You have not yet added any article to your bookmarks!

Join 10k+ people to get notified about new posts, news and tips.
Do not worry we don't spam!

Post by : Anis Farhan
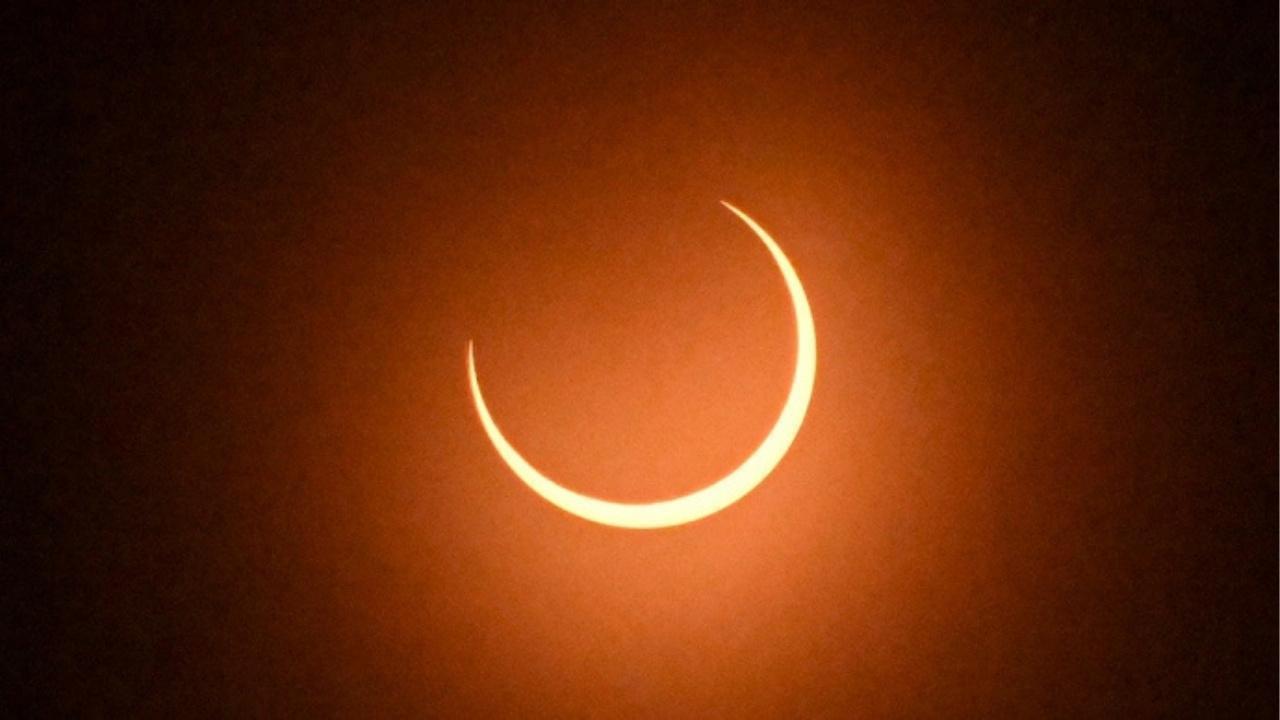
An annular solar eclipse happens when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun but is at a point in its orbit where it appears slightly smaller than the Sun in the sky. This geometry means it does not completely cover the Sun, leaving a glowing ring-like solar corona — often called a “ring of fire” — at the peak of the eclipse. The event is different from a total solar eclipse because the central disc of the Sun remains visible even at maximum coverage.
The Feb. 17, 2026 eclipse will be the first major solar eclipse of the year and is expected to be a spectacular sight for astronomers and eclipse chasers, even if most of the general public will not be within the narrow band where the full annular phase occurs.
The annular phase — the dramatic “ring of fire” effect — will be visible only along a narrow path across Antarctica and portions of the Southern Ocean. This path is estimated to stretch approximately 2,661 miles (4,282 km) and be up to about 383 miles (616 km) wide. In this region, observers (primarily at research stations such as Concordia and Mirny) will see the Moon cover most of the Sun’s disc, leaving a bright ring around its edges at maximum eclipse.
Most of this region is uninhabited or scarcely populated, meaning relatively few human observers will witness the full annular effect in person — leading commentators to joke that more penguins than people will likely see the full eclipse.
While the full “ring of fire” is largely confined to Antarctica, a partial solar eclipse — where only a portion of the Sun is obscured by the Moon — will be visible over a much wider region of the southern hemisphere.
Regions that will be able to observe the partial eclipse phase include:
Much of Antarctica outside the narrow annularity path
Southern Africa (including nations such as South Africa, Mozambique, Madagascar and others)
Southern tip of South America (notably parts of Argentina and Chile)
Surrounding oceanic areas in the Pacific, Indian and Atlantic Oceans
Remote island groups such as Heard and McDonald Islands, French Southern and Antarctic Lands, Mauritius and Réunion are also expected to see partial eclipse coverage.
While partial eclipses do not produce the full “ring,” they still offer a striking sight, with the Moon visibly taking a “bite” out of the Sun’s disc. Safe viewing practices — including eclipse glasses or indirect viewing methods — are essential during all phases of the eclipse to prevent eye damage.
For viewers in the Northern Hemisphere, including countries such as India, the United States and much of Europe and Asia, this annular eclipse will not be visible at all. The geometry of the alignment and the eclipse’s path across the southern hemisphere mean that places farther north will not experience any portion of the event.
Observers curious about the eclipse from such regions may still enjoy live streams of the event, which will be provided by astronomy organizations and space agencies, but they will not be able to view it directly without traveling to the southern hemisphere or using digital feeds.
According to eclipse observers and astronomical forecasts, the lunar shadow will begin to interact with the Sun on February 17, 2026, with the partial phase starting first as the Moon begins to cover a portion of the Sun.
Peak annularity — the point when the Moon is centered on the Sun’s disc but unable to fully obscure it — will occur within the narrow Antarctic path. Maximum ring visibility is expected to last for roughly 1 to 2 minutes in the best observing locations — such as at Concordia Station or Mirny Station in Antarctica.
Outside this band, observers in African or South American regions will see a partial solar eclipse, with varying degrees of coverage depending on their distance from the eclipse’s central path.
Whether watching a partial or annular eclipse, directly viewing the Sun without proper eye protection can cause severe permanent eye damage. Standard sunglasses are not sufficient. Instead:
Use ISO-certified solar eclipse glasses
View via solar filters on telescopes or binoculars
Use indirect methods such as a pinhole projector
These precautions are especially important during partial phases, when the Sun remains mostly visible and can damage the eyes even if partly obscured by the Moon.
The annular solar eclipse of February 17, 2026 will be a spectacular astronomical event, though its most dramatic “ring of fire” spectacle will largely be confined to remote Antarctic regions. A broader partial eclipse, however, will be visible from parts of southern Africa, southern South America, and across the southern oceans.
Despite its limited direct visibility from much of the world, this eclipse provides a unique opportunity for skywatchers in eligible regions — and for global audiences via online coverage — to witness one of nature’s most dramatic celestial alignments.
Disclaimer: This article synthesises current astronomical forecasts and visibility maps available at the time of writing. Observational conditions can vary due to weather, local horizon effects and atmospheric conditions. Readers should consult official astronomical resources and use recommended eye protection when viewing solar eclipses.









Taylor Swift Moves to Block ‘Swift Home’ Trademark in U.S. Legal Challenge
Global pop icon Taylor Swift has petitioned the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office to deny a trademark

Discord’s Global Age Verification Rollout Sparks Privacy Backlash After Data Breach
Messaging platform Discord has announced a global age-verification system that will automatically ma

India’s T20 World Cup Reality Check: Middle-Overs Batting Exposed Despite Convincing Win
In a commanding India vs Namibia T20 World Cup performance, India secured a convincing victory, but

New Dhaka Era: How the BNP Seized Power in Bangladesh’s Historic Election
Bangladesh’s 2026 parliamentary elections yielded a dramatic political shift as the Bangladesh Natio

Trump Plans First Meeting of New Peace Board in Washington This February
Former U.S. President Donald Trump is reportedly preparing to convene the inaugural session of a new

Apple’s iOS 26.3 Update Is Here — Why Millions of iPhone Users Should Install It Now
Apple has rolled out iOS 26.3 as a critical update for eligible iPhones, bringing important security