You have not yet added any article to your bookmarks!

Join 10k+ people to get notified about new posts, news and tips.
Do not worry we don't spam!

Post by : Anis Farhan
Financial inclusion is the process of ensuring that individuals and businesses have access to affordable and appropriate financial products and services. This includes savings accounts, credit, insurance, and payment systems. Despite global economic growth, millions remain unbanked, particularly in emerging markets. Financial exclusion often arises from geographic, economic, and social barriers, limiting individuals’ ability to participate in formal financial systems.
The consequences of exclusion are far-reaching: households rely on informal lending with high interest, face challenges in saving, and struggle to access essential services. Businesses, particularly small and medium enterprises, find it difficult to secure financing for growth. As a result, addressing financial inclusion is both a social and economic imperative.
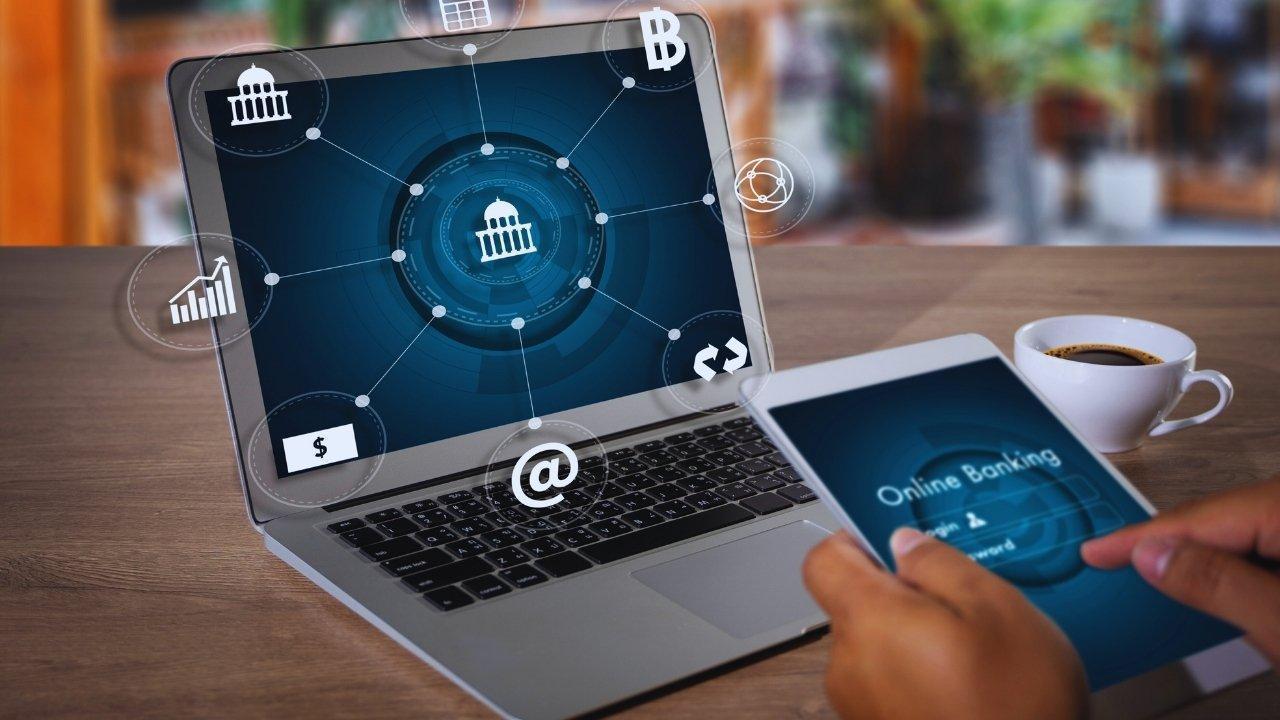
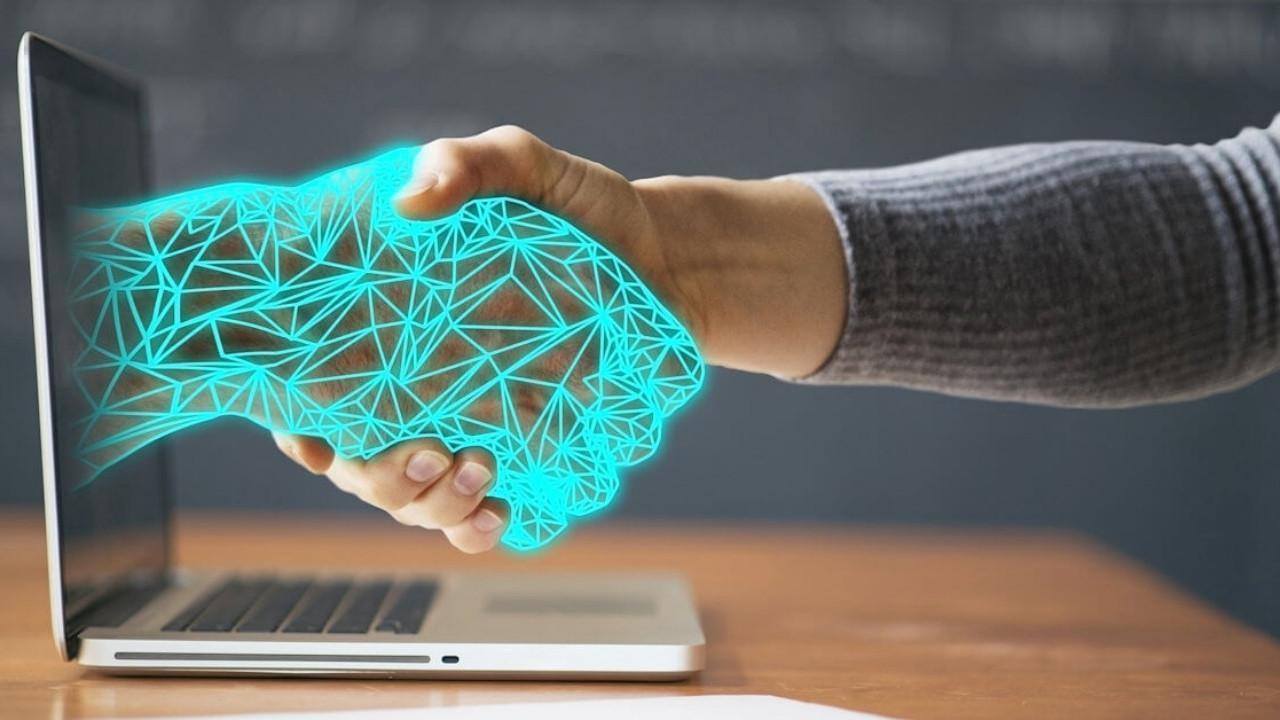
Digital banking has emerged as a key tool for financial inclusion. Unlike traditional banks, digital banking platforms offer services through mobile apps, online portals, and digital wallets. This eliminates the need for brick-and-mortar branches, significantly reducing costs and increasing accessibility.
1. Accessibility for Remote Populations
Mobile banking allows individuals in rural and remote areas to access financial services without traveling long distances. In regions where traditional banks are scarce, digital platforms provide a lifeline, enabling account creation, fund transfers, and bill payments with minimal infrastructure.
2. Cost-Effective Solutions
Digital banks operate with lower overheads, allowing them to offer reduced fees or free services. For low-income individuals, this affordability can make the difference between being able to save or being excluded entirely.
3. Real-Time Transactions
Digital banking provides real-time processing of payments and transfers. For users who rely on immediate access to funds, this capability reduces delays and increases financial reliability.
4. Financial Literacy Integration
Many digital platforms incorporate educational tools to improve financial literacy. Tutorials, notifications, and spending analytics empower users to make informed decisions, further enhancing financial inclusion.
Mobile wallets complement digital banking by allowing users to store, send, and receive money via their smartphones. Their adoption has surged in recent years, particularly in emerging markets.
1. Reaching the Unbanked
Mobile wallets often serve individuals without traditional bank accounts. By linking mobile numbers to digital wallets, users can conduct transactions, pay bills, and receive remittances, bypassing traditional banking infrastructure.
2. Enabling Micro-Transactions
For low-income households, even small financial transactions are crucial. Mobile wallets facilitate micro-payments, allowing users to purchase essentials, send money to family members, and participate in digital commerce.
3. Enhancing Security
Digital wallets often provide stronger security measures than cash transactions, including encryption, two-factor authentication, and transaction tracking. This builds trust among users previously wary of financial services.
4. Integration with E-Commerce
The rise of e-commerce has made mobile wallets even more indispensable. By providing seamless payment options for online shopping, users gain exposure to digital marketplaces, creating new economic opportunities.
1. India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI)
India’s UPI has revolutionized digital payments, connecting millions of users to banking services via their smartphones. By enabling instant fund transfers and bill payments, UPI has facilitated financial access for rural and urban populations alike.
2. M-Pesa in Kenya
M-Pesa allows users to store and transfer money through mobile phones. Its widespread adoption has transformed financial behavior in Kenya, enabling savings, credit access, and digital transactions for millions of previously unbanked individuals.
3. Brazil’s Digital Banking Expansion
Brazil has seen a surge in digital banks targeting lower-income segments. Platforms offer simplified account creation, micro-loans, and payment services, promoting economic participation for the underbanked population.
These examples illustrate how technology can overcome geographic, social, and economic barriers to financial inclusion.
Despite rapid growth, several obstacles remain:
1. Digital Literacy
Many potential users lack the skills to navigate digital banking platforms. Educational initiatives are essential to ensure that new technologies do not exacerbate existing inequalities.
2. Infrastructure Gaps
Reliable internet connectivity and access to smartphones are prerequisites for digital banking. Regions with poor infrastructure may continue to face exclusion.
3. Regulatory Hurdles
Governments must balance innovation with consumer protection. Excessive regulation can slow the adoption of digital banking, while insufficient oversight may expose users to fraud and misuse.
4. Trust Issues
Financial inclusion requires trust in digital platforms. Concerns about security, data privacy, and fraud can hinder adoption, particularly among populations unfamiliar with formal financial systems.
Financial inclusion has profound economic and social benefits:
1. Poverty Reduction
Access to credit, savings, and insurance allows individuals to invest in education, health, and entrepreneurship. This can lift households out of poverty and generate long-term economic growth.
2. Empowering Women
Digital financial services often target women, who are disproportionately excluded from traditional banking. Empowering women with financial tools promotes gender equality, economic participation, and family well-being.
3. Boosting Entrepreneurship
Small businesses and micro-entrepreneurs benefit from access to capital and payment systems. Financial inclusion fosters innovation, job creation, and local economic development.
4. Strengthening National Economies
Increased participation in the formal financial system leads to better tax compliance, higher savings rates, and improved monetary policy effectiveness. Collectively, these factors strengthen national economic stability.
Collaboration between governments, fintech companies, and traditional banks is essential to expand financial inclusion:
1. Government Initiatives
Governments can implement policies to incentivize digital banking, such as subsidies for mobile devices, regulatory sandboxes for fintech innovation, and public awareness campaigns.
2. Fintech Innovation
Private sector fintech companies drive innovation, creating user-friendly platforms, developing micro-loan models, and designing solutions for previously underserved communities.
3. Partnerships and Collaboration
Joint ventures between banks and fintech firms can combine regulatory expertise with technological innovation, offering scalable and sustainable solutions for financial inclusion.
4. Social Impact Programs
Programs that integrate digital financial services with social benefits, such as subsidies or welfare payments, increase adoption and demonstrate tangible value to users.
Looking ahead, several trends will shape the next phase of financial inclusion:
1. AI and Personalization
Artificial intelligence can provide personalized financial advice, detect fraud, and offer credit scoring for unbanked individuals based on alternative data, expanding access to financial services.
2. Blockchain and Digital Currencies
Blockchain technology can facilitate secure, transparent transactions and cross-border payments, reducing costs and increasing trust among users. Digital currencies issued by central banks may further enhance inclusion.
3. Expansion of Digital Lending
Micro-lending and peer-to-peer platforms will continue to grow, offering small-scale credit to underserved populations with minimal collateral requirements.
4. Integration with E-Government Services
Linking digital financial platforms with government services can streamline benefit distribution, reduce leakage, and increase financial participation.
By 2025, digital banking and mobile wallets have become central to the global financial inclusion agenda. These technologies empower millions of previously unbanked individuals, providing access to essential financial services and promoting economic growth.
The benefits extend beyond individual households to broader economic and social development. Empowering women, fostering entrepreneurship, reducing poverty, and strengthening national economies are just some of the tangible outcomes of enhanced financial inclusion.
Challenges remain, including digital literacy, infrastructure gaps, regulatory hurdles, and trust issues. However, collaboration between governments, fintech innovators, and financial institutions can address these barriers, ensuring that the next generation of unbanked individuals can participate fully in the global economy.
Financial inclusion in 2025 is not merely a technological achievement—it is a transformative movement that bridges gaps, empowers communities, and creates a more equitable economic future.
This article is for informational purposes only. It does not constitute financial advice or endorse any specific financial institution or service. Readers should exercise independent judgment and consult professional advisors for financial decisions.
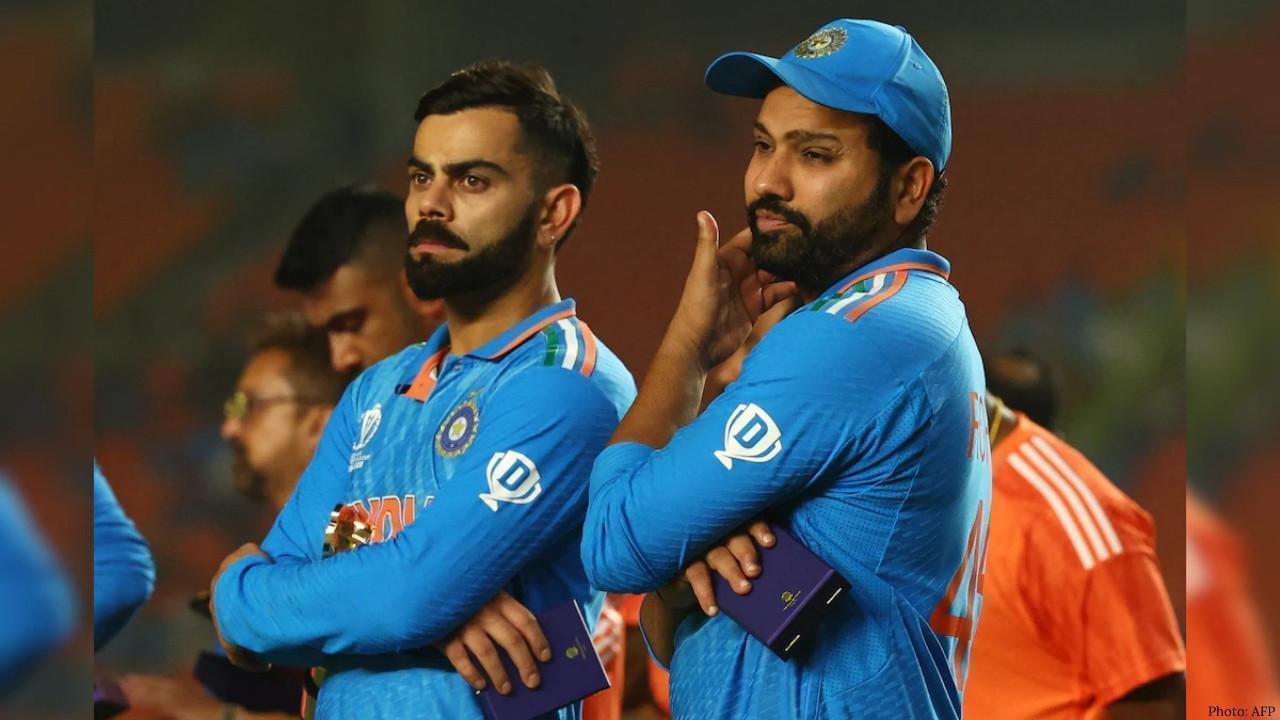







BCCI Central Contracts Shake-Up: Kohli, Rohit Moved to Grade B as Board Reshapes 2025–26 List
Virat Kohli and Rohit Sharma have been placed in Grade B in the BCCI’s 2025–26 central contract list

Dalal Street Spotlight: Top 10 Stocks Investors Are Watching as Markets Open on a High
Indian stock markets begin the week with strong momentum, and several blue-chip and mid-cap stocks a

Market Movers Today: Key Stocks Set To Watch In Indian Markets
Indian equity markets are poised for active trading as several major companies, including Bharti Air

Milan Welcomes the World: Inside the Grand Opening Ceremony of the 2026 Winter Olympics
The 2026 Winter Olympics opening ceremony in Milan marked a defining moment for global sport, blendi
Unfolding Market Drama: Sensex & Nifty Trade Volatility Amid Budget Fallout and India-US Trade Breakthrough
Indian equity markets exhibited high volatility this week as the 2026 Union Budget triggered sharp s

Dhurandhar 2 Teaser Countdown Ignites Fan Frenzy: All You Need to Know
The highly anticipated sequel to the blockbuster Dhurandhar is building intense excitement as the Dh