You have not yet added any article to your bookmarks!

Join 10k+ people to get notified about new posts, news and tips.
Do not worry we don't spam!

Post by : Anis Farhan
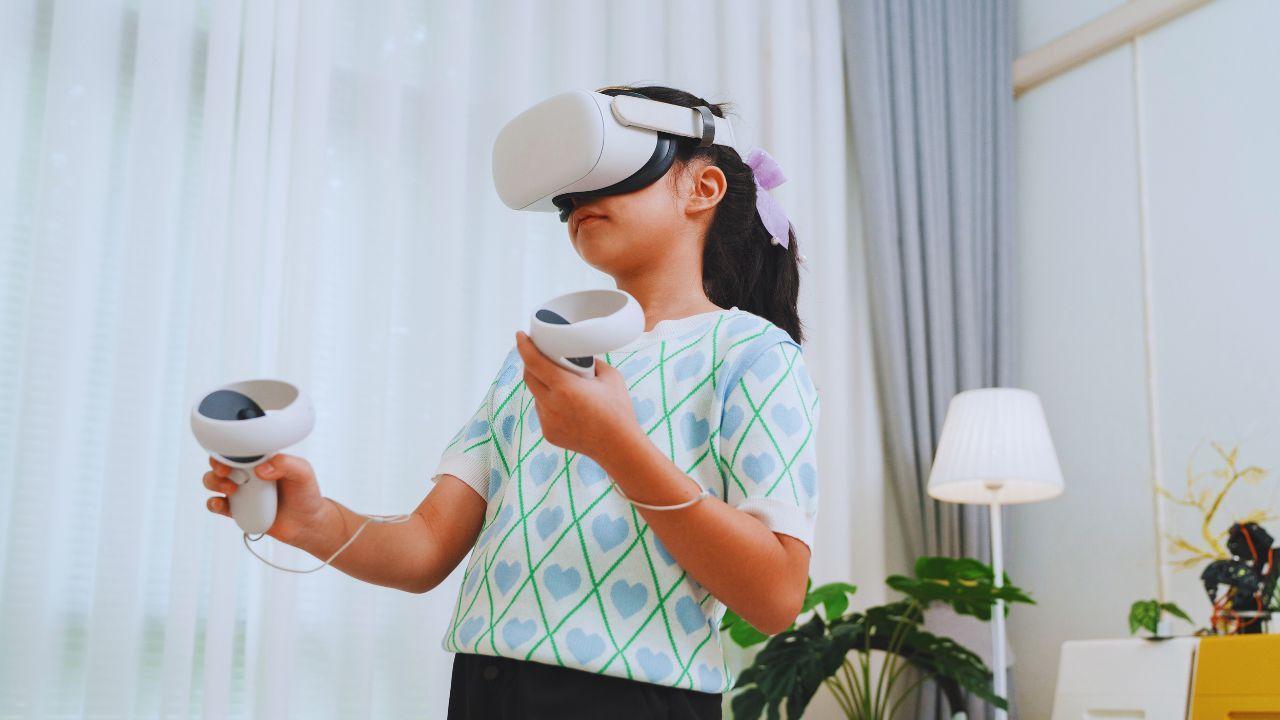
Extended Reality, often referred to as XR, is an umbrella term that includes Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR). VR immerses users in a fully digital environment, AR overlays digital elements onto the real world, and MR combines the two by allowing interaction between virtual objects and the physical environment. Together, these technologies have created new dimensions for engagement, creativity, and productivity.
What makes XR particularly compelling is its versatility. It can transport a medical student into a virtual operating theater, guide a factory worker through a step-by-step assembly process, or allow a teacher to bring historical events alive for students. Unlike traditional digital experiences, XR provides interactive, multisensory environments that make learning and training both engaging and effective.
Education has always relied on visual and experiential methods to strengthen learning, and XR is taking this to a whole new level. Instead of relying solely on textbooks or slideshows, teachers can now immerse students in environments that were once impossible to access. Imagine a history lesson where students can walk through the streets of ancient Rome, or a science class where they can shrink to the size of a molecule to observe chemical reactions up close.
These immersive scenarios make abstract concepts tangible, catering to different learning styles. Visual learners can observe complex processes, kinesthetic learners can interact with objects, and auditory learners can follow narrative guides within the XR environment. This flexibility makes XR an inclusive tool for diverse classrooms.
Beyond engagement, XR also improves knowledge retention. Studies suggest that immersive learning environments help learners remember information more effectively compared to traditional methods. This is particularly useful in subjects like biology, geography, and engineering, where hands-on visualization enhances comprehension.
In higher education, XR is revolutionizing teaching methods. Universities are already deploying VR labs for medical students, AR apps for engineering courses, and MR tools for architecture students to design and test structures virtually before physical construction.
For students in remote areas or those unable to travel, XR provides access to experiences previously limited to expensive labs or real-world field trips. A geology student, for example, can virtually explore rock formations across the world without leaving the classroom. Similarly, law students can role-play courtroom simulations, gaining practical skills without needing a physical setup.
XR also encourages collaboration across campuses. Students from different universities can join a shared virtual classroom, allowing for global knowledge exchange in real time. This is fostering cross-cultural communication and breaking geographical barriers in education.
The corporate world is one of the fastest adopters of XR. Training employees through traditional methods often involves significant costs, risks, and logistical challenges. XR eliminates many of these hurdles by simulating real-life scenarios in a safe and controlled environment.
For example, in the aviation industry, pilots and cabin crew are trained using VR simulations that replicate emergencies and standard procedures. Manufacturing companies use AR to guide workers through machinery repairs, reducing errors and downtime. Retail businesses are adopting VR to train employees in customer service, while logistics companies employ XR to train drivers and warehouse staff on safety protocols.
Beyond training, XR is also transforming day-to-day enterprise operations. Virtual meeting rooms, collaborative design spaces, and AR-driven workflow guides are becoming common in global companies. These tools enhance productivity, reduce travel costs, and allow employees to work effectively across borders.
While XR is powerful for technical training, it is equally effective for developing soft skills. Communication, leadership, and problem-solving are areas where XR simulations are making a difference. For instance, VR role-playing can help managers practice handling sensitive conversations or employees improve negotiation skills in a risk-free environment.
Healthcare organizations are using XR to train medical staff on empathy by allowing them to experience scenarios from a patient’s perspective. This kind of immersive training goes beyond traditional teaching by fostering emotional intelligence and building interpersonal awareness.
The rise of hybrid and remote work has created demand for better collaboration tools. While video calls have been the norm, they lack the immersive and interactive feel of in-person meetings. XR is filling this gap by creating virtual offices where employees can brainstorm on shared whiteboards, manipulate 3D models, or simply connect in a more engaging way than video calls allow.
Some companies are already experimenting with XR-based platforms to onboard new hires, host team-building activities, and conduct product demonstrations. As remote work continues to evolve, XR is poised to become a cornerstone of digital collaboration.
Despite its promise, XR faces hurdles before it can be universally adopted. The high cost of hardware, such as VR headsets and AR glasses, remains a barrier for schools and smaller enterprises. Additionally, XR systems require robust internet connectivity and advanced computing power, which are not always available in developing regions.
There are also challenges related to content creation. Building realistic, interactive XR experiences requires skilled developers and designers, which can be costly and time-consuming. Moreover, prolonged use of XR devices can cause motion sickness, eye strain, or fatigue for some users.
Finally, data privacy and security concerns arise as XR collects large amounts of user data, including biometric and behavioral patterns. Without proper regulations, these technologies could raise ethical issues in both education and enterprise settings.
The future of XR looks promising as technology becomes more affordable and accessible. Advances in lightweight headsets, cloud computing, and 5G connectivity will make XR experiences smoother and more widespread. Educational institutions are likely to see XR as an integral part of curriculum delivery, while enterprises will increasingly rely on XR for collaboration, product development, and workforce training.
Moreover, the convergence of XR with artificial intelligence and machine learning will create intelligent, adaptive learning environments. Students will receive personalized guidance within XR modules, while workers will have real-time, AI-powered feedback during training.
The long-term impact of XR will likely mirror the revolution brought by the internet two decades ago. Just as online learning platforms and video conferencing reshaped education and work, XR has the potential to create an entirely new digital dimension for human interaction.
Extended Reality is no longer a futuristic experiment but a practical tool driving transformation across education and enterprise. It bridges the gap between theory and practice, enhances collaboration, and makes complex processes more accessible and engaging. While challenges exist, the trajectory of XR suggests a future where immersive learning and working environments become the norm.
As adoption grows, XR will redefine how we prepare students for real-world challenges and train professionals for evolving workplace demands. In short, XR represents not just a technological upgrade but a new chapter in how humanity learns, works, and connects.
This article is for informational purposes only. The insights provided are based on current trends and research surrounding Extended Reality (XR). Readers are encouraged to verify details and consult relevant experts before making decisions related to XR adoption.










Meta Shuts Down 150,000 Scam Accounts Worldwide
Joint international operation involving Singapore police and global agencies targets scam networks o

Singapore–Batam Ferries Add Fuel Surcharge
Ferry operators introduce S$6 surcharge on Singapore–Batam routes as rising global fuel prices incre
SC Orders Policy for COVID Vaccine Side Effects
Landmark ruling asks Centre to frame a no-fault compensation scheme for people who suffered severe a

Japan Marks 15 Years Since Earthquake and Tsunami
Nation observes moment of silence as thousands remember victims of the 2011 triple disaster that res

Six Dead After Bus Fire Near Bern in Switzerland
Regional PostBus vehicle catches fire near Kerzers, triggering investigation by Swiss authorities

China Exports Surge Despite Trump Tariffs
Strong global demand for electronics and manufactured goods pushes China’s exports higher despite ri