devices reduce reliance on non-renewable energy, lowering greenhouse gas emissions associated with electricity production.
Cost Efficiency Over Time: While initial production costs may be higher, long-term benefits include reduced disposal expenses, energy savings, and extended operational lifespan of devices.
Job Creation and Innovation: Investment in clean-tech hardware fosters new industries, research opportunities, and skilled employment in sustainable technologies.
Countries across the globe are exploring these innovations:
Europe: Many EU nations are investing in biodegradable medical devices and environmental sensors to reduce industrial waste.
Asia: Countries like Japan and Singapore are integrating solar-powered sensors in smart city initiatives, demonstrating the feasibility of urban-scale deployment.
North America: The U.S. is funding research on transient electronics for healthcare, focusing on bioresorbable implants and environmental monitoring solutions.
Pilot projects have shown that these technologies can function reliably while maintaining eco-friendly properties, signaling strong potential for broader adoption.
This article discusses emerging technologies in biodegradable electronics and solar-powered sensors. While research and early applications are promising, large-scale implementation depends on continued development, regulatory approval, and commercial adoption. Readers should consult specialized resources for detailed technical or investment decisions.









Dalal Street Spotlight: Top 10 Stocks Investors Are Watching as Markets Open on a High
Indian stock markets begin the week with strong momentum, and several blue-chip and mid-cap stocks a

Market Movers Today: Key Stocks Set To Watch In Indian Markets
Indian equity markets are poised for active trading as several major companies, including Bharti Air

Milan Welcomes the World: Inside the Grand Opening Ceremony of the 2026 Winter Olympics
The 2026 Winter Olympics opening ceremony in Milan marked a defining moment for global sport, blendi
Unfolding Market Drama: Sensex & Nifty Trade Volatility Amid Budget Fallout and India-US Trade Breakthrough
Indian equity markets exhibited high volatility this week as the 2026 Union Budget triggered sharp s

Dhurandhar 2 Teaser Countdown Ignites Fan Frenzy: All You Need to Know
The highly anticipated sequel to the blockbuster Dhurandhar is building intense excitement as the Dh

Vietnam Overtakes Thailand as Top Choice for Chinese Tourists
Vietnam has quietly surpassed Thailand as the favorite destination for Chinese tourists in 2025.